Abstract
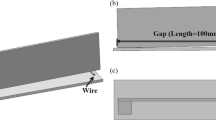
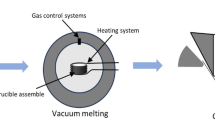
A new low melting point filler metal, Al-Si-Cu-Ni-RE, was developed for the furnace brazing of aluminum alloy 6063. Flux-assisted brazing was conducted at 560 °C using the new filler metal and AlF3-CsF-KF flux. Microstructure of the brazed joints were studied by means of SEM, TEM, and EDS. Shear strength and micro-Vickers hardness of joints had been tested. Results show that sound joints could be obtained with the filler metal and the flux. Microstructure characterization of the brazed joint shows dendritic CuAl2 phase was distributed evenly and Si-phase was spheroidized and refined, which was embedded in CuAl2 dendrites with modification of rare-earth element. Shear strength test results show that the joints with Al-Si-Cu-Ni-RE filler metal achieved average shear strength of 62.5 MPa, 14.5% more than the shear strength of brazed joints with Chinese HL401 filler metal. The micro-Vickers hardness of joint after T6 treatment is about 83 HV. The hardness of the joints after just brazing and after solution treatment was higher than the hardness of the base metal.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.C. Tsao, T.C. Tsai, C.S. Wu, and T.H. Chuang, Brazeability of the 6061-T6 Aluminum Alloy with Al-Si-20Cu-Based Filler Metals, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2001, 10(6), p 705–709
J. Lacaze, S. Tierce, M.C. Lafont, Y. Thebault, N. Pebere, G. Mankowski, C. Blanc, H. Robidou, D. Vaumousse, and D. Daloz, Study of the Microstructure Resulting from Brazed Aluminum Materials Used in Heat Exchangers, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 413–414, p 317–321
K. Suzuki, M. Kagayama, and Y. Takeuchi, Eutectic Phase Equilibrium of Al-Si-Zn System and Its Applicability for Lower Temperature Brazing, Jpn. Inst. Light Met., 1993, 43, p 533–538
T. Kayamoto, J.H. Kim, S. Saito, and T. Onzawa, Brazing of Al-Mg Alloy and Al-Mg-Si Alloy with Al-Ge Based Filter Metals. Proc. Workshop Jpn. Weld. Soc., Vol. 12, 1994, p 495–501
D.M. Jocbson, G. Humpston, and S.P.S. Sangha, A New Low-Melting-Point Aluminum Braze, Weld. Res. Suppl., 1966, p 243–250
“Test Method of Spreadabillity and Clearance Filling Ability for Filler Meal,” GB 11364-89, Metal Welding National Standards Committee, Chinese National Standard, 1989, p 168–170
F. Gao et al., Solid State Si Diffusion and Joint Formation Involving Aluminum Brazing Sheet, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2002, A337, p 228–235
K. Noqita, S.D. McDonald, and A.K. Dahle, Eutectic Modification of Al-Si Alloys with Rare Earth Metals, Mater. Trans., 2005, 45, p 323–326
X.M. Qiu et al., Thermodynamical Analysis on Al Eutectic Reaction Brazing, Chin. J. Nonferr. Met., 2001, 11(6), p 1017–1020
Acknowledgment
The work was supported by the Director, Office of Science and Technology, of Nanjing Research Institute of Electronics Technology, under Contract No. B1120060474.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Bao, Y., Jiang, Y. et al. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 6063 Aluminum Alloy Brazed Joints with Al-Si-Cu-Ni-RE Filler Metal. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 20, 1451–1456 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9802-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9802-2