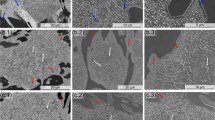
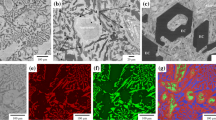
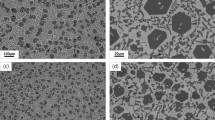
The initial as-cast microstructure of a high-chromium (2.35% C, 18.23% Cr) white cast iron consisting of primary austenitic dendrites and a eutectic mixture of M7C3 carbides/austenite was extensively modified by four different heat treatments: H.T.A: destabilization (970 °C-2.5 h), H.T.B: destabilization/subcritical treatments (970 °C-2.5 h + 600 °C-13 h), H.T.C: subcritical treatment (600 °C-13 h) and H.T.D: subcritical/destabilization treatments (600 °C-13 h + 970 °C-2.5 h). H.T.A leads to martensitic structures that present considerable precipitation of cubic secondary carbide particles of M23C6 type. H.T.B produces pearlitic structures and causes further carbide precipitation and pre-existent carbide particle shape modifications. H.T.C extensively modifies the initial as-cast structure to more pearlitic morphologies accompanied with spheroidization/degradation of the M7C3 primary carbide structure. H.T.D causes extensive formation of secondary carbide particles within the primary austenitic matrix; the latter has been mainly transformed to martensite. The effect of each heat treatment on the hardness of the alloy was correlated with the attained microstructure.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
C·P. Tabrett, I.R. Sare M.R. Ghomashchi (1996) Microstructure-Property Relationships in High Chromium White Iron Alloys, Int. Mater. Rev., 41(2), 52–89
K.-H. Zum Gahr, G.T. Eldis (1980) Abrasive Wear of White Cast Irons, Wear, 64, 175–194
C. Çetinkaya (2006) An Investigation of the Wear Behaviours of White Cast Irons Under Different Compositions, Mater. Des., 27, 437–445
Y. Matsubara, N. Sasaguri, K. Shimizu, and S.K. Yu, Solidification and Abrasion Wear of White Cast Irons Alloyed with 20% Carbide Forming Elements, Wear, 2001, 250, p 502–510
S. Turenne, F. Lavallee, J. Masounave (1989) Matrix Microstructure Effect in the Abrasion Resistance of High Chromium White Cast Iron, J. Mater. Sci., 24, 3021–3028
C·P. Tabrett, I.R. Sare (1998) Effect of High Temperature and Sub-Ambient Treatments on the Matrix Structure and Abrasion Resistance of a High-Chromium White Iron, Scr. Mater., 38 (12), 1747–1753
M. Durand-Charre, Microstructure of Steels and Cast Irons, Springer-Verlag, New York LLC, April 2004, ISBN-13: 9783540209638
C·P. Tabrett, I.R. Sare (1997) The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Abrasion Resistance of Alloy White Irons, Wear, 203–204, 206–219
C·P. Tabrett, I.R. Sare (2000) Fracture Toughness of High-Chromium White Irons: Influence of Cast Structure, J. Mater. Sci., 35, 2069–2077
S·K. Hannes, J.D. Gates (1997) A Transformation Toughening White Cast Iron, J. Mater. Sci., 32, 1249–1259
J. Asensio, J.A. Pero-Sanz, J.I. Verdeja (2003) Microstructure Selection Criteria for Cast Irons with More than 10 wt% Chromium for Wear Applications, Mater. Charact., 49, 83–93
J. Wang, C. Li, H. Liu, H. Yang, B. Shen, S. Gao, S. Huang (2006) The Precipitation and Transformation of Secondary Carbides in a High Chromium Cast Iron, Mater. Charact., 56, 73–78
J. Wang, R.L. Luo, Z.P. Sun, C. Li, H·H. Liu, H·S. Yang, B.L. Shen, S.J. Huang (2005) Influence of Secondary Carbides Precipitation and Transformation on Hardening of a 15Cr–1Mo-1.5 V White Iron, Mater. Charact., 55, 234–240
M.X. Zhang, P.M. Kelly, J.D.Gates (2001) The Effect of Heat Treatment on the Toughness Hardness and Microstructure of Low Carbon White Cast Irons, J. Mater. Sci., 36, 3865–3875
G.L.F. Powell and J.V. Bee, Secondary Carbide Precipitation in an 18 wt% Cr–1 wt% Mo White Iron, J. Mater. Sci., 1996, 31, p 707–711
G.L.F. Powell, G. Laird II (1992) Structure, Nucleation, Gowth and Morphology of Secondary Carbides in High Chromium and Cr-Ni White Irons, J. Mater. Sci., 27, 29–35
A. Wiengmoon, T. Chairuangsri, A. Brown, R. Brydson, D.V. Edmonds, J.T.H. Pearce (2005) Micorstructural and Crystallographical Study of Carbides in 30 wt% Cr Cast Irons, Acta Mater., 53, 4143–4154
S.D. Carpenter, D. Carpenter (2003) X-ray Study of M7C3 Carbide Within a High Chromium White Iron, Mater. Lett., 57, 4456–4459
J.T.H Pearce, D.W.L Elwell (1986) Duplex Nature of Eutectic Carbides in Heat Treated 30% Chromium Cast Iron, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 5, 1063–1064
J.T.H Pearce (1983) Examination of M7C3 Carbides in High Chromium Cast Iron Using Thin Foil Transmission Electron Microscopy, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 2, 428–432
A. Inoque and T. Masumoto, Carbide Reactions (M3C =>M7C3 =>M23C6 =>M6C) During Tempering of Rapidly Solidified High Carbon Cr-W and Cr-Mo Steels, Metall. Transact. A, 1980, 11A, 739–747
S.D. Carpenter, D. Carpenter, J.T.H. Pearce (2007) XRD and Electron Microscope Study of a Heat Treated 26.6% Chromium White Iron Microstructure, Mater. Chem. Phys., 101, 49–55
Z. Sun, R. Zuo, C. Li, B. Shen, J. Yan, S. Huang (2004) TEM Study on Precipitation and Transformation of Secondary Carbides in 16Cr-1Mo-1Cu White Iron Subjected to Subcritical Treatment, Mater. Charact., 53, 403–409
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to acknowledge the Greek Modern Castings (GMC) S.A foundry for their kind assistance in the preparation of the examined alloy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karantzalis, A., Lekatou, A. & Mavros, H. Microstructural Modifications of As-Cast High-Chromium White Iron by Heat Treatment. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 18, 174–181 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-008-9285-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-008-9285-6