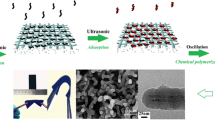
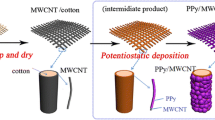
Abstract
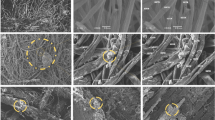
Pure natural cotton has flexible and foldable characteristics with a high response rate which makes it an excellent candidate for the development of low-cost electrodes for electrochemical supercapacitors. Here, a composite of cotton (C/P:P) with different ratios of conducting polymer, poly(3, 4-ethylene dioxythiophene):poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS), was developed through polymerization using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as a physical cross-linker. A hydrogel electrolyte has been developed using natural polymer starch and sodium alginate. The fabricated supercapacitor utilizing the developed composite and the hydrogel electrolyte has been analyzed by employing different characterization techniques. The structural properties of pure and composite electrodes (C/P:P) were investigated by x-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy; the surface morphology was elucidated by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). Thermal properties were investigated using thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Sheet resistance was measured for the composite with different ratios of PEDOT:PSS in which 2.5 wt.% of PEDOT PSS showed the lowest sheet resistance of 1.22 Ω/square. Electrochemical studies were carried out utilizing cyclic voltammetry and the composite cotton-based symmetric supercapacitor was found to achieve a specific capacitance of 296 F/g at 100 mA g−1. The intrinsic properties of the symmetric composite cotton supercapacitors were also verified by operating a light-emitting diode (LED).














Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Lin, C. Zhang, Z. Yan, Y. Zhu, Z. Peng, R.H. Hauge, D. Natelson, and J.M. Tour, 3-Dimensional graphene carbon nanotube carpet-based microsupercapacitors with high electrochemical performance. Nano Lett. 13, 72–78 (2013).
D. Pech, M. Brunet, H. Durou, P. Huang, V. Mochalin, Y. Gogotsi, P.-L. Taberna, and P. Simon, Ultrahigh-power micrometre-sized supercapacitors based on onion-like carbon. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 651–654 (2010).
C. Meng, C. Liu, L. Chen, C. Hu, and S. Fan, Highly flexible and all-solid-state paperlike polymer supercapacitors. Nano Lett. 10, 4025–4031 (2010).
J. Chen, K. Sheng, P. Luo, C. Li, and G. Shi, Graphene hydrogels deposited in nickel foams for high-rate electrochemical capacitors. Adv. Mater. 24, 4569–4573 (2012).
H. Jiang, P.S. Lee, and C. Li, 3D carbon based nanostructures for advanced supercapacitors. Energy Environ. Sci. 6, 41–53 (2013).
Z. Liu, Y. Xu, X. Zhang, Y. Pei, Y. Cheng, and W. Yin, Simulation study on the Characteristics of Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Plastics in Electromagnetic Tomography Nondestructive Evaluation Systems. In Proceedings of International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation vol 2010, pp. 382–385 (2010).
J. Chmiola, C. Largeot, P.-L. Taberna, P. Simon, and Y. Gogotsi, Monolithic carbide-derived carbon films for micro-supercapacitors. Science 328, 480–483 (2010).
M. Endo, T. Takeda, Y. Kim, K. Koshiba, and K. Ishii, High power electric double layer capacitor (EDLC’s); from operating principle to pore size control in advanced activatedcarbons. Carbonletters 1, 117–128 (2001).
A. Motaghi, A. Hrymak, and G.H. Motlagh, Electrical conductivity and percolation threshold of hybrid carbon/polymer composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41744.
R. Schueler, S.P. Joshi, and K. Schulte, Damage detection in CFRP by electrical conductivity mapping. Compos. Sci. Technol. 61, 921–930 (2001).
N. Angelidis, C.Y. Wei, and P.E. Irving, Response to discussion of paper: the electrical resistance response of continuous carbon fibre composite laminates to mechanical strain. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 37, 1495–1499 (2006).
K.M. Batoo, N.M. Badawi, and S.F. Adil, Highly sensitive coated cotton thread for applications in soft circuit. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron 32, 10880–10889 (2021).
S.N. Vernon, A single-sided eddy current method to measure electrical resistivity. Mater. Eval. 46, 1581–1587 (1988).
J. Deng, J. Li, S. Song, Y. Zhou, and L. Li, Electrolyte-dependent supercapacitor performance on nitrogen-doped porous bio-carbon from gelatin. Nanomaterials 10, 353 (2020).
M. Skunik-Nuckowska, P. Rączka, J. Lubera, A.A. Mroziewicz, S. Dyjak, P.J. Kulesza, I. Plebankiewicz, K.A. Bogdanowicz, and A. Iwan, Iodide electrolyte-based hybrid supercapacitor for compact photo-rechargeable energy storage system utilising silicon solar cells. Energies 14, 2708 (2021).
C. Wang, K. Hu, Y. Liu, M.-R. Zhang, Z. Wang, and Z. Li, Flexible supercapacitors based on graphene/boron nitride nanosheets electrodes and PVA/PEI gel electrolytes. Materials 14, 1955 (2021).
N.M. Badawi and K.M. Batoo, Conductive nanocomposite cotton thread strands for wire and industrial applications. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 6483–6491 (2020).
C. Cochrane and A. Cayla, 5-Polymer-Based Resistive Sensors for Smart Textiles, Multidisciplinary Know-How for Smart-Textiles Developers. ed. T. Kirstein (United Kingdom: Woodhead Publishing, Sawston, 2013), pp. 129–153.
H.J. In, S. Kumar, Y. Shao-Horn, and G. Barbastathis, Origami fabrication of nanostructured, three-dimensional devices: electrochemical capacitors with carbon electrodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 083104 (2006).
C.M.A. Brett, Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in the characterisation and application of modified electrodes for electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Molecules 27(5), 1497 (2022).
R. Srinivasan and F. Fasmin, An Introduction to Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2021), p.932.
M. Kaempgen, C.K. Chan, J. Ma, Y. Cui, and G. Gruner, Printable thin film supercapacitors using single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 9, 1872–1876 (2009).
C. Du, J. Yeh, and N. Pan, High power density supercapacitors using locally aligned carbon nanotube electrodes. Nanotechnology 16, 350–353 (2005).
J. Cheng, J. Qiu, H. Ji, E. Wang, T. Takagi, and T. Uchimoto, Application of low frequency ECT method in noncontact detection and visualization of CFRP material. Compos. Part B Eng. 110, 141–152 (2017).
H. Menana and M. Féliachi, Electromagnetic characterization of the CFRPs anisotropic conductivity: modeling and measurements. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 53, 21101 (2011).
I.M.D. Rosa, R. Mancinelli, F. Sarasini, M.S. Sarto, and A. Tamburrano, Electromagnetic design and realization of innovative fiber-reinforced broad-band absorbing screens. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 51, 700–707 (2009).
C. Du and N. Pan, Supercapacitors using carbon nanotubes films by electrophoretic deposition. J. Power Sources 160, 1487–1494 (2006).
J. Ram, R.G. Singh, F. Singh, V. Kumar, V. Chauhan, R. Gupta, U. Kumar, B.C. Yadav, and R. Kumar, Development of WO3-PEDOT: PSS hybrid nanocomposites based devices for liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) sensor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 13593–13603 (2019).
Y. Kim, Y. Kim, and J.H. Kim, Highly conductive PEDOT:PSS thin films with two-dimensional lamellar stacked multi-layers. Nanomaterials 10(11), 2211 (2020).
F. Alhashmi Alamer, and N.M. Badawi, Fully flexible, highly conductive threads based on single walled carbon nanotube (SWCNTs) and poly(3,4 ethylenedioxy thiophene) poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS). Adv. Eng. Mater. 23(10), 2100448 (2020).
L.V. Kayser and D.J. Lipomi, Stretchable conductive polymers and composites based on PEDOT and PEDOT:PSS. Adv. Mater. 31, 1806133 (2019).
J.H. Min, M. Patel, and W.-G. Koh, Incorporation of conductive materials into hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Polymers 10, 1078 (2018).
J. Wang, G. Chen, and S. Song, Na-ion conducting gel polymer membrane for flexible supercapacitor application. Electrochim. Acta. 330, 135322 (2020).
A. Ahmad, K.M. Isa, and Z. Osman, Conductivity and structural studies of plasticized polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-lithium triflate polymer electrolyte films. Sains Malaysiana 40, 691–694 (2011).
F.A. Aouada, M.R. Guilherme, G.M. Campese, E.M. Girotto, A.F. Rubira, and E.C. Muniz, Electrochemical and mechanical properties of hydrogels based on conductive poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene)/poly(styrenesulfonate) and PAAm. Polym. Test. 25, 158–165 (2006).
H. Miao, B. Chen, S. Li, X. Wu, Q. Wang, C. Zhang, Z. Sun, and H. Li, All-solid-state flexible zinc-air battery with polyacrylamide alkaline gel electrolyte. J. Power Sources. 450, 227653 (2020).
Q. Rong, W. Lei, and M. Liu, Conductive hydrogels as smart materials for flexible electronic devices. Chem. A Eur. J. 24, 16930–16943 (2018).
M.Y. Chong, C.-W. Liew, A. Numan, K. Yugal, K. Ramesh, H.M. Ng, T.V. Chong, and S. Ramesh, Effects of ionic liquid on the hydroxylpropylmethyl cellulose (HPMC) solid polymer electrolyte. Ionics 22, 2421–2430 (2016).
G. Li, L. Gao, L. Li, and L. Guo, An electrochromic and self-healing multi-functional supercapacitor based on PANI/nw-WO2.7/Au NPs electrode and hydrogel electrolyte. J. Alloys Compd. 786, 40–49 (2019).
C. Yang, P. Zhang, A. Nautiyal, S. Li, N. Liu, J. Yin, K. Deng, and X. Zhang, Tunable three-dimensional nanostructured conductive polymer hydrogels for energy-storage applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 4258–4267 (2019).
F. Qi, Z. Xia, R. Sun, X. Sun, X. Xu, W. Wei, S. Wang, and G. Sun, Graphitization induced by KOH etching for the fabrication of hierarchical porous graphitic carbon sheets for high performance supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A. 6, 14170–14177 (2018).
P. Simon and A.F. Burke, Nanostructured carbons: double-layer capacitance and more. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 17, 38–43 (2008).
A.G. Pandolfo and A.F. Hollenkamp, Carbon properties and their role in supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 157, 11–27 (2006).
N. Ben Messaoud, M.E. Ghica, C. Dridi, M.B. Ali, and C.M.A. Brett, Electrochemical sensor based on multiwalled carbon nanotube and gold nanoparticle modified electrode for the sensitive detection of bisphenol A. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 253, 513–522 (2017).
C.M.A. Brett, A.N.A. Maria, and O. Brett, Principles, methods, and applications. Electrochemistry 67(2), 444 (1993).
D. Wang, S. Wang, D.D.L. Chung, and J.H. Chung, Sensitivity of the two-dimensional electric potential/resistance method for damage monitoring in carbon fiber polymer-matrix composite. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 4839–4846 (2006).
A. Todoroki, Y. Tanaka, and Y. Shimamura, Multi-prove electric potential change method for delamination monitoring of graphite/epoxy composite plates using normalized response surfaces. Compos. Sci. Technol. 64, 749–758 (2004).
J. Wang, X. Yu, C. Wang, K. Xiang, M. Deng, and H. Yin, PAMPS/MMT composite hydrogel electrolyte for solid-state supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 709, 596–601 (2017).
M.G. Saborío, Š Zukić, S. Lanzalaco, J. Casanovas, J. Puiggalí, F. Estrany, and C. Alemán, Prototyping flexible supercapacitors produced with biohydrogel. Mater. Today Commun. 16, 60–70 (2018).
Z. Wang, F. Tao, and Q. Pan, A self-healable polyvinyl alcohol-based hydrogel electrolyte for smart electrochemical capacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 4, 17732–17739 (2016).
F. Alhashmi Alamer and N.M. Badawi, Manufacturing organic environmentally friendly electrical circuits using the composites’ single-walled carbon nanotubes and pedot:PSS. Energy Technol. 10(2), 2100830 (2022).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Universiti Malaya for providing the facilities to conduct the project. No funding involved.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Nujud Badawi: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing–review & editing. Mamta Bhatia:Writing & editing. Syed Farooq Adil: review & editing. Mujeeb Khan: review. S. Ramesh: Supervision, review & editing. K. Ramesh: Supervision, review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nujud Badawi, M., Bhatia, M., Ramesh, S. et al. Enhancement of the Performance Properties of Pure Cotton Fabric by Incorporating Conducting Polymer (PEDOT:PSS) for Flexible and Foldable Electrochemical Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 52, 2201–2215 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10170-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-022-10170-3