Abstract
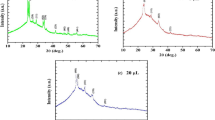
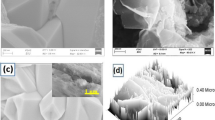
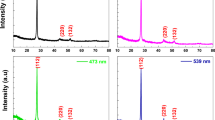
One important component of modern thin film solar cell designs is the photo-anode. TiO2 is the most common photo-anode material. However, TiO2 has no response over its wide band-gap to most of the visible light spectrum. Semiconductor coupling can improve the photoelectric conversion efficiency of TiO2 thin film photo-anodes. In our study, TiO2 arrays were coupled with the narrow band gap material Bi2S3 to form a TiO2/Bi2S3 composite. The Bi2S3 was deposited by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method (SILAR), then the effect of the number of deposition cycles on the composite film performance was studied. The as-obtained samples were characterized by x-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, UV–Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy and photo-electrochemical measurements. When the number of deposition cycles reached 10, the composite film showed the best optical and electrical properties. To improve the film performance, the SILAR method was modified with an ultrasound-assist. Under the same deposition cycle number (3 and 5), the current density of TiO2/Bi2S3 by ultrasound-assisted SILAR method was larger than that with the SILAR method alone. During the ultrasound-assisted SILAR process, the high temperature and high pressure provide by ultrasound accelerated the formation of new nuclei and increased the ion diffusion rate in the reaction solution, thus forming more Bi2S3 materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.W. Cheng, S.K. Karuturi, L.J. Liu, J.P. Liu, H.X. Li, L.T. Su, A.I.Y. Tok, and H.J. Fan, Small 8, 37 (2012).
P. Baviskar, A. Ennaoui, and B. Sankapal, Sol. Energy 105, 445 (2014).
T.K. Truong, T.V. Doan, H.H. Tran, H.V. Le, V.Q. Lam, H.N. Tran, T.M. Cao, and V.V. Pham, J. Electron. Mater. 48, 7378 (2019).
S.V. Nair, A. Bakakrishnan, K.R.V. Subramanian, A.M. Anu, A.M. Asha, B. Deepika, and B. Mater, Science 35, 489 (2012).
G. Wu, J. Zhang, X. Wang, J. Liao, H. Xia, S.A. Akbar, J. Li, S. Lin, X. Li, and J. Wang, Ceram. Int. 38, 6341 (2012).
V.A. Ganesh, A.S. Nair, H.K. Raut, T.M. Walsh, and S. Ramakrishna, RSC Adv. 2, 2067 (2012).
S.P. Pishekloo, R.S. Dariani, and F. Salehi, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 43, 182 (2016).
G. Liu, T. Schulmeyer, A. Thissen, A. Klein, and W. Jaegermann, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 2269 (2003).
Y. Xie, S.H. Yoo, C. Chen, and S.O. Cho, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 177, 106 (2012).
X. Li, X. Han, D. Zhu, Y. Chen, L. Li, Z. Ma, Y. Gu, F. Ren, and J. Huang, Opt. Mater. 91, 101 (2019).
X. Li, X. Han, D. Zhu, Y. Chen, L. Li, F. Ren, and J. Huang, Mater. Res. Express 6, 055910 (2019).
S. Li, J. Huang, X. Ning, Y. Chen, and Q. Shi, Funct. Mater. Lett. 11, 1850055 (2018).
Q. Wang, Z. Liu, R. Jin, Y. Wang, and S. Gao, Sep. Purif. Technol. 210, 798 (2019).
D.B. Salunkhe, D.P. Dubal, J.V. Sali, and B.R. Sankapal, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 30, 33516-342 (2015).
V. Senthamilselvi, K. Saravanakumar, N.J. Begum, R. Anandhi, A.T. Ravichandran, B. Sakthivel, and K. Ravichandran, J. Mater. Sci-Mater. Electron. 23, 302 (2012).
X. Li, Y. Chen, L. Li, and J. Huang, Materials 11, 1759 (2018).
X. Li, L. Li, Z. Ma, J. Lu, A.A. Volinsky, and F. Ren, J. Alloy. Compd. 684, 582 (2016).
Q. Wang, R. Jin, C. Yin, M. Wang, J. Wang, and S. Gao, Sep. Purif. Technol. 172, 303 (2017).
Z.C. Guan, X. Wang, P. Jin, Y.Y. Tang, H.P. Wang, G.L. Song, and R.G. Du, Corros. Sci. 143, 31 (2018).
N. Guijarro, T.L. Villarreal, Q. Shen, T. Toyoda, and R. Gomez, J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 21928 (2010).
F.G. Cai, F. Yang, J.F. Xi, Y.F. Jia, C.H. Cheng, and Y. Zhao, Mater. Lett. 107, 39 (2013).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Henan International Science and Technology Cooperation Project of China [No. 152102410035]; the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation [No. 2018M632771]; the University Key Research Project of the Henan Province [No. 15A430023].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. All authors of this manuscript have directly participated in planning, execution and analysis of this study. The contents of this manuscript have not been copyrighted or published previously. The contents of this manuscript are not now under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Yang, M., Zhu, D. et al. Preparation of TiO2/Bi2S3 Composite Photo-Anode Through Ultrasound-Assisted Successive Ionic Layer Adsorption and Reaction Method for Improving the Photoelectric Performance. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 3242–3250 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08012-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08012-1