Abstract
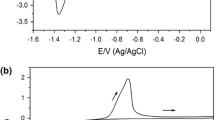
Thin layers of ZnS with thicknesses of 400 nm, 500 nm, and 700 nm have been electrodeposited on glass/fluorine-doped tin oxide substrates using a simple two-electrode setup under similar conditions. Structural characterization of the layers using x-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements showed that they were amorphous. The results of optical characterization carried out in the wavelength range of 315 nm to 800 nm using spectrophotometry revealed that the optical properties of the layers are strongly influenced by the film thickness as well as annealing conditions. The values of the refractive index, extinction coefficient, absorption coefficient, and dielectric constant obtained from normal-incidence transmittance spectra were generally lower after annealing, showing also the influence of postdeposition annealing on the deposited ZnS layers. Electrical characterization of the layers, using direct-current current–voltage measurement under dark conditions at room temperature, shows that the resistivity of the as-deposited and annealed layers is in the range of 1.4 × 104 Ω cm to 2.5 × 104 Ω cm and 2.5 × 104 Ω cm to 3.1 × 104 Ω cm, respectively. The results suggest that the optoelectronic properties can be tuned for particular applications by adjusting the thickness of the layers appropriately.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.M. Andriesh, Semiconductors 32, 867 (1998).
S.M. Sze and K.K. Ng, Physics of Semiconductor Devices, Vol. 3 (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2007).
P.L. Jones, D.R. Cotton, and D. Moore, Thin Solid Films 88, 163 (1982).
T.L. Chu and S.S. Chu, Solid-State Electron. 38, 533 (1995).
K. Anuar, Z. Zainal, N. Saravanan, and N. Asikin, Mater. Sci. 44, 290 (2008).
S.M. Sze, Physics of Semiconductor Devices, Vol. 2 (New Delhi: Wiley Eastern, 1985), p. 683.
X. Fang, Y. Bando, U.K. Gautam, T. Zhai, H. Zeng, X. Xu, M. Liao, and D. Golberg, Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 34, 190 (2009).
J. Wu, W. Shen, H. Li, X. Liu, and P. Gu, Chin. Opt. Lett. (supplement) 8, 32 (2010).
J. Videl, O. deMelo, O. Vigil, N. Lopez, G. Contreras-Puente, and O. Zelaya-Angel, Thin Solid Films 419, 118 (2002).
D. Hariskos, S. Spiering, and M. Powalla, Thin Solid Films 480, 91 (2005).
K. Kassim, S. Nagalingam, H.S. Min, and N. Karrim, Arab. J. Chem. 3, 243 (2010).
B.W. Sanders and A.H. Kitai, J. Cryst. Growth 100, 405 (1990).
O.K. Echendu, A.R. Weerasinghe, D.G. Diso, F. Fauzi, and I.M. Dharmadasa, J. Electron. Mater. 42, 692 (2013). doi:10.1007/s11664-012-2393-y.
Y.P.V. Subbaiah, P. Prathap, and K.T.R. Reddy, Appl. Surf. Sci. 253, 2409 (2006).
M. Janai, D.D. Allred, D.C. Booth, and B.D. Seraphin, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 1, 11 (1979).
C. Kittel, Introduction to Solid State Physics, Vol. 8 (New York: Wiley, 2005), p. 430.
R.F. Shaw, W.Y. Liang, and A.D. Yoffe, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 4, 29 (1970).
I.M. Dharmadasa, Advances in Thin Film Solar Cells (Singapore: Pan Stanford, 2012), p. 46.
F. Gode, Physica B 406, 1653 (2011).
S. Senthilkumaar and S.R. Thamil, Appl. Phys. A 94, 123 (2009).
R.S. Quimby, Photonics and Lasers: An Introduction (Hoboken, NJ: Wiley, 2006), p. 259.
S. Halas, Mater. Sci. (Poland) 24, 951 (2006).
R.C. Cheichei, E.A. Weiss, M.D. Dickey, and G.M. Whitesides, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 142 (2008).
K. Zanio, Semiconductors and Semimetals, Vol. 13 (New York: Academic, 1978), p. 148.
S. Dennison, J. Mater. Chem. 4, 41 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Echendu, O.K., Dharmadasa, I.M. Effects of Thickness and Annealing on Optoelectronic Properties of Electrodeposited ZnS Thin Films for Photonic Device Applications. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 791–801 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-013-2943-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-013-2943-y