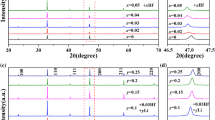
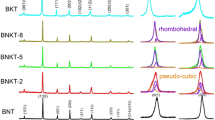
Chemical stability of (Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3 (BNT) ceramics against water was studied through a comparison experiment. Immersion of BNT in 0.01 M NaOH solution showed no noticeable influence, while BNT ceramics were seriously affected when hydrogen was deposited on them through the electrolysis of water in the solution: the capacitance was obviously decreased and the dielectric loss was dramatically increased in the low-frequency range. X-ray diffraction analysis indicated that hydrogen was first dissolved into BNT and then caused decomposition, with some other phases formed. As water-induced degradation is an important cause of degradation for piezoelectric devices, it is important to ensure that the chemical stability of BNT is not decreased when using doping and/or the formation of a solid-state solution with other perovskite-type oxides in order to improve the piezoelectric properties of BNT-based ceramics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Saito, H. Takao, T. Tani, T. Nonoyama, K. Takatori, T. Homma, T. Nagaya, and M. Nakamura, Nature 432, 84 (2004).
X.X. Wang, X.G. Tang, and H.L.W. Chan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 91 (2004).
T. Takenaka, K. Maruyama, and K. Sakata, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 30, 2236 (1991).
A. Sasaki, T. Chiba, Y. Mamiya, and E. Otsuki, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 38, 5564 (1999).
S.H. Choy, X.X. Wang, H.L.W. Chan, and C.L. Choy, Appl. Phys. A 89, 775 (2007).
H. Zhang, Y.J. Su, L.J. Qiao, W.Y. Chu, D. Wang, and Y.X. Li, J. Electron. Mater. 37, 368 (2008).
W.P. Chen, H.L.W. Chan, F.C.H. Yiu, K.M.W. Ng, and P.C.K. Liu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 3587 (2002).
J.D. Baniecki, J.S. Cross, M. Tsukada, and J. Watanabe, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 3837 (2002).
H.Y. Huang, W.Y. Chu, Y.J. Su, K.W. Gao, J.X. Li, and L.J. Qiao, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 2062 (2007).
W.P. Chen, J.Q. Qi, Y. Wang, X.P. Jiang, and H.L.W. Chan, J. Appl. Phys. 95, 5920 (2004).
J.Q. Qi, W.P. Chen, M. Lu, Y. Wang, H.Y. Tian, L.T. Li, and H.L.W. Chan, Nanotechnology 16, 3097 (2005).
Acknowledgements
This program has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 50772077, the State Key Laboratory of New Ceramic and Fine Processing of Tsinghua University, and the Centre for Smart Materials of␣The Hong␣Kong Polytechnic University (Project 1-BB84).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, Y.H., Chen, W.P., Qi, J.Q. et al. Water-Induced Degradation in (Bi1/2Na1/2)TiO3 Lead-Free Ceramics. J. Electron. Mater. 38, 2207–2210 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0892-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-009-0892-2