Abstract
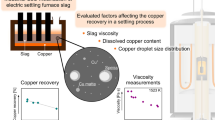
Converter copper slag can be viewed as an important secondary resource for valuable metals, considering its high commercial value. The current research investigates the recycling of copper by a combination of theoretical and experimental methods. Based on a modified Stokes equation, it was determined that copper droplets in the molten slag exhibited a low terminal settling velocity of 2.140 × 10−6 m/s. The copper particles will collide with each other during settling, resulting in particle growth. The results from high temperature experimentation, scanning electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive spectroscopy confirm that in the absence of reducing agents, copper droplets are encased in magnetite to form composite ‘Cu droplet–magnetite’ particles. Other copper droplets adhere to magnetite particles which are suspended in the slag in a short-range-ordered array. The study also confirms that in the presence of increasing amounts of anthracite as a reducing agent, the magnetite content of the slag is progressively decreased and the recovery of copper from the slag is significantly improved. Based on the findings from this work, a new processing route is proposed to treat copper slag for the recovery of copper.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. R. Sharma and R.A. Khan: J. Clean. Prod., 2017, vol. 151, pp. 179-192.
R.U. Pagador, N. Wachgama, C. Khuankla, and J.P.T. Kapusta: TMS Annual Meeting, 2009, pp. 367–81.
3. J.G. Whellock and J.W. Matousek: JOM, 1990, vol. 42, pp. 23-25.
4. P. E. Queneau and R. Schuhmann: JOM, 1974, vol. 26, pp. 14-16.
5. R.R. Moskalyk and A.M. Alfantazi: Miner. Eng., 2003, vol. 16, pp. 893-919.
6. J.H. Heo, Y. Chung, and J.H. Park: J. Clean. Prod., 2016, vol. 137, pp. 777-787.
7. İ. Alp, H. Deveci, and H. Süngün: J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, vol. 159, pp. 390-395.
B. Gorai, R.K. Jana, and Premchand: 2003. Resour. Conserv. Recycl., 2003, vol. 39, pp. 299-313
9. C. Shi, C. Meyer, and A. Behnood: Resour. Conserv. Recycl., 2008, vol. 52, pp. 1115-1120.
10. K. Kambham, S. Sangameswaran, S.R. Datar, and B. Kura: J. Clean. Prod., 2007, vol. 15, pp. 465-473.
11. L. Miganei, E. Gock, M. Achimovičová, L. Koch, H. Zobel, and J. Kähler: J. Clean. Prod., 2017, vol. 164, pp. 534-542.
12. I.K. Suh, Y. Waseda, and A. Yazawa: High Temp. Mater. Processes., 1988, vol. 8, pp. 65-88.
13. N. Cardona, P. Coursol, P.J. Mackey, and R. Parra: Can. Metall. Q., 2011, vol. 50, pp. 318-329.
I. Imris, M. Sanchez, and G. Achurra: in Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Molten Slags, Fluxes and Salts., Johannesburg, South Africa, 2004, pp. 177–82.
15. R. Sridhar, J.M. Toguri, and S. Simeonov: Metal. Mater. Trans. B., 1997, vol. 28, pp. 191-200.
16. S.W. Ip, and J.M. Toguri: Metall. Trans. B., 1992, vol. 23, pp. 303-311.
17. H.C. Maru, D.T. Wasan, and R.C. Kintner: Chem. Eng. Sci., 1971, vol. 26, pp. 1615-1628.
18. R. Minto and W.G. Davenport: Canadian Mining and Metallurgical Bulletin., 1972, vol. 65, pp. C36-42.
19. K. Starodub, Y. Kuminova, A. Dinsdale, V. Cheverikin, V. Filichkina, A. Saynazarov, A. Khvan, and A. Kondratiev: Metal. Mater. Trans. B., 2016, vol. 47, pp. 2904-2918.
20. H. M. Henao, C. Nexhip, D.P. George-Kennedy, P.C. Hayes, and E. Jak: Metal. Mater. Trans. B., 2010, vol. 41, pp. 767-779.
21. P. Tan: JOM., 2011, vol. 63, pp. 51-57.
22. P. Coursol, N.C. Valencia, P. Mackey, S. Bell, and B. Davis: JOM., 2012, vol. 64, pp. 1305-1313.
23. B. Zhao, P. Hayes, and E. Jak: J. Min. Metal. B., 2013, vol. 49, pp. 153-159.
24. A. Rusen, A. Geveci, Y.A. Topkaya, and B. Derin: JOM., 2016, vol. 68, pp. 2323-2331.
25. H. Zhang, X. Shi, B. Zhang, and X. Hong: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2014, Vol. 45B, pp. 582-589.
26.Z. Zuo, Q. Yu, M. Wei, H. Xie, W. Duan, K. Wang, and Q. Qin: J. Therm. Anal. Calorim., 2016, Vol. 126, pp. 481-491.
27. W. J. Bruckard, M. Somerville, and F. Hao: Miner. Eng., 2004, vol. 17, pp. 495-504.
28. E. Rudnik, L. Burzyńska, and W. Gumowska: Miner. Eng., 2009, vol. 22, pp. 88-95.
29. H.S. Altundogan, M. Boyrazli, and F. Tumen: Miner. Eng., 2004, vol. 17, pp. 465-467.
30. A. Sarrafi, B. Rahmati, H.R. Hassani, and H.H.A. Shirazi: Miner. Eng., 2004, vol. 17, pp. 457-459.
31. P. Coursol, N.C. Valencia, P. Mackey, S. Bell, and B. Davis: JOM, 2012, vol. 64, pp. 1305-1313.
32. I. Imris, M. Sánchez, and G. Achurra: Miner. Process. Extr. Metall., 2013, vol. 114, pp. 135-140.
33. W. Wołczyński and A.W. Bydałek: Archives of Foundry Engineering, 2016, vol. 16, pp. 95-98.
34.W. Wołczyński, A. Sypien, A. Tarasek, and A.W. Bydałek: Arch. Metall. Mater., 2017, vol. 62, pp. 289-296.
35. E. D. Wilde, I. Bellemans, L. Zheng, M. Campforts, M. Guo, B. Blanpain, N. Moelans, and K. Verbeken: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2016, vol. 32, pp. 1911-1924.
36.N. Korakas: Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. C, 1962, vol. 72, pp. 35-53.
37.M.H. Chen, D.Z. Cong, T.N. Fang, M.Z. Qi, and H.L. Pan: Principles of Chemical Engineering, 4th Ed, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2015.
38. P.K. Iwamasa, and R.J. Fruehan: ISIJ Int., 1996, vol. 36, pp. 1319-1327.
39.J. Happel, and H. Brenner: Low Reynolds Number Hydrodynamics, 2nd ed. Noordhoff International Publishing, Leyden, 1973.
40. R. Clift, J.R. Grace, and M.E. Weber: Bubbles, Drops, and Particles. Academic Press, New York, 1978.
41. M. Nagamori: Metall. Trans., 1974, vol. 5, pp. 531-538.
42. N. Cardona, P. Coursol, J. Vargas, and R. Parra: Can. Metall. Q. 2011b, Vol. 50, pp. 330-340.
43. R.B. Bird, W.E. Stewart, and E.N. Lightfoot: John Wiley & Sons., 1961, vol. 28, pp. 338-359.
44. S. Francisco, J.W. Taunton, and E.N. Lightfoot: AlChE J., 2010, vol. 16, pp. 386-391.
45.N. Eustathopoulos, M.G. Nicholas, and B. Drevet: Wettability at High Temperatures. Pergamon, Oxford (1999).
46. R. Sangiorgi, M.L. Muolo, D. Chatain, and N. Eustathopoulos: J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1988, vol. 71, pp. 742-748.
47. Y.V. Naidich: in Progress in Surface and Membrane Science, vol. 14, ed. by D. A. Cadenhead and J. F. Danielli, Academic Press, New York,1981, p. 353.
48. I. Rivollet, D. Chatain, and N. Eustathopoulos: J. Mater. Sci., 1990, vol. 25, pp. 3179-3185.
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this study was supplied from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1602272 and 51664039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted October 9, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, S., Wei, Y., Shi, Y. et al. Characterization and Recovery of Copper from Converter Copper Slag Via Smelting Separation. Metall Mater Trans B 49, 2458–2468 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1364-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1364-y