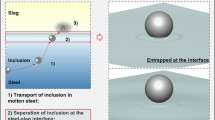
Abstract
A particle-capture model based on local force balances has been developed, implemented into computational models of turbulent fluid flow and particle transport, and applied to simulate the entrapment of slag inclusions and bubbles during the continuous casting of steel slabs. Turbulent flow of molten steel is computed in the nozzle and mold using transient computational fluid flow models, both with and without the effects of argon gas injection. Next, the transport and capture of many particles are simulated using a Lagrangian approach. Particles touching the dendritic interface may be pushed away, dragged away by the transverse flow, or captured into the solidifying shell according to the results of a local balance of ten different forces. This criterion was validated by reproducing experimental results in two different systems. The implications of this criterion are discussed quantitatively. Finally, the fluid flow/particle transport model results and capture criterion are applied together to predict the entrapment distributions of different sized particles in a typical slab caster. More large particles are safely removed than small ones, but the entrapment rate into the solidifying shell as defects is still very high.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ρ :
-
Density (kg/m3)
- ρ f :
-
Liquid density (kg/m3)
- ρ p :
-
Particle density (kg/m3)
- u :
-
Liquid velocity (m/s)
- v :
-
Particle velocity (m/s)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity of fluid (Pa s)
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity of fluid (m2/s)
- f :
-
Body force density (per unit volume) (N/m3)
- x p :
-
Particle position vector (m)
- m p :
-
Mass of a particle (kg)
- F D :
-
Drag force (N)
- F L :
-
Lift force (N)
- F added-mass :
-
Added mass force (virtual mass force) (N)
- F G :
-
Gravitational force (N)
- F press :
-
Pressure gradient force (N)
- F stress :
-
Stress gradient force (N)
- F I :
-
Magnitude of Van de Waals interfacial force (N)
- F Grad :
-
Magnitude of surface energy gradient force (N)
- F lub :
-
Magnitude of lubrication force (N)
- V sol :
-
Solidification front advancing speed (m/s)
- R p :
-
Particle radius (m)
- r tip :
-
Dendrite tip radius (m)
- a 0 :
-
Liquid atomic radius (m)
- h 0 :
-
Distance between dendrite tip and particle (m)
- Δσ 0 :
-
Surface energy difference (J/m2)
- σ sp :
-
Surface tension between shell and particle (J/m2)
- σ sl :
-
Surface tension between shell and liquid (J/m2)
- σ pl :
-
Surface tension between particle and liquid (J/m2)
- ξ :
-
Distance between dendrite tip center to particle center (m)
- χ :
-
Solidification direction (m)
- η :
-
Direction across solidification (m)
- g :
-
Gravity acceleration (m/s2)
- d p :
-
Particle diameter (m)
- C D :
-
Drag coefficient
- Rep :
-
Particle Reynolds number
- u 1 :
-
Streamwise liquid velocity (m/s)
- v 1 :
-
Streamwise particle velocity (m/s)
- U s :
-
Relative streamwise velocity between liquid and particle (m/s)
- G :
-
Wall normal velocity gradient of u 1 (1/s)
- C A :
-
Correction factor on added mass force
- Ac:
-
Acceleration parameter
- α :
-
Constant for surface energy gradient force
- β :
-
Constant for surface energy gradient force (m)
References
B.G. Thomas: in Making, Shaping and Treating of Steel: Continuous Casting, vol. 5, A. Cramb, ed., 2003, pp. 14.1–14.41.
Q. Yuan, B.G. Thomas and S.P. Vanka: Metal. & Material Trans. B., 2004, vol. 35B (4), pp. 703-714.
L.C. Hibbeler and B.G. Thomas: in 7th Eur. Contin. Cast. Conf., Dusseldorf, Germany. 2011. Vol. 1.
R.A. Rege, E.S. Szekeres and W.D. Forgeng: Met. Trans. AIME, 1970, vol. 1, p. 2652.
L. Zhang and B.G. Thomas: ISIJ International, 2003, vol. 43 (3), pp. 271-291.
L. Zhang, S. Yang, X. Wang, K. Cai, J. Li, X. Wan, and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater.Trans. B, 2007, vol. 28B, pp. 63-83.
Y. Miki and S. Takeuchi: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 1548-55.
L. Zhang, Jun Aoki and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2006, vol. 37B, pp. 361-379.
W.H. Emling, T.A. Waugaman, S.L. Feldbauer, and A.W. Cramb: in Steelmak. Conf. Proc., Chicago, IL. 1994. Vol. 77, pp. 371–79.
B.G. Thomas and L. Zhang: ISIJ Internat., 2001, vol. 41 (10), pp. 1181-1193.
B.G. Thomas: in Making, Shaping and Treating of Steel: Continuous Casting, vol. 5, A. Cramb, ed., AISE Steel Foundation, Pittsburgh, PA, 2003, pp. 5.1–5.24.
Q. Yuan, B.G. Thomas and S.P. Vanka: Metal. & Material Trans. B., 2004, vol. 35B, pp. 685-702.
R. Chaudhary, C. Ji, B.G. Thomas and S.P. Vanka: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42B, pp. 987-1007.
FLUENT6.2, User Manual, Ansys Inc., 10 Cavendish Court, Lebanon, New Hampshire, 2009.
B.G. Thomas, A. Dennisov and H. Bai: in 80th Steelmak. Confer. Proc., 1997, pp. 375–384.
L. Zhang, Y. Wang and X. Zuo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2008, vol. 39B, pp. 534–550.
Y. Wang and L. Zhang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B., 2011, vol. 42(6), pp. 1319–51.
L. Zhang, Y. Wang, E. Martinez, and K.D. Peaslee: in CFD Modeling and Simulation in Materials. L. Nastac, L. Zhang, B.G. Thomas, A. Sabau, N. El-Kaddah, A.C. Powell and H. Combeau, eds., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2012, pp. 3–16.
D. Shangguan, S. Ahuja and D.M. Stefanescu: Metallurgical Transactions A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 669-680.
J. Potschke and V. Rogge: Journal of Crystal Growth, 1989, vol. 94, pp. 726-738.
D.M. Stefanescu and A.V. Catalina: ISIJ Internat., 1998, vol. 38, pp. 503-505.
G. Wilde and J.H. Perepezko: Materials Science & Engineering A, 2000, vol. 283, pp. 25-37.
Y. Wang, M. Valdez and S. Sridhar: Z. Metallkd., 2002, vol. 93, pp. 12-20.
J.K. Kim and P.K. Rohatgi: Metall. & Mater. Trans. B, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 351-375.
D.R. Uhlmann and B. Chalmers: J. Appl. Phys., 1964, vol. 35, pp. 2986-2993.
G.F. Bolling and J.A. Cisse: J. Cryst. Growth, 1971, vol. 10, pp. 55-66.
D.M. Stefanescu, F.R. Juretzko, B.K. Dhindaw, A. Catalina and S. Sen: Metall.Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 1697-1706.
D.M. Stefanescu, F.R. Juretzko, B.K. Dhindaw, A. Catalina and S. Sen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 1691-1696.
A. Catalina, D.M. Stefanescu and S. Mukherjee: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31A (10), pp. 2559-2568.
G. Kaptay: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A (7), pp. 1887-1890.
G. Kaptay: Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2001, vol. 32A (4), pp. 993-1005.
G. Kaptay and K.K. Kelemen: ISIJ International, 2001, vol. 41 (3), pp. 305-307.
G. Kaptay: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A (6), pp. 1869-1873.
Z. Wang, K. Mukai and J. Lee: ISIJ International, 1999, vol. 39 (6), pp. 553-562.
Q. Han and J.D. Hunt: J. Crystal Growth, 1995, vol. 152, pp. 221-227.
Q. Han: “The Mechanisms for Particle Pushing,” University of Oxford, Oxford, UK, 1994.
B. Grimm, P. Andrzejewski, K. Muller, and K.-H. Tacke: Steel Res., 1999, vol. 70, pp. 420–29.
Yufeng Wang, Anping Dong and L. Zhang: Steel Res. Int., 2011, vol. 82, pp. 428–39.
C. Pfeiler, B.G. Thomas, M. Wu, A. Ludwig and A. Kharicha: Steel Research International, 2008, vol. 79 (8), pp. 599-607.
Q. Yuan and B.G. Thomas: Proc. 3rd Int. Congr. Sci. Technol. Steelmak., Charlotte, NC. 2005. pp. 745–62.
B.E. Launder and D.B. Spalding: Comp. Meth. Applied Mechanics and Engr., 1974, vol. 13 (3), pp. 269-289.
B. Kader: Int. J. Heat Mass Trans., 1981, vol. 24 (9), pp. 1541-1544.
H. Werner and H. Wengle: 8th Symp. Turbul. Shear Flows, Munich. 1991.
S. Mahmood: MS Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2006, 202 pp.
H. Bai and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2001, vol. 32B (2), pp. 253-267.
F. Nicoud and F. Ducros: Flow Turb. Comb., 1999, vol. 63, pp. 183-200.
B.E. Launder and D.B. Spalding: Mathematical Models of Turbulence, London: Academic Press, 1972.
T.H. Shih, W.W. Liou, A. Shabbir, Z. Yang and J. Zhu:: Comput. Fluid., 1995, vol. 24 (3), pp. 227-238.
R. Chaudhary, S.P. Vanka, and B.G. Thomas: CCC Report 201017, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Aug 12, 2010.
Y. Meng and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2003, vol. 34B (5), pp. 685-705.
S. Koric, L.C. Hibbeler, R. Liu and B.G. Thomas: Numerical Heat Transfer, Part B: Fundamentals, 2010, vol. 58 (6), pp. 371-392.
Q. Yuan: Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, IL, 2004, 196 pp.
W.H. Press, B.P. Flannery, S.A. Teukolsky and W.T. Vetterling: Numerical Recipes, Cambridge University Press, New York, NY, 1988, pp. 289-293.
Q. Yuan, B. Zhao, S.P. Vanka and B.G. Thomas: Steel Res. Int., 2005, vol. 76 , pp. 33-43 (Special Issue: Simulation of Fluid Flow in Metallurgy).
B.G. Thomas, Q. Yuan, S. Sivaramakrishnan, T. Shi, S.P. Vanka and M.B. Assar ISIJ Int. Jpn, 2001, vol. 41 (10), pp. 1262–71.
H. Shibata, H. Yin, S. Yoshinaga, T. Emi and M. Suzuki: ISIJ International, 1998, vol. 38 (2), pp. 149-156.
Y. Miki and B.G. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999, vol. 30B (4), pp. 639-654.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the National Science Foundation (Grants DMI-01-15486 and CMMI-11-30882) and the Continuous Casting Consortium at the University of Illinois for support of this project. Thanks are also due to the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois for computing time.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 30, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, B.G., Yuan, Q., Mahmood, S. et al. Transport and Entrapment of Particles in Steel Continuous Casting. Metall Mater Trans B 45, 22–35 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-013-9916-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-013-9916-7