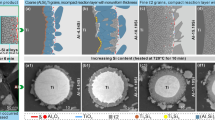
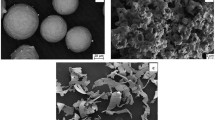
Abstract
Using Ti@Ni core–shell powder is in favor of enhancing the sintering densification, obtaining the linear shrinkage response, forming equiaxed α-Ti grain, and reducing the oxygen contamination, compared to the elemental powder mixtures. The enhanced sintering densification is responsible for the improved tensile strength, while a combination of the equiaxed α-Ti grain formation, the low oxygen increment, and the reduced porosity content noticeably doubled the tensile ductility. The linear shrinkage response is good for accurately controlling the dimension of the sintered parts. All of the improved issues are largely attributed to the unique dissolution phenomenon of Ni from Ti@Ni core–shell powder. The detailed mechanism will be discussed in this paper.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.A. Zhang, C.M. Wang, Y.G. Zhang, Y.H Wei, S.F. Xiao, and Y.G. Chen: Mater. Manuf. Processes, 2018, vol. 33, pp.849-55.
X.X. Ye, B. Chen, J.H. Shen, J. Umeda, and K. Kondoh: J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 709, pp. 381-93.
S.J. Gerdemann and P.D. Jablonski: Metall. Mat. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42, pp. 1325-33.
S. Luo, Y. Yang, G. Schaffer, and M. Qian: J. Mater. Process. Tech., 2014, vol. 214, pp. 660-6.
M. Qian: Int. J. Powder Metall., 2010, vol. 46, pp. 29-44.
M. Qian and F.H. Froes: Titanium Powder Metallurgy: Past, Current and Future, 1st ed. Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam, 2015.
Y.F. Yang, S.D. Luo, G.B. Schaffer, and M. Qian: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 7381-87.
B.B. Panigrahi: Mater. Lett., 2007, vol. 61, pp. 152-55.
I.M. Robertson and G.B. Schaffer: Powder Metall., 2009, vol. 52, pp. 316-21.
I. M. Robertson and G. B. Schaffer: Powder Metall., 2009, vol. 52, pp. 213-24.
G. Chen, K.D. Liss, and P. Cao: Acta Mater., 2014, vol. 67, pp. 32-44.
O.M. Ferri, T. Ebel, and R. Bormann: Adv. Eng. Mat., 2011, vol. 13, pp. 436-47.
S.D. Luo, Y.F. Yang, G.B. Schaffer, and M. Qian: J. Alloys Compd., 2013, vol. 555, pp. 339-46.
H.W. Liu, D.P. Bishop, and K.P. Plucknett: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, vol. 644, pp. 392-404.
R.J. Low, I.M. Robertson, and G.B. Schaffer: Scr. Mater., 2007, vol. 56, pp. 895-8.
L.F. Hu, Y.Z. Xue, and F.R. Shi: Mater. Des., 2017, vol. 130, pp. 175-82.
I.M. Robertson and G.B. Schaffer: Powder Metall., 2009, vol. 52, pp. 225-32.
R. Thyarajan, G.M.D. Cantin, B.P. Kashyap, and C.J. Bettles: Powder Technol., 2015, vol. 274, pp. 53-61.
N. Barbat and K. Zangeneh-Madar: Powder Metall., 2014, vol. 57, pp. 97-102.
J.H. Chen, S.B. Ren, X.B. He, and X.H. Qu: Carbon, 2017, vol. 121, pp. 25-34.
J.L. Song, W.G. Chen, L.L. Dong, J.J. Wang, and N. Deng: J. Alloys Compd., 2017, vol. 720, pp. 54-62.
M.J. Donachie: Titanium, A Technical Guide, 2nd ed., ASM International, Metals Park, OH, 2000, pp. 13-24.
R.R. Boyer and G.W. Kuhlman: Metall. Mat. Trans. A, 1987, vol. 18, pp. 2095-2103.
Y. Yue, L.Y. Dai, H. Zhong, C.L. Tan, M.Z. Ma, X.Y Zhang, and R.P. Liu: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2016, vol. 678, pp. 286-90.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences (Grant No. QYZDB-SSW-JSC045), Chinese Academy of Sciences, and National Youth Thousand Plan Program. This work was also financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51602313).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted March 22, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, C., Li, S.F., Yang, Y.F. et al. Sintering Response and Equiaxed α-Ti Grain Formation in the Ti Alloys Sintered from Ti@Ni Core–Shell Powders. Metall Mater Trans A 49, 3394–3401 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4698-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4698-9