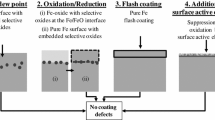
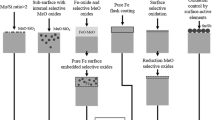
Abstract
The influence of the addition of Sn on the selective oxidation and the reactive wetting of CMnSi transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) steels was studied by means of galvanizing simulator tests. A reference TRIP steel and TRIP steels containing Sn in the range of 0.05 to 1 wt pct were intercritically annealed at 1093 K (820 °C) in an N2+ 5 pct H2 gas atmosphere with a dew point of −60 °C. The thin-film oxides formed on the surface of the Sn-added CMnSi TRIP steel were investigated using transmission electron microscopy and 3-dimensional atom probe tomography. The addition of Sn (≥0.05 wt pct) changed the morphology of the xMnO·SiO2 surface oxides from a continuous film morphology to a lens-shaped island morphology. It also suppressed the formation of the Mn-rich oxides of MnO and 2MnO·SiO2. The changes in the morphology and chemistry of the surface oxides were clearly related to the surface segregation of Sn, which appeared to result in a decrease of the oxygen permeability at the surface. The formation of lens-shaped oxides improved the wettability of the CMnSi TRIP steel surface by the molten Zn. The improved wetting effect was attributed to an increased area fraction of the surface where the oxide layer was thinner. This enabled a direct, unhindered reaction between Fe and the Al in the liquid Zn and the formation of the inhibition layer in the initial stages of the hot dipping. The addition of a small amount of Sn was also found to decrease significantly the density of Zn-coating defects on CMnSi TRIP steel.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. E.M. Bellhouse, J.R. McDermid: Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2010, vol. 41, pp. 1539-53.
2. M.S. Kim, J.H. Kwak, J.S. Kim, Y.H. Liu, N. Gao, N.Y. Tang: Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2009, vol. 40, pp. 1903-10.
L. Cho, S.J. Lee, M.S. Kim, Y.H. Kim, B.C. De Cooman: Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013, vol. 44, pp. 362-71.
4. H. Liu, Y. He, S. Swaminathan, M. Rohwerder, L. Li: Surface and Coatings Technology, 2011, vol. 206, pp. 1237-43.
5. H.G. Lee, Chemical Thermodynamics for Metals and Materials, Imperial College Press, London, UK, 1999.
6. Z.T. Zhang, I.R. Sohn, F.S. Pettit, G.H. Meier, S. Sridhar: Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2009, vol. 40, pp. 567-84.
7. E. Clauberg, C. Uebing, H. Grabke: Applied Surface Science, 1999, vol. 143, pp. 206-14.
8. Y.L. Zhang, Y.Y. Zhang, F.H. Yang, Z.T. Zhang: Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2013, vol. 20, pp. 39-56.
9. G. Lyudkovsky: IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 1986, vol. 22, pp. 508-10.
10. L. Cho, M.S. Kim, Y.H. Kim, B.C. De Cooman: Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 4484-98.
11. D. Melford: Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 1980, vol. 295, pp. 89-103.
12. D. Huin, P. Flauder, J.B. Leblond: Oxid Met, 2005, vol. 64, pp. 131-67.
13. K.K. Wang, C.W. Hsu, L. Chang, D. Gan, T.R. Chen, K.C. Yang: Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2012, vol. 159, pp. 561-70.
14. J.B. Brunac, D. Huin, J.B. Leblond: Oxid Met, 2010, vol. 73, pp. 565-89.
15. H. Viefhaus, M. Rüsenberg: Surface Science, 1985, vol. 159, pp. 1-23.
16. K. Kumar, P. Wollants, L. Delaey: Calphad, 1996, vol. 20, pp. 139-49.
17. T. Okoshi: Applied optics, 1971, vol. 10, pp. 2284-91.
18. R.E. Galindo, E. Forniés, J. Albella: Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2005, vol. 20, pp. 1108-15.
19. V. Hoffmann, R. Dorka, L. Wilken, V.D. Hodoroaba, K. Wetzig: Surface and Interface Analysis, 2003, vol. 35, pp. 575-82.
20. L. Yin, S. Sridhar: Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2010, vol. 41, pp. 1095-107.
21. H.J. Grabke: ISIJ International, 1989, vol. 29, pp. 529-38.
22. H.J. Grabke: Kovine, Zlitine, Tehnologije, 1996, vol. 30, pp. 483-95.
23. N. Kaiser: Applied Optics, 2002, vol. 41, pp. 3053-60.
24. A.J. Kinloch, Adhesion and Adhesives-Science and Technology, Chanpman and Hall, London, UK, 1987, pp. 30.
25. S. Brunauer, D.L. Kantro, C.H. Weise: Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 1956, vol. 34, pp. 1483-96.
26. L. Vitos, A.V. Ruban, H.L. Skriver, J. Kollar: Surface Science, 1998, vol. 411, pp. 186-202.
27. R.W. Olesinski, G.J. Abbaschian: Journal of Phase Equilibria, 1984, vol. 5, pp. 273-76.
28. Y.F. Gong, H.S. Kim, B.C. De Cooman: ISIJ International, 2008, vol. 48, pp. 1745-51.
29. L. Cho, B.C. De Cooman: Steel Research International, 2012, vol. 83, pp. 391-97.
30. J.H. Lee, J.C. Park, S.H. Jeon: Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2009, vol. 40, pp. 1035-40.
31. J.H. Lee, J.C. Park, Y.K. Kim, S.H. Jeon: Journal of Materials Science, 2010, vol. 45, pp. 2112-17.
32. R. Kavitha, J.R. McDermid: Surface and Coatings Technology, 2012, vol. 212, pp. 152-58.
33. H. Liu, Y. He, L. Li: Applied Surface Science, 2009, vol. 256, pp. 1399-403.
N. Gao, D.Y.H. Liu, N. Tang, R.B. Park, and M.S. Kim: in Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Zinc and Zinc Alloy Coated Steel Sheet (GALVATECH 2011), Associazione Italiana di Metallurgia, Genova, Italy, 2011, pp. 123–30.
35. J. Takada, M. Adachi: Journal of Materials Science, 1986, vol. 21, pp. 2133-37.
36. H. Oikawa: Technology Reports, Tohoku University, 1983, vol. 48, pp. 76-77.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of Dr. Myung Soo Kim and Dr. Young Ha Kim from the POSCO Technical Research Laboratories, Gwangyang, South Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 10, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, L., Seo, E.J., Jung, G.S. et al. Surface Selective Oxidation of Sn-Added CMnSi TRIP Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 47, 1705–1719 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3331-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-016-3331-z