Abstract
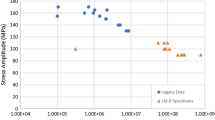
High-cycle fatigue tests were carried out on a newly developed high-strength AA 2026 Al alloy, which was in the form of extrusion bars with square and rectangular cross sections, using a self-aligning four-point-bend rig at room temperature, 15 Hz, and R = 0.1, in lab air. The fatigue strength of the square and rectangular bars was measured to be 85 and 90 pct of their yield strength, respectively, more than twice that of the predecessor to the 2026 alloy (the AA 2024 Al alloy). Fatigue cracks were found to be always initiated at large Θ′ (Al7Cu2(Fe,Mn)) particles and to propagate predominantly in a crystallographic mode in the AA 2026 alloy. The fatigue fractographies of the square and rectangular extrusion bars were found to be markedly different, due to their different grain structures (fibril and layered, respectively). Fracture steps on the crack face were found in both of these extrusion bars. Since the 2026 alloy was purer in terms of Fe and Si content, it contained much less coarse particles than in a 2024 alloy. This partially accounted for the superior fatigue strength of the 2026 alloy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Ratchev, B. Verlinden, P.D. Smet, and P.V. Houtte: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 3523–33.
V. Radmilovic, R. Kilaas, U. Dahmen, and G.J. Shiflet: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47, pp. 3987–97.
S.E. Axter, W.B. Jones, and D.H. Polonis: Metallography, 1975, vol. 8, pp. 425–38.
E.A. Debartolo and B.M. Hillberry: Int. J. Fatigue, 1998, vol. 20, pp. 727–35.
W.L. Haworth, A.F. Hieber, and R.K. Mueller: Metall. Trans. A, 1977, vol. 8A, pp. 1597–1604.
D. Sigler, M.C. Montpetit, and W.L. Haworth: Metall. Trans. A, 1983, vol. 14A, pp. 931–38.
B. Sarkar and W.B. Lisagor: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1992, vol. 26, 169–74.
A. Zabett and A. Plumtree: Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 1995, vol. 18, pp. 801–09.
C. Kaynak and A. Ankara: Eng. Fract. Mech., 1992, vol. 43, pp. 769–78.
J. Zuidema and M. Mannesse: Eng. Fract. Mech., 1989, vol. 34, pp. 445–56.
B.G. Journet, A. Lefrancois, and A. Pineau: Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 1989, vol. 12, pp. 237–46.
F. Sarioğlu and F.Ő. Orhaner: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1998, vol. A248, pp. 115–19.
J. Liu, G.H. Bray, D.A. Lukasak, and R.C. Pahl: U.S. Patent 6,325,869, Dec. 4, 2001.
M.D. Garratt, G.H. Bray, and D.A. Koss: Proc. Materials Solutions Conf., Indianapolis, IN, 2001, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 2001, pp. 151–59.
P. Kadolkar and N.B. Dahotre: Mater. Sci. Eng., 2003, vol. A342, pp. 183–91.
T. Shimokawa and Y. Hamaguchi: J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 1985, vol. 107, pp. 214–20.
T. Zhai, Y.G. Xu, J.W. Martin, A.J. Wilkinson, and G.A.D. Briggs: Int. J. Fatigue, 1999, vol. 21, pp. 889–94.
B. Ren: U.S. Patent 6,602,363, Aug. 5, 2003.
C.R. Hutchinson and S.P. Ringer: Metall. and Mater. Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31A, pp. 2721–33.
L.M. Wang, H.M. Flower, and T.C. Lindley: Scripta Mater., 1999, vol. 41, pp. 391–96.
B.Q. Li and F.E. Wawner: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 5483–90.
C.Y. Kung and M.E. Fine: Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 603–10.
L.F. Mondolfo: Aluminum Alloys, Structure and Properties, Butterworths, Boston, MA, 1976, p. 842.
Steven R. Lampman: ASM Handbook, ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1994, vol. 19, pp. 786.
S.E. Aster, W.B. Jones, and D.H. Polonis: Metallography, 1975, vol. 8, pp. 425–38.
R. Gürbüz and S.P. Alpay: Scripta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 30, pp. 1373–76.
S. Suresh and R.O. Ritchie: Int. Met. Rev., 1984, vol. 29, pp. 445–76.
T. Zhai, A.J. Wilkinson, and J.W. Martin: Acta Mater., 2000, vol. 48, pp. 4917–27.
K.S. Chan, Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 2021–29.
T. Zhai, A.J. Wilkinson, J.W. Martin, and I.G. Palmer: Proc 7th Int. Conf. on Fatigue ’99, Beijing, 1999, Higher Education Press, Beijing, China, 1999, pp. 627–32.
K.S. Chan and D.S. Shih: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1997, vol. 28A, pp. 79–90.
K.S. Chan and D.S. Shih: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 73–87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J.X., Zhai, T., Garratt, M.D. et al. Four-point-bend fatigue of AA 2026 aluminum alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 36, 2529–2539 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-005-0126-z
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-005-0126-z