Abstract
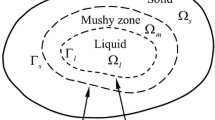
A constitutive equation for thermal strain in the mushy zone during solidification of aluminum alloys has been determined based on a two-phase volume-averaged description of the mushy zone. The change of linear dimensions in the horizontal plane of cast samples during solidification is investigated experimentally. The temperature when the solid part of the mushy zone starts to contract, and the total contraction of the solid part of the mushy zone, are determined experimentally. The constitutive model for thermal strain in the mushy zone reflects that there is no thermal strain in the solid part of the mushy zone at a low solid fraction and that the thermal strain in the mushy zone approaches thermal contraction in fully solid as the solid fraction increases towards one. The parameters in the constitutive model for thermal strain in the mushy zone are determined by combining experimental results with thermomechanical simulations of the experiments. The heat-transfer coefficients and the parameters in the model are tuned to make the simulations reproduce the experimentally determined temperature field and contraction. Al-Cu alloys with Cu concentrations from 0.3 to 9 wt pct Cu and an Al-7 wt pct Si-0.3 wt pct Mg alloy are tested both with and without grain refinement and at various cooling rates. The solid fractions when the alloys start to contract (g th s ) are in the range of 0.48 to 0.97. A lower solute concentration, grain refinement, and higher cooling rate increase g th s .
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Campbell: Castings, Butterworth Heinemann, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1991.
M. Rappaz, J.-M. Drezet, and M. Gremaud: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A, pp. 449–455.
I. Farup and A. Mo: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31A, pp. 461–72.
Y.F. Guven and J.D. Hunt: Cast Met. 1998, vol. 1, pp. 104–11.
M. M’Hamdi, A. Mo, and C.L. Martin: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 2081–93.
J. Ni and C. Beckermann: Metall. Trans. B, 1991, vol. 22B, pp. 349–61.
C.L. Martin, M. Braccini, and M. Suéry: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, vol. A325, pp. 293–302.
C.L. Martin, O. Ludwig, and M. Suéry: Proc. World Congr. on Computational Mechanics V (2002), H.A. Mang, F.G. Rammerstorfer, and J. Eberhardsteiner, eds., Vienna University of Technology, Vienna, Austria, 2002.
P. Kolby, M. M’Hamdi, A. Mo, Ø. Nielsen, and P. Misic: AFS Trans, vol. 110, p. 2002.
I. I. Novikov: Goryachelomkost Tsvetnykh Metallov i Splavov (Hot Tearing of Nonferrous Metals and Alloys), Nauka, Moscow, 1966.
D. Eskine, J. Zuidema, Jr., and L. Katgerman: Int. J. Cast Met. Res., 2002, vol. 14, pp. 217–24.
D.G. Eskin, Suyitno, J.F. Mooney, and L. Katgerman: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 1325–35.
M. M’Hamdi, A. Pilipenko, and D. Eskin: AFS Trans., 2003, vol. 111, pp. 333–40.
C.L. Martin, D. Favier, and M. Suéry: Int. J. Plasticity, 1997, vol. 13 (3), pp. 215–35.
M. Braccini: Ph.D. Thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Grenoble, Grenoble, France, 2000.
M.C. Flemings: Metall. Trans. B, 1991, vol. 22B, pp. 269–93.
MARC Analysis Research Corporation, Palo Alto, CA.
A.L. Dons, E.K. Jensen, Y. Langsrud, E. Trømborg, and S. Brusethang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A, pp. 2135–46.
M. Braccini, C.L. Martin, and M. Suéry: in Modeling of Casting, Welding and Advanced Solidification Processes IX, P.R. Sahm, P.N. Hansen, and J.G. Conley, eds., Shaker Verlag, Germany, 2000, pp 18–24.
MARC ® Volume A: Theory and User Information, Version 7.3, MARC Analysis Research Corporation. Palo Alto, CA, Aug. 1998.
L. Arnberg, L. Bäckerud, and G. Chai: Solidification Characteristics of Aluminium Alloys, vol 3, Dendrite Coherency, AFS, Des Plaines, IL, 1996.
G. Chai: Ph.D. Thesis, Chem. Com. Nr 1, Stockholm University, Stockholm, 1994.
http://www.sintef.no/static/mt/norlight/, Mar. 5, 2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stangeland, A., MO, A., Nielsen, Ø. et al. Development of thermal strain in the coherent mushy zone during solidification of aluminum alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 35, 2903–2915 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-0238-x
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-004-0238-x