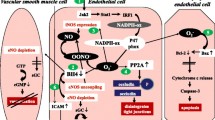
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the synergistic effect of Naoxintong Capsule (NXTC, 脑心通胶囊) and Guhong Injection (GHI, 谷红注射液) on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury.
Methods
Forty-eight Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into 6 groups: control group, oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD) group, nimodipine group (9.375 mg/kg), NXTC group (0.5 g/kg), GHI group (5 mL/kg) and NXTC+GHI group (0.5 g/kg NXTC+5 mL/kg GHI), after the onset of reperfusion and once per day for the following 7 days. Blood was collected 1 h after final administration, and the sera were collected. Cultured primary rat brain microvascular endothelial cells (rBMECs) were subjected to OGD to establish a cell injury model. Untreated rBMECs were used as blank control. The cell counting kit-8 assay was used to assess cell viability using the sera. Malondialdehyde (MDA) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels were assessed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Apoptosis was evaluated after Hoechst33342 staining using fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. JC-1 staining was performed to assess changes in mitochondrial membrane potential.
Results
Statistical analysis indicated that more than 95% of the cells were rBMECs. Compared with the OGD group, the cellular morphology of the all drug delivery groups improved. In particular, the combined drug group had the most significant effect. Compared with the OGD group, all drug intervention groups induced a decrease in the apoptotic rate of rBMECs, increased the SOD levels, and decreased the MDA levels (all P<0.01). Compared with the mono-therapy groups, the NXTC+GHI group exhibited a significant improvement in the number of apoptotic rBMECs (P<0.01). All drug intervention groups showed different degrees of increase in membrane potential, and the NXTC+GHI group was higher than the NXTC or GHI group (P<0.01).
Conclusion
The combinationa application of NXTC and GHI on cerebral I/R injury clearly resulted in protective benefits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim BJ, Lee EJ, Kwon SU, Park JH, Kim YJ, Hong KS, et al. Prevention of cardiovascular events in Asian patients with ischaemic stroke at high risk of cerebral haemorrhage (PICASSO): a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 2018;17:509–618.
Bager JE, Hjalmarsson C, Manhem K, Andersson B. Acute blood pressure levels and long-term outcome in ischemic stroke. Brain Behav 2018;8:1–7.
Li X, Zheng L, Xia Q, Liu L. A novel cell-penetrating peptide protects against neuron apoptosis after cerebral ischemia by inhibiting the nuclear translocation of annexin A1. Cell Death Differ 2018;26:260–275.
Wang LQ, He Y, Wan HF, Zhou HF, Yang JH, Wan HT. Protective mechanisms of hypaconitine and glycyrrhetinic acid compatibility in oxygen and glucose deprivation injury. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 2017;18:586–596.
Hetz C, Vitte PA, Bombrun A, Rostovtseva TK, Montessuit S, Hiver A, et al. Bax channel inhibitors prevent mitochondrion-mediated apoptosis and protect neurons in a model of global brain ischemia. J Biol Chem 2005;280:42960–42970.
Lv Z, Liu C, Zhai M, Zhang Q, Li J, Zheng F, et al. LPS pretreatment attenuates cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem 2018;45:2246–2256.
Cheon SY, Kim EJ, Kim JM, Koo BN. Cell type-specific mechanisms in the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke: the role of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018;2018:2596043.
Ai J, Wan H, Shu M, Zhou H, Zhao T, Fu W, et al. Guhong Injection protects against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via anti-inflammatory effects in rats. Arch Pharm Res 2017;40:610–622.
Wang PR, Wang JS, Yang MH, Kong LY. Neuroprotective effects of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction on ischemic stroke rats revealed by (1)H NMR metabolomics approach. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2014;88:106–116.
Guo H, Li MJ, Liu QQ, Guo LL, Ma MM, Wang SX, et al. Danhong Injection attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain damage which is associating with Nrf2 levels in vivo and in vitro. Neurochem Res 2014;39:1817–1824.
Li J, Bai Y, Bai Y, Zhu R, Liu W, Cao J. Pharmacokinetics of caffeic acid, ferulic acid formononetin, cryptotanshinone, and tanshinone II A after oral administration of Naoxintong Capsule in rat by HPLC-MS/MS. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2017;2017:1–12.
Liu LT. Chinese experts consensus on clinical application of Naoxintong Capsule. Chin J Integr Med 2018;24:232–236.
Shen Y, Huang Z, Huang J. Clinical effect of Guhong Injection on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. World Chin Med (Chin) 2016;11:2637–2640.
Zhang R, Yang N, Ji C, Zheng J, Liang Z, Hou CY, et al. neuroprotective effects of aceglutamide on motor function in a rat model of cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Restor Neurol Neurosci 2015;33:741–759.
Cui D, Zhao D, Wang B, Liu B, Yang L, Xie H, et al. Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) polysaccharide attenuates cellular apoptosis in steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head by targeting caspase-3-dependent signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol 2018;116:106–112.
Deng L, Wan H, Zhou H, Yu L, He Y. Protective effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A alone or in combination with acetylglutamine on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rat: A PET study using (18)F-fuorodeoxyglucose. Eur J Pharmacol 2018;825:119–132.
Jiang YR, Miao Y, Yang L, Xue M, Guo CY, Ma XJ, et al. Effect of Chinese herbal drug-containing serum for activating-blood and dispelling-toxin on ox-LDL-induced inflammatory factors' expression in endothelial cells. Chin J Integr Med 2012;18:30–33.
Yang G, Wang N, Seto SW, Chang D, Liang H. Hydroxysafflor yellow A protects brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen glucose deprivation/reoxygenation injury: involvement of inhibiting autophagy via class I PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Brain Res Bull 2018;140:243–257.
Chazotte B. Labeling mitochondria with JC-1. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2011;2011:990–995.
Dong YZ, Meng XM, Li GS. Long non-coding RNA SNHG15 indicates poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer and promotes cell proliferation and invasion. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2018;22:2671–2679.
Xu Y, Yang X, Wang T, Yang L, He YY, Miskimins K, et al. Knockdown delta-5-desaturase in breast cancer cells that overexpress COX-2 results in inhibition of growth, migration and invasion via a dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid peroxidation dependent mechanism. BMC Cancer 2018;18:330–345.
Wu J, Yang Y, Xun N, Zeng L, Li Z, Yang W, et al. Osthole attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting apoptosis and inflammation. Am J Transl Res 2018;10:1109–1116.
Jiang S, Shi Z, Li C, Ma C, Bai X, Wang C. Hydroxysafflor yellow A attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced liver injury by suppressing macrophage activation. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:2595–2608.
Chang CF, Lai JH, Wu JC, Greig NH, Becker RE, Luo Y, et al. (-)-Phenserine inhibits neuronal apoptosis following ischemia/reperfusion injury. Brain Res 2017;1677:118–128.
Liu Y, Xue Q, Tang Q, Hou M, Qi H, Chen G, et al. A simple method for isolating and culturing the rat brain microvascular endothelial cells. Microvasc Res 2013;90:199–205.
Yang H, Xi X, Zhao B, Su Z, Wang Z. KLF4 protects brain microvascular endothelial cells from ischemic stroke induced apoptosis by transcriptionally activating MALAT1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2018;495:2376–2382.
Xiang W, Tian C, Peng S, Zhou L, Pan S, Deng Z. Let-7i attenuates human brain microvascular endothelial cell damage in oxygen glucose deprivation model by decreasing toll-like receptor 4 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2017;493:788–793.
Han JY, Li Q, Ma ZZ, Fan JY. Effects and mechanisms of compound Chinese medicine and major ingredients on microcirculatory dysfunction and organ injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion. Pharmacol Ther 2017;177:146–173.
Geng X, Chen L, Zhao BC, Li CX, Qiu LZ, You XY, et al. Preliminary investigation on mechanism of Naoxintong Capsule's preventive treatment of cardio-cerebrovascular disease based on serum proteomics. Chin J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2016;41:2864–2871.
Zitnanova I, Siarnik P, Kollar B, Chomova M, Pazderova P, Andrezalova L, et al. Oxidative stress markers and their dynamic changes in patients after acute ischemic stroke. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016;2016:9761697.
Zhao P, Chang RY, Liu N, Wang J, Zhou R, Qi X, et al. Neuroprotective effect of oxysophocarpine by modulation of MAPK pathway in rat hippocampal neurons subject to oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion. Cell Mol Neurobiol 2018;38:529–540.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wan HT and Yang JH designed the experiments. Wang HY, Zhou HF and He Y perform the experiments. Yu L and Li C analyzed the data. Wang HY wrote the manuscript. Wang HT and Yang JH supervise the whole experimental process and the preparation of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors have no financial or commercial conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81630105, 81973560); Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. LZ17H270001 and LZ18H270001) and Zhejiang Provincial Program for the Cultivation of High-level Innovative Health Talents
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Hy., Zhou, Hf., He, Y. et al. Protective Effect of Naoxintong Capsule (脑心通胶囊) Combined with Guhong Injection (谷红注射液) on Rat Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells during Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 27, 744–751 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-020-3215-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-020-3215-3