Abstract
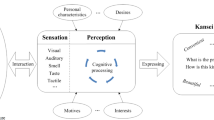
Kansei engineering, also known as kansei ergonomics or emotional engineering, aims at analysing and incorporating customer’s feeling and demands into product function and product design. Founded in the late 1970’s, kansei is now considered as a key consumer-oriented technology for new product development. This paper described a system called FuzEmotion for the purpose of assessing the kansei aspects of a product by considering design attributes of a product. Fuzzy logic is used to represent kansei words and process fuzzy input. The system has been successfully implemented to ascertain gender inclination of a mobile phone. Principal parameters of a mobile phone are considered, i.e., length, width, thickness, and mass. The system can inform gender inclination of a mobile phone with accuracy up to 76%. This is based on a set of 92 mobile phone samples from the five major mobile phone manufacturers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Nagamachi. A study of emotion-technology. The Japanese Journal of Ergonomics, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 121–130, 1974.
M. Nagamachi. An image technology expert system and its application to design consultation. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 267–279, 1991.
M. Nagamachi. Kansei engineering as a powerful consumeroriented technology for product development. Applied Ergonomics, vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 289–294, 2002.
Mobile Phone Forums, [Online], Available: http://www.phoneforums.org/, August 14, 2011.
J. W. T. Lee, S. C. F. Chan, D. S. Yeung. Modelling constraints in part structures. Computers and Industrial Engineering, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 645–657, 1995.
R. S. Peak, J. Lubell, V. Srinivasan, S. C. Waterbury. STEP, XML, and UML: Complementary technologies. Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 379–390, 2004.
J. Hohenegger, A. Bufardi, P. Xirouchakis. A new concept of compatibility structure in new product development. Advanced Engineering Informatics, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 101–116, 2007.
R. Stouffs. Constructing design representations using a sortal approach. Advanced Engineering Informatics, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 71–89, 2008.
N. Leon. The future of computer-aided innovation. Computers in Industry, vol. 60, no. 8, pp. 539–550, 2009.
D. McDonagh, A. Bruseberg, C. Haslam. Visual product evaluation: Exploring users’ emotional relationships with products. Applied Ergonomics, vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 231–240, 2002.
H. H. Lai, Y. M. Chang, H. C. Chang. A robust design approach for enhancing the feeling quality of a product: A car profile case study. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 445–460, 2005.
S. Bahn, C. Lee, C. S. Nam, M. H. Yun. Incorporating affective customer needs for luxuriousness into product design attributes. Human Factors and Ergonomics in Manufacturing, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 105–127, 2009.
C. Barnes, S. P. Lillford. Decision support for the design of affective products. Journal of Engineering Design, vol. 20, no. 5, pp. 477–492, 2009.
K. Choi, C. Jun. A systematic approach to the Kansei factors of tactile sense regarding the surface roughness. Applied Ergonomics, vol. 38, no. 1, pp. 53–63, 2007.
L. Y. Zhai, L. P. Khoo, Z. W. Zhong. A dominance-based rough set approach to Kansei engineering in product development. Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 393–402, 2009.
S. Schutte, J. Eklund. Design of rocker switches for workvehicles — An application of Kansei engineering. Applied Ergonomics, vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 557–567, 2005.
T. Ogawa, Y. Nagai, M. Ikeda. An ontological approach to designers’ idea explanation style: Towards supporting the sharing of kansei-ideas in textile design. Advanced Engineering Informatics, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 157–164, 2009.
S. Akioka, H. Fukumori, Y. Muraoka. Search in the mood: The information filter based on ambiguous queries. International Journal of Computer Applications in Technology, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 322–329, 2009.
Y. Koda, I. Kanaya, K. Sato. Modeling real objects for Kansei-based shape retrieval. International Journal of Automation and Computing, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 14–17, 2007.
H. H. Lai, Y. C. Lin, C. H. Yeh, C. H. Wei. User-oriented design for the optimal combination on product design. International Journal of Production Economics, vol. 100, no. 2, pp. 253–267, 2006.
J. Kuang, P. Jiang. Product platform design for a product family based on Kansei engineering. Journal of Engineering Design, vol. 20, no. 6, pp. 589–607, 2009.
Y. C. Lin, H. H. Lai, C. H. Yeh. Consumer-oriented product form design based on fuzzy logic: A case study of mobile phones. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, vol. 37, no. 6, pp. 531–543, 2007.
R. Roy, M. Goatman, K. Khangura. User-centric design and Kansei engineering. CIRP Journal of Manufacturing Science and Technology, vol. 1, no. 3, pp. 172–178, 2009.
Mobile phones, [Online], Available: http://www.sogi.com.tw/, August 14, 2011.
L. A. Zadeh. Fuzzy sets. Information and Control, vol.8, no. 3, pp. 338–353, 1965.
M. Nagamachi. Kansei engineering. The Occupational Ergonomics Handbook, W. Karwowski, W. S. Morris, Eds., New York, USA: CRC Press, pp. 0–2, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xun Xu is a professor at the Department of Mechanical Engineering, the University of Auckland, New Zealand. He received the Ph. D. degree from the University of Manchester (then UMIST), UK in 1996. He heads the Manufacturing Systems Laboratory and is the director of Intelligent & Interoperable Manufacturing Systems (IIMS) research unit in the University of Auckland. He is a fellow of ASME. He has published over 150 research monographs and serves as a member of the editorial board for 7 international journals.
His research interests include design, CAD/CAPP/CAM, STEP, and STEP-NC.
Hsiang-Hung Hsiao received his B. Eng. (Hons) and M.Eng. degrees in Mechanical Engineering from the School of Engineering, University of Auckland in 2009 and 2010, respectively.
His research interests include product design, manufacturing information systems, and product services.
William Wei-Lin Wang received his Bachelor Honors degree in mechanical engineering from the University of Auckland, New Zealand in 2010. He is currently a member of ASME and JSKE.
His research interests include product design and professional training.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Hsiao, HH. & Wang, W.WL. FuzEmotion as a backward kansei engineering tool. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 9, 16–23 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-012-0611-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11633-012-0611-y