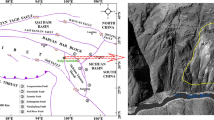
Abstract
On 18 January 2016, the Zhangjiazhuang high-speed railway tunnel in Ledu, Qinghai Province, China, underwent serious deformation and structural damage. A crack formed at the top of the tunnel and the concrete on the crown peeled off. As a result, the tunnel could not be operated for three months. In order to determine the types and spatial distribution of the landslides in the region and the surface deformation characteristics associated with the tunnel deformation, we used field geological and geomorphological surveys, unmanned aerial vehicle image interpretation and differential interferometric synthetic aperture radar (D-InSAR) surface deformation monitoring. Nine ancient and old landslides were identified and analysed in the study area. Surface deformation monitoring and investigation of buildings in several villages on the slope front showed that the tunnel deformation was not related to deep-seated gravitational slope deformation. However, surface deformation monitoring revealed an active NEE-SWW fault in the area intersecting the tunnel at the location of the tunnel rupture. This constitutes a plausible mechanism for the deformation of the tunnel. Our study highlights the need for detailed engineering geomorphological investigations to better predict the occurrence of tunnel deformation events in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aimaiti Y, Yamazaki F, Liu W, et al. (2017) Monitoring of land-surface deformation in the Karamay Oilfield, Xinjiang, China, using SAR interferometry. Appl Sci 7(8): 772. https://doi.org/10.3390/app7080772
Bandini A, Berry P, Boldini D (2015) Tunnelling-induced landslides: The Val di Sambro tunnel case study. Eng Geol 196: 71–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.07.001
Barla G, Debernardi D, Perino A (2015) Lessons learned from deep-seated landslides activated by tunnel excavation. Geomech Tunn 8(5): 394–401. https://doi.org/10.1002/geot.201500028
Bieninwski ZT (1973) Engineering classification of jointed rock masses. Trans South Afr Institut Civil Eng 15(12): 335–343.
Casu F, Manzo M, Lanari R (2006) A quantitative assessment of the SBAS algorithm performance for surface deformation retrieval from D-InSAR data. Remote Sens Environ 102: 195–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2006.01.023
Causse L, Cojean R, Fleurisson J (2015) Interaction between tunnel and unstable slope-Influence of time-dependent behavior of a tunnel excavation in a deep-seated gravitational slope deformation. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 50: 270–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2015.07.018
Costantini M (1998) A novel phase unwrapping method based on network programming. IEEE Trans. Geosci Romote Sens 36(3): 813–821. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.673674
Derbyshire E, Meng XM, Dijkstra TA (2000) Landslides in the thick loess terrain of North-West China. John Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester and New York. p 288.
Dijkstra TA, Rogers CDF, Smalley IJ, et al. (1994) The loess of north-central China: Geotechnical properties and their relation to slope stability. Eng Geol 36(3): 153–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(94)90001-9
Farhadian H, Aalianvari A, Karibeh H (2012) Optimization of analytical equations of groundwater seepage into tunnels: a case study of Amikabir tunnel. J Geol Soc India 80: 96–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-012-0122-z
Fernandez G, Moon J (2010) Excavation-induced hydraulic conductivity reduction around a tunnel-part 1: Guideline for estimate of ground water inflow rate. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 25(5): 567–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2010.03.006
Flessandro A, Prati C, Rocca F (2001) Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 39: 8–20. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.898661
Gattinoni P, Consonni M, Francani V, et al. (2019) Tunnelling in landslide areas connected to deep seated gravitational deformations: An example in Central Alps (northern Italy). Tunn Undergr Space Technol 93: 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2019.103100
Goldstein RM, Werner CL (1998) Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys Res Lett 25(21): 4035–4038. https://doi.org/10.1029/1998GL900033
He C, Wang B (2013) Research process and development trends of highway tunnels in China. J Mod Transport 21(4): 209–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40534-013-0029-4
Hoek E, Brown ET (1997). Practical estimates of rock mass strength. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 34(8): 1365–1609. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(97)80069-X
Hoek E, Marinos P (2000) Predicting tunnel squeezing problems in weak heterogeneous rock masses. Tunn Tunnell Int 32(11): 45–51.
Komu M, Guney U, Kilickaya TE, et al. (2020) Using 3D Numerical analysis for the assessment of tunnel-landslide relationship: Bahce-Nurdag Tunnel (South of Turkey). Geotech Geol Eng 38(4): 1237–1254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-019-01084-9
Konagai K, Numada M, Zafeirako A, et al. (2005) An example of landslide-inflicted damage to tunnel in the 2004 mid-Niigata prefecture earthquake. Landslides 2: 159–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-005-0057-1
Li S, Chen Y (1999) Tunnel effect of fractal fault and transient S-wave velocity rupture (TSVR) of in-plane shear fault. Earth Sci 12: 19–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11589-999-0003-8
Liu C, Chen P, Matsuo T, et al. (2015) Rapidly responding to landslides and debris flow events using a low-cost unmanned aerial vehicle. J App Remote Sens 9(1): 096016. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JRS.9.096016
Ma H, Wu H (2016) Progress and expectation of research on tunnel-landslide system. Chin J Undergr Space Eng 12: 522–530. (In Chinese)
Ma J, Tang H, Hu X, et al. (2014) Application of 3D laser scanning technology to landslide physical model test. Rock Soil Mech 35(5): 1495–1505. (In Chinese)
Ma L, Cheng L, Li M, et al. (2015) Training set size, scale, and features in Geographic Object-Based Image Analysis of very high resolution unmanned aerial vehicle imagery. J Photogramm Remote Sens 102: 14–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.12.026
Mao J, Zhou D (2002) Deformation analysis for landslide-tunnel interaction. J Southwest Jiaotong Univ 37(4): 371–376. (In Chinese)
Nikadat N, Fatehi M, Abdollahipour A (2015) Numerical modelling of stress analysis around rectangular tunnels with large discontinuities (fault) by a hybridized indirect BEM. J Cent South Univ 22: 4291–4299. https://doi.org/CNKI:SUN:ZNGY.0.2015-11-024
Obradovic J (1990) Influence of Neotectonic activity on the pumped storage scheme tunnel lining behavior and failure. Thomas Telford 21: 403–413. https://doi.org/10.1680/ps.15869
Peng JB, Fan ZJ, Wu D, et al. (2015) Heavy rainfall triggered loess-mudstone landslide and subsequent debris flow in Tianshui, China. Eng Geol 186: 79–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.08.015
Qi TJ, Meng XM, Qing F, et al. (2021) Distribution and characteristics of large landslides in a fault zone: A case study of the NE Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geomorphology 379: 107952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2021.107592
Rehman MU, Zhang Y, Meng XM, et al. (2020) Analysis of landslide movements using interferometric synthetic aperture radar: a case study in Hunza-Nagar valley, Pakistan. Remote Sens 12(12): 2054. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12122054
Singh Y, Sharma V, Pandita S, et al. (2014) Investigation of landslide at Sangaldan near tunnel-47, on Katra- Qazigund railway track, Jammu and Kashmir. J Geol Soc India 84(6): 686–692.
Song CH (2006) Tectonic uplift and Cenozoic Sedimentary evolution in the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. PhD thesis, Lanzhou University. p 46. (In Chinese)
Syahmi M, Aziz W, Zulkarnaini M, et al. (2011) The movement detection on the landslide surface by using Terrestrial Laser Scanning. IEEE Control & System Graduate Research Colloquium pp 174–180. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSGRC.2011.5991851
Tang MA, Wang Y, Sun BL (2013) Application and research of geologic radar in groundwater disease of tunnel engineering inspection. Appl Mech Mater 256: 1167–1171. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/201913101063
Tian ZY, Zhang MS, Wu YZ (2019) Application of intergrated geophysical exploration in the cracks detection of the front edge in Gaojiawan. Chinese J Eng Geop 16(6): 822–828. (In Chinese)
Troncone A, Conte E, Donato A (2014) Two and three-dimensional numerical analysis of the progressive failure that occurred in an excavation-induced landslide. Eng Geol 183(3): 265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.08.027
Vassallo T, Mishra M, Santarsiero G, et al. (2019) Modeling of Landslide-Tunnel Interaction: the Varco d’Izzo Case Study. Geotech Geol Eng 37: 5507–5531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-019-01020-x
Wang T, Li J, Chui Y, et al. (2011) Tunnel Deformation and Lining Anomalies Induced by Deep-seated Gravitational Slope Deformation. Tunn Cons 31(S1): 116–122. (In Chinese)
Wu H, Pai L (2020) Research on the Deformation Mechanisms of a Tunnel-Landslide System based on the Point Safety Factor of the Interface. E3S Web of Conferences 165: 04068. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202016504068
Wu H, Wu D, Ma H, et al. (2012) Research on type of tunnellandslide system and tunnel deformation mode. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 31(S2): 3632–3642. (In Chinese)
Ye X, Kaufmann H, Guo X (2004) Landslide monitoring in the Three Gorges area using D-InSAR and Corner Reflectors. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 10: 1167–1172. https://doi.org/10.14358/PERS.70.10.1167
Zeng R, Meng X, Zhang F, et al. (2016) Characterizing hydrological processes on loess slopes using electrical resistivity tomography — A case study of the Heifangtai Terrace, Northwest China. J Hydrol 541: 742–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.07.033
Zhang M, Liu J (2010) Controlling factors of loess landslides in western China. Environ Earth Sci 59: 1671–1680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0149-7
Zhang J, Wang YN, Zhang BH, et al. (2016) Tectonics of the Xining Basin in NW China and its implications for the evolution of the NE Qinghai — Tibetan Plateau. Basin Res 28(2): 159–182. https://doi.org/10.1111/bre.12104
Zhang Y, Lan H, Zhang Y, et al. (2013) Nonlinear dynamic failure process of tunnel-fault system in response to strong seismic event. J Asian Earth Sci 64: 125–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.006
Zhang Y, Yang J, Yang F (2015) Field investigation and numerical analysis of landslide induced by tunneling. Eng Fail Anal 47: 25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2014.09.011
Zhang Y, Meng XM, Chen G, et al. (2016) Detection of geohazards in the Bailong River Basin using synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Landslides 13: 1273–1284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0660-8
Zhang ZG, Zhao QH, Chen XU, et al. (2017) Interaction analyses between tunnel and landslide in mountain area. J Mt Sci 14(6): 1124–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-016-3999-y
Zhou SH, Tian ZY, Di HG, et al. (2020) Investigation of a loessmudstone landslide and the induced structural damage in a high-speed railway tunnel. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79: 2201–2212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01711-y
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFC1504704), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41661144046), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. lzujbky-2018-k14), and the Key Research and Development Program of Gansu Province (Grant No. 18YF1WA114). We thank the Qinghai Environmental Geological Survey who provided the DEM, aerial images and drilling data, and the reviewers for their constructive comments which have substantially improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Xm., Qi, Tj., Zhao, Y. et al. Deformation of the Zhangjiazhuang high-speed railway tunnel: an analysis of causal mechanisms using geomorphological surveys and D-InSAR monitoring. J. Mt. Sci. 18, 1920–1936 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6493-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6493-5