Summary
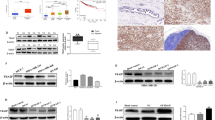
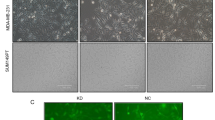
Filamin A and 14-3-3-σ are closely associated with the development of breast cancer. However, the exact relationship between them is still unknown. The present study aimed to examine the interaction of filamin A with 14-3-3-σ in the invasion and migration of breast cancer. RNA interference technology was employed to silence filamin A in MDA-MB-231 cells. Real-time PCR and Western blotting were used to detect the expression of filamin A and 14-3-3-σ at mRNA and protein levels, respectively. Double immunofluorescence was applied to show their colocalization morphologically. Wound healing assay and Trans-well assay were used to testify the migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells in filamin A-silenced cells. The results showed that silencing filamin A significantly increased the mRNA and protein levels of 14-3-3σ. In addition, double immunofluorescence displayed that filamin A and 14-3-3σ were predominantly colocalized in the cytoplasm of MDA-MB-231 cells. Silencing filamin A led to the enhanced fluorescence of 14-3-3σ. Furthermore, cell functional experiments showed that silencing filamin A inhibited the migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells in vitro. In conclusion, silencing filamin A may inhibit the invasion and migration of breast cancer cells by upregulating 14-3-3σ.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015,65(2):87–108
Sharma R, Khaket TP, Dutta C, et al. Breast cancer metastasis: Putative therapeutic role of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Cell Oncol, 2017,40(3): 199–208
Chen Y, Zhang B, Bao L, et al. ZMYND8 acetylation mediates HIF-dependent breast cancer progression and metastasis. J Clin Invest, 2018,128(5):1937–1955
Moore BW, Perez VJ, Gehring M. Assay and regional distribution of a soluble protein characteristic of the nervous system. JNeurochem, 1968,15:265–272
Freeman AK, Morrison DK. 14-3-3 Proteins: diverse functions in cell proliferation and cancer progression. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2011,22(7):681–687
Peng Z, Wang Y, Fan J, et al. Costunolide and dehydrocostuslactone combination treatment inhibit breast cancer by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through c-Myc/p53 and AKT/14-3-3 pathway. Sci Rep, 2017,7:41254
Khorrami A, Sharif Bagheri M, Tavallaei M, et al. The functional significance of 14-3-3 proteins in cancer: focus on lung cancer. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig, 2017,32(3): doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2017-0032
Raungrut P, Petjaroen P, Geater SL, et al. Methylation of 14-3-3sigma gene and prognostic significance of 14-3-3 sigma expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett, 2017,14(5):5257–5264
Phan L, Chou PC, Velazquez-Torres G, et al. The cell cycle regulator 14-3-3sigma opposes and reverses cancer metabolic reprogramming. Nat Commun, 2015,6:7530
Stossel TP, Hartwig JH. Interactions between actin, myosin, and an actin-binding protein from rabbit alveolar macrophages. Alveolar macrophage myosin Mg-2+-adenosine triphosphatase requires a cofactor for activation by actin. J Biol Chem, 1975,250:5706–5712
Uramoto H, Akyurek LM, Hanagiri T. A positive relationship between filamin and VEGF in patients with lung cancer. Anticancer Res, 2010,30(10):3939–3944
Tian HM, Liu XH, Han W, et al. Differential expression of filamin A and its clinical significance in breast cancer. Oncol Lett, 2013,6(3):681–686
Savoy RM, Ghosh PM. The dual role of filamin A in cancer: can't live with (too much of) it, can't live without it. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2013,20(6):R341–R356
Yue J, Huhn S, Shen Z. Complex roles of filamin-A mediated cytoskeleton network in cancer progression. Cell Biosci, 2013,3(1):7
Leung R, Wang Y, Cuddy K, et al. Filamin A regulates monocyte migration through Rho small GTPases during osteoclastogenesis. J Bone Miner Res, 2010,25:1077–1091
Kim H, Nakamura F, Lee W, et al. Regulation of cell adhesion to collagen via betal integrins is dependent on interactions of filamin A with vimentin and protein kinase C epsilon. Exp Cell Res, 2010,316:1829–1844
Zhou AX, Hartwig JH, Akyurek LM. Filamins in cell signaling, transcription and organ development. Trends Cell Biol, 2010, 20:113–123
Jiang X, Yue J, Lu H, et al. Inhibition of filamin-A reduces cancer metastatic potential. Int J Biol Sci, 2013,9(1):67–77
Nallapalli RK, Ibrahim MX, Zhou AX, et al. Targeting filamin A reduces K-RAS-induced lung adenocarcinomas and endothelial response to tumor growth in mice. Mol Cancer, 2012,11:50
Jin J, Smith FD, Stark C, et al. Proteomic, functional, and domain-based analysis of in vivo 14-3-3 binding proteins involved in cytoskeletal regulation and cellular organization. Curr Biol, 2004,14:1436–1450
Nurmi SM, Gahmberg CG, Fagerholm SC. 14-3-3 proteins bind both filamin and alphaLbeta2 integrin in activated T cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2006,1090:318–325
Takala H, Nurminen E, Nurmi SM, et al. Beta2 integrin phosphorylation on Thr758 acts as a molecular switch to regulate 14-3-3 and filamin binding. Blood, 2008, 112(5): 1853–1862
Vercoutter-Edouart AS, Lemoine J, Le Bourhis X, et al. Proteomic analysis reveals that 14-3-3sigma is downregulated in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res, 2001,61(1):76–80
Ferguson AT, Evron E, Umbricht CB, et al. High frequency of hypermethylation at the 14-3-3 sigma locus leads to gene silencing in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2000,97(11): 6049–6054
Moreira JM, Ohlsson G, Rank FE, et al. Downregulation of the tumor suppressor protein 14-3-3sigma is a sporadic event in cancer of the breast. Mol Cell Proteomics, 2005,4(4):555–569
Aktary Z, Kulak S, Mackey J, et al. Plakoglobin interacts with the transcription factor p53 and regulates the expression of 14-3-3sigma. J Cell Sci, 2013,126:3031–3042
Hui L, Zheng Y, Yan Y, et al. Mutant p53 in MDAMB-231 breast cancer cells is stabilized by elevated phospholipase D activity and contributes to survival signals generated by phospholipase D. Oncogene, 2006,25(55):7305–7310
Geng C, Sang M, Yang R, et al. Overexpression of 14-3-3 sigma counteracts tumorigenicity by positively regulating p73 in vivo. Oncol Lett, 2011,2(6):1177–1182
Zhu J, Jiang J, Zhou W, et al. The potential tumor suppressor p73 differentially regulates cellular p53 target genes. Cancer Res, 1998,58(22):5061–5065
Kim EJ, Park JS, Um SJ. Filamin A negatively regulates the transcriptional activity of p73alpha in the cytoplasm. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2007,362(4): 1101–1106
Ling C, Zuo D, Xue B, et al. A novel role for 14-3-3sigma in regulating epithelial cell polarity. Genes Dev, 2010,24(9): 947–956
Acknowledgments
We are deeply indebted to Dr. Chun-wei SHI for her technique assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, Zm., Yang, Ll., Ni, J. et al. Silencing Filamin A Inhibits the Invasion and Migration of Breast Cancer Cells by Up-regulating 14-3-3σ. CURR MED SCI 38, 461–466 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1901-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1901-6