Abstract
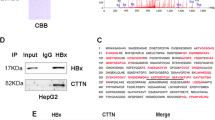
Hepatitis B virus X (HBx) protein plays a pivotal role in the development of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Although regulation of cytosolic calcium is essential for HBV replication and is mediated by HBx protein, the mechanism of HBx protein regulating intracellular calcium level remains poorly understood. The present study examined whether HBx protein elevated the intracellular calcium through interacting with storeoperated calcium entry (SOCE) components, Orail and stromal interaction molecule 1, and then identified the targets of HBx protein, with an attempt to understand the mechanism of HBx protein upsetting intracellular calcium homeostasis. By employing co-immunoprecipitation and GST-pull-down assay, we found that Orail protein interacted with HBx protein, and the C-terminus of Orail was implicated in the interaction. Confocal microscopy also revealed that HBx protein could co-localize with full-length Orail protein in HEK293 cells. Moreover, live cell calcium imaging exhibited that HBx protein elevated intracellular calcium, possibly by binding to SOCE components. Our results suggest that HBx protein binds to STIM1-Orail complexes to positively regulate the activity of plasma membrane store-operated calcium channels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kew MC. Epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection, hepatocellular carcinoma, and hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Biol (Paris), 2010, 58(4): 273–277
Ng SA, Lee C. Hepatitis B virus X gene and hepatocarcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol, 2011, 46(8): 974–990
Paterlini P, Poussin K, Kew MC, et al. Selective accumulation of the x transcript of hepatitis B virus in patients negative for hepatitis B surface antigen with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology, 1995, 21(2): 313–321
Murata M, Matsuzaki K, Yoshida K, et al. Hepatitis B virus x protein shifts human hepatic transforming growth factor (TGF) -P signaling from tumor suppression to oncogenesis in early chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology, 2009, 49(4): 1203–1217
Azam F, Koulaouzidis A. Hepatitis B virus and hepatocarcinogenesis. Ann Hepatol, 2008, 7(2): 125–129
Rawat S, Clippinger AJ, Bouchard MJ. Modulation of Apoptotic Signaling by the Hepatitis B Virus X Protein. Viruses, 2012, 4(11): 2945–2972
Matsuda Y, Ichida T. Impact of hepatitis B virus X protein on the DNA damage response during hepatocarcinogenesis. Med Mol Morphol, 2009, 42(3): 138–142
Chin R, Earnest-Silveira L, Koeberlein B, et al. Modulation of MAPK pathways and cell cycle by replicating hepatitis B virus: factors contributing to hepatocarcinogenesis. J Hepatol, 2007, 47(3): 325–337
Bouchard MJ, Wang L, Schneider RJ. Activation of focal adhesion kinase by hepatitis B virus HBx protein: multiple functions in viral replication. J Virol, 2006, 80(9): 4406–4414
Diao J, Khine AA, Sarangi F, et al. X protein of hepatitis B virus inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis and is associated with up-regulation of the SAPK/JNK pathway. J Biol Chem, 2001,276(ll): 8328–8340
Bouchard MJ, Puro RJ, Wang L, et al. Activation and inhibition of cellular calcium and tyrosine kinase signaling pathways identify targets of HBx protein involved in hepatitis B virus replication. J Virol, 2003, 77(4): 7713–7719
Bouchard MJ, Wang LH, Schneider RJ. Calcium Signaling by HBx Protein in Hepatitis B Virus DNA Replication. Science, 2001, 294(5550): 2376–2378
McClain SL, Clippinger AJ, Lizzano R, et al. Hepatitis B virus replication is associated with an HBx-dependent mitochondrion-regulated increase in cytosolic calcium levels. J Virol, 2007, 81(21): 12 061–12 065
Gearhart TL, Bouchard MJ. The hepatitis B virus X protein modulates hepatocyte proliferation pathways to stimulate viral replication. J Virol, 2010, 84(6): 2675–2686
Chami M, Ferrari D, Nicotera P, et al. Caspase-dependent Alterations of Ca2+ Signaling in the Induction of Apoptosis by Hepatitis B Virus X Protein. J Biol Chem, 2003, 278(34): 31 745–31 755
Geng X, Harry BL, Zhou Q, et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein targets the Bcl-2 protein CED-9 to induce intracellular Ca2+ increase and cell death in Caenorhabditis elegáns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2012, 109(45): 18 465–18 470
Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signaling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodeling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2003, 4(7): 517–529
Parekh AB. Store-operated CRAC channels: function in health and disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2010, 9(5): 399–410
Hoover PJ, Lewis RS. Stoichiometric requirements for trapping and gating of calcium release-activated calcium (CRAC) channels by stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2011,108(32): 13 299–13 304
Hogan PG, Lewis RS, Rao A. Molecular basis of calcium signaling in lymphocytes: STIM and ORAL Annu Rev Immunol, 2010, 28:491–533
Cai X, Zhou Y, Nwokonko RM, et al. The Orail store-operated calcium channel functions as a hexamer. J Biol Chem, 2016, 291(50): 25 764–25 775
Wu MM, Buchanan J, Luik RM, et al. Ca2+ store depletion causes STIM1 to accumulate in ER regions closely associated with the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol, 2006, 174(6): 803–813
Srikanth S, Gwack Y. Orail, STIM1 and their associating partners. J Physiol, 2012,590(pt 17):4169–4177
Ni H, Baty CJ, Li N, et al. Bid agonist regulates murine hepatocyte proliferation by controlling endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis. Hepatology, 2010,52(1): 338–348
Gearhart TL, Bouchard MJ. Replication of the hepatitis B virus requires a calcium-dependent HBx-induced G1 phase arrest of hepatocytes. Virology, 2010,407(1): 14–25
Fuks F, Burgers WA, Brehm A, et al. DNA methyltransferase Dnmtl associates with histone deacetylase activity. Nat Genet, 2000, 24(1): 88–91
Walsh CM, Chvanov M, Haynes LP, et al. Role of phosphoinositides in STIM1 dynamics and store-operated calcium entry. Biochem J, 2009, 425(1): 159–168
Choi Y, Park SG, Yoo JH, et al. Calcium ions affect the hepatitis B virus core assembly. Viology, 2005,332(1): 454–463
Walsh CM, Doherty MK, Tepikin AV, et al. Evidence for an interaction between Golli and STIM1 in store-operated calcium entry. Biochem J, 2010, 430(3): 453–460
Luik RM, Wu MM, Buchanan J, et al. The elementary unit of store-operated calcium entry: local activation of CRAC channels by STIM1 at ER-plasma membrane junctions. J Cell Biol, 2006, 174(6): 815–825
Zheng H, Zhou MH, Hu C, et al. Differential roles of the C and N termini of Orail protein in interacting with Stromal Interaction Molecule 1 (STIM1) for calcium Release-activated calcium (CRAC) Channel Activation. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(16): 11 263–11 272
Yang N, Tang Y, Wang F, et al. Blockade of store-operated calcium entry inhibits hepatocarcinoma cell migration and invasion by regulating focal adhesion turnover. Cancer Lett, 2013, 330(2): 163–199
Oh-hora M. Calcium signaling in the development and function of T lineage cells. Immunol Rev, 2009,231 (1): 210–224
Felix R, Crottes D, Delalande A, et al. The Orai-1 and STIM-1 complex controls human dendritic cell maturation. PLoS One, 2013,8(5): e61595
Yang B, Bouchard MJ. The Hepatitis B Virus X Protein elevates cytosolic calcium signals by modulating mitochondrial calcium uptake. J Virol, 2012,86(1): 313–327
Park CY, Hoover PJ, Mullins FM, et al. STIM1 clusters and activates CRAC channels via direct binding of a cytosolic domain to Orail. Cell, 2009, 136(5): 876–890
Xu P, Lu J, Li Z, et al. Aggregation of STIM1 underneath the plasma membrane induces clustering of Orail. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2006, 350(4): 969–976
Hull JJ, Lee JM, Kajigaya R, et al. Bombyx mori homologs of STIM1 and Orail are essential components of the signal transduction cascade that regulates sex pheromone production. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284(45): 31 200–31 213
Cahalan MD, Zhang SL, Yeromin AV, et al. Molecular basis of the CRAC channel. Cell Calcium, 2007, 42(2): 133–144
Frischauf I, Muik M, Derler I, et al. Molecular determinants of the coupling between STIM1 and Orai channels: differential activation of Orail-3 channels by a STIM1 coiled-coil mutant. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284(32): 21 696–21 706
Muik M, Frischauf I, Derler I, et al. Dynamic coupling of the putative coiled-coil domain of Orail with STIM1 mediates orail channel activation. J Biol Chem, 2008, 283(12): 8014–8022
Calloway N, Holowka D, Baird B. A basic sequence in STIM1 promotes calcium influx by interacting with the C-terminal acidic coiled coil of Orail. Biochemistry, 2010, 49(6): 1067–1071
Feitelson MA, Lee J. Hepatitis B virus integration, fragile sites, and hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett, 2007, 252(2): 157–170
Wang WH, Hullinger RL, Andrisani OM. Hepatitis B virus x protein via the p38MAPK pathway induces E3-2F1 release and ATR kinase activation mediating p53 apoptosis. J Biol Chem, 2008, 283(37): 25 455–25 467
Lopez JJ, Albaran L, Gomez LJ, et al. Molecular modulators of store-operated calcium entry. Biochim Biopgys Acta, 2016, 1863(8): 2037–2043
Yen TT, Yang A, Chiu WT, et al. Hepatitis B virus PreS2-mutant large surface antigen activates store-operated calcium entry and promotes chromosome instability. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(17): 23 346–23 360
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81001063) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2015QN150).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Jh., Liu, Zj., Yi, Jh. et al. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Upregulates Intracellular Calcium Signaling by Binding C-terminal of Orail Protein. CURR MED SCI 38, 26–34 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1843-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1843-z