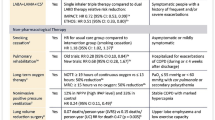
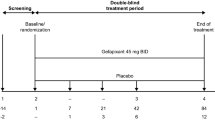
Summary
It remains controversial whether tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α antagonism is effective for asthma. This meta-analysis was performed to evaluate efficacy of TNF-α antagonism in treatment of patients with asthma. MEDLINE, EMBASE, LILACS, and CINAHL databases were searched for English-language studies published through January 3, 2010. Randomized-controlled trials comparing TNF-α antagonism with control therapy were selected. For each report, data were extracted in relation to the outcomes analyzed: asthma exacerbation, asthma quality of life questionnaire scores, and forced expiratory volume in 1 second. Four assessable trials were identified including 641 patients with asthma. TNF-α antagonism therapy was superior to control therapy in preventing exacerbations in asthmatics [pooled odds ratio 0.52 (95% confidence interval 0.29–0.88), P=0.02]; however, there was a nonsignificant reduction in asthma quality of life questionnaire scores [0.23 (0 to 0.47), P=0.05], forced expiratory volume in 1 second [0.03, (−0.14 to 0.10), P=0.74] when analyzed using standardized mean differences. TNF-α antagonism was superior to control chemotherapy in terms of asthma exacerbation, but not asthma quality of life questionnaire scores or forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fanta CH. Asthma. N Engl J Med, 2009,360(10): 1002–1014
Ito K, Chung KF, Adcock IM. Update on glucocorticoid action and resistance. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2006, 117(3):522–543
Wenzel S, Szefler SJ. Managing severe asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2006, 117(3):508–511
The ENFUMOSA cross-sectional European multicentre study of the clinical phenotype of chronic severe asthma. European Network for Understanding Mechanisms of Severe Asthma. Eur Respir J, 2003,22(3): 470–477
Moore WC, Bleecker ER, Curran-Everett D, et al. Characterization of the severe asthma phenotype by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s Severe Asthma Research Program. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2007,119(2): 405–413
Cookson W, Moffatt M. Making sense of asthma genes. N Engl J Med, 2004, 351(17):1794–1796
Gao J, Shan G, Sun B, et al. Association between polymorphism of tumour necrosis factor alpha-308 gene promoter and asthma: a meta-analysis. Thorax, 2006,61(6): 466–471
Cembrzynska-Nowak M, Szklarz E, Inglot AD, et al. Elevated release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma by bronchoalveolar leukocytes from patients with bronchial asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis, 1993, 147(2):291–295
Obase Y, Shimoda T, Mitsuta K, et al. Correlation between airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation in a young adult population: eosinophil, ECP, and cytokine levels in induced sputum. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2001,86(3):304–310
Thomas PS, Yates DH, Barnes PJ. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases airway responsiveness and sputum neutrophilia in normal human subjects. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 1995,152(1):76–80
Thomas PS, Heywood G. Effects of inhaled tumour necrosis factor alpha in subjects with mild asthma. Thorax, 2002,57(9):774–778
Howarth PH, Babu KS, Arshad HS, et al. Tumour necrosis factor (TNFalpha) as a novel therapeutic target in symptomatic corticosteroid dependent asthma. Thorax, 2005, 60(12):1012–1018
Rouhani FN, Meitin CA, Kaler M, et al. Effect of tumor necrosis factor antagonism on allergen-mediated asthmatic airway inflammation. Respir Med, 2005,99(9):1175–1182
Robinson KA, Dickersin K. Development of a highly sensitive search strategy for the retrieval of reports of controlled trials using PubMed. Int J Epidemiol, 2002, 31(1):150–153
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials, 1996,17(1): 1–12
Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, et al. Empirical evidence of bias. Dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA, 1995,273(5):408–412
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials, 1986,7(3):177–188
Deeks JJ, Altman D, Bradburn MJ. Statistical methods for examining heterogeneity and combining results from several studies in meta-analysis. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG, eds. Systematic reviews in health care. London, UK: BMJ Publishing. 2001:285–312
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ, 2003,327(7414): 557–560
Curtin F, Altman DG, Elbourne D. Meta-analysis combining parallel and cross-over clinical trials. I: Continuous outcomes. Stat Med, 2002,21(15):2131–2144
Berry MA, Hargadon B, Shelley M, et al. Evidence of a role of tumor necrosis factor alpha in refractory asthma. N Engl J Med, 2006,354(7):697–708
Erin EM, Leaker BR, Nicholson GC, et al. The effects of a monoclonal antibody directed against tumor necrosis factor-alpha in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2006,174(7): 753–762
Morjaria JB, Chauhan AJ, Babu KS, et al. The role of a soluble TNFalpha receptor fusion protein (etanercept) in corticosteroid refractory asthma: a double blind, randomised, placebo controlled trial. Thorax, 2008,63(7): 584–591
Wenzel SE, Barnes PJ, Bleecker ER, et al. T03 Asthma Investigators. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of tumor necrosis factor-alpha blockade in severe persistent asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2009,179(7):549–558
Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA), 2008. (Accessed August 23, 2009, at http://www.ginasthma.org.)
Tantisira KG, Lake S, Silverman ES, et al. Corticosteroid pharmacogenetics: association of sequence variants in CRHR1 with improved lung function in asthmatics treated with inhaled corticosteroids. Hum Mol Genet, 2004, 13(13):1353–1359
Lazarus SC, Chinchilli VM, Rollings NJ, et al. National Heart Lung and Blood Institute’s Asthma Clinical Research Network. Smoking affects response to inhaled corticosteroids or leukotriene receptor antagonists in asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2007,175(8): 783–790
Rodrigo GJ, Rodrigo C, Hall JB. Acute asthma in adults: a review. Chest, 2004,125(3):1081–1102
Weiss KB, Sullivan SD. The health economics of asthma and rhinitis. I. Assessing the economic impact. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2001, 107(1):3–8
Haraoui B. Differentiating the efficacy of the tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2005, 34(5 Suppl1):7–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by a grant from National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 30925032) and by grants from National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 30872343 and No. 30770648).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Xiong, L., Qin, S. et al. Effect of tumor necrosis factor-α antagonism in asthma: a meta-analysis of the published literature. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 31, 137–141 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0165-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0165-1