Summary
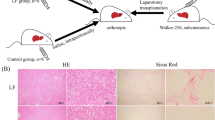
In order to investigate the inhibitory effects of all trans-retinoitc acid (ATRA) on differentiation and apoptosis of Walker-256 hepatocellular carcinoma cells and the therapeutic effects of ATRA combined with transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) on rat Walker-256 transplanted hepatocarcinoma, Walker-256 hepatocarcinoma cell lines were treated with ATRA at different concentrations. After culture for 48 h, the inhibitory rate of cell proliferation was determined by MTT assay; the changes of Fas and Bcl-2 mRNA expression were determined by RT-PCR, and the expression levels of Caspase3 and Caspase8 proteins were detected by Western blot. Twenty-seven Wistar rat models of hepatocarcinoma were set up successfully by implanting Walker-256 cell lines. The tumor volume at the 11th day after implantation (Vpreoperation) was measured by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The 27 rats were randomly and equally divided into three groups, and the therapy scheme was performed as follows: group A (ATRA 0.1 mg+mitomycin 0.05 mL+lipiodol 0.05 mL+gelfoam powder 0.025 mg); group B (mitomycin 0.05 mg+lipiodol 0.05 ml+gelfoam 0.025 mg; group C (0.9% NaCl 0.2 mL). After another 11 days, MRI was performed once again to measure the tumor volume (Vpostoperation). The expression of factor and Ki VIII -67 in the tumor tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry. The results showed that ATRA could suppress proliferation of Walker-256 cell lines. After treatment of Walker-256 cell lines with ATRA, the expression of Fas mRNA was significantly up-regulated and the Bcl-2 mRNA was significantly down-regulated by ATRA at the concentration of 10 μmol/L as compared with the control group (P<0.05). After treatment with 10 μmol/L ATRA for 48 h, the Caspase3 and Caspase8 were significantly activated as compared with the control group (P<0.05). Significant difference existed in growth rate among the three groups (P<0.01) and between either two groups (P<0.05). The expression rate of factor VIII and Ki-67 was gradually increased from group A, group B to group C. The study suggests that ATRA could inhibit the proliferation of Walker-256 cells and the effectiveness of the combined therapy (ATRA+TACE) for treating transplanted hepatoma of rats is superior to that of TACE alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Dekken H, Verhoef C, Wink J, et al. Cell biological evaluation of liver cell carcinoma, dysplasia and adenoma by tissue micro-array analysis. Acta Histochem, 2005,107(3):161–171
Sergio A, Cristofori C, Cardin R, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): the role of angiogenesis and invasiveness. Am J Gastroenterol, 2008,103(4):914–921
Wang CT, Meng M, Zhang JC, et al. Growth inhibition and gene induction in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell exposed to sodium 4-phenylbutanoate. Chin Med J (Engl), 121(17):1707–1711
Yin C, Lin Y, Zhang X, et al. Differentiation therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice with recombinant adenovirus carrying hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha gene. Hepatology, 2008,48(5):1528–1539
Bertagnolo V, Grassilli S, Bavelloni A, et al. Vav1 modulates protein expression during ATRA-induced maturation of APL-derived promyelocytes: a proteomic-based analysis. J Proteome Res, 2008,7(9):3729–3736
Cordoba R, Ramirez E, Lei SH, et al. Hypercalcemia due to an interaction of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and itraconazole therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia successfully treated with zoledronic acid. Eur J Clin Pharmacol, 2008,64(10):1031–1032
Maiti TK, Ghosh KS, Debnath J, et al. Binding of all-trans retinoic acid to human serum albumin: fluorescence, FT-IR and circular dichroism studies. Int J Biol Macromol, 2006,38(3–5):197–202
Arce F, Gätjens-Boniche O, Vargas E, et al. Apoptotic events induced by naturally occurring retinods ATRA and 13-cis retinoic acid on human hepatoma cell lines Hep3B and HepG2. Cancer Lett, 2005,229(2):271–281
Zheng GH, Li HQ. Effects of garlic oil combined with resveratrol on inducting of apoptosis and expression of Fas, bcl-2 and bax in human gastric cancer cell line. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi (Chinese), 2008,42(1):39–42
Das A, Banik NL, Ray SK. Retinoids induce differentiation and downregulate telomerase activity and N-Myc to increase sensitivity to flavonoids for apoptosis in human malignant neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Int J Oncol, 2009,34(3):757–765
Lue H, Thiele M, Franz J, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) promotes cell survival by activation of the Akt pathway and role for CSN5/JAB1 in the control of autocrine MIF activity. Oncogene, 2007,26(35):5046–5059
Bromberg KD, Kluger HM, Delaunay A, et al. Increased expression of the E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF5 is associated with decreased survival in breast cancer. Cancer Res, 2007,67(17):8172–8179
Spalding KL, Dharmarajan AM, Harvey AR. Caspaseindependent retinal ganglion cell death after target ablation in the neonatal rat. Eur J Neurosci, 2005,21(1):33–45
Gilbert S, Ruel A, Loranger A, et al. Switch in Fas-activated death signaling pathway as result of keratin 8/18-intermediate filament loss. Apoptosis, 2008,13(12):1479–1493
Norris KL, Youle RJ. Cytomegalovirus proteins vMIA and m38.5 link mitochondrial morphogenesis to Bcl-2 family proteins. J Virol, 2008,82(13):6232–6243
Tophkhane C, Yang S, Bales W, et al. Bcl-2 overexpression sensitizes MCF-7 cells to genistein by multiple mechanisms. Int J Oncol, 2007,31(4):867–874
Szajerka A, Dziegiel P, Szajerka T, et al. Immunohistochemical evaluation of metallothionein, Mcm-2 and Ki-67 antigen expression in tumors of the adrenal cor tex. Anticancer Res, 2008,28(5B):2959–2965
Jamali M, Chetty R. Predicting prognosis in gastroentero- pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: an overview and the value of Ki-67 immunostaining. Endocr Pathol, 2008,19(4):282–288
García-Velasco A, Mendiola C, Sánchez-Muñoz A, et al. Prognostic value of hormonal receptors, p53, ki67 and HER2/neu expression in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol, 2008,10(6):367–371
Koide N, Nishio A, Sato T, et al. Significance of macrophage chemoattractant protein-1 expression and macrophage infiltration in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol, 2004,99(9):1667–1674
Liu YM, Yang GW, Bai SM, et al. Expression of C-erb B-2 and its relation to angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao (Chinese), 2007,27(10):1588–1589
Robert C, Delva L, Balitrand N, et al. Apoptosis induction by retinoids in eosinophilic leukemia cells: implication of retinoic acid receptor-alpha signaling in all-trans-retinoic acid hypersensitivity. Cancer Res, 2006,66(12):6336–6344
Tarkanyi I, Dudognon C, Hillion J, et al. Retinoid/arsenic combination therapy of promyelocytic leukemia: induction of telomerase-dependent cell death. Leukemia, 2005,19(10):1806–1811
Liu YB, Xu B, Wang JW, et al. Effects of all-trans retinoic acid on expression of connexin genes and gap junction communication in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Chinese), 2005,85(20):1414–1418
Suzuki S, Kawakami S, Chansri N, et al. Inhibition of pulmonary metastasis in mice by all-trans retinoic acid incorporated in cationic liposomes. J Control Release, 2006,116(1):58–63
Kojima S, Okuno M, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, et al. Acyclic retinoid in the chemoprevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol, 2004,24(4):797–805
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by a grant from Natural Sciences Foundation of Hubei Province, China (No. 2007A-BA284).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, J., Zheng, C., Tao, H. et al. Therapeutic effects of all trans-retinoitc acid combined with transarterial chemoembolization on Walker-256 hepatoma in rats. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 30, 113–118 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-010-0121-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-010-0121-5