Summary
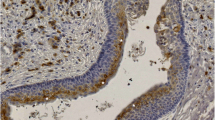
The correlation between the expression of COX-2 and p53 protein in basal cell carcinoma (BCC) of eyelid and apoptosis was investigated. Specimens of BCC were collected from 40 cases (aged 28–68 y) at the Department of Pathology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, and Department of Pathology, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University during from 1999 to 2006. Five specimens of paracancerous tissues served as control group. Immunohistochemical staining was performed to detect the expression of COX-2 and p53 in the tissues. The average absorbance (A) and the average positive area rate of COX-2 and p53 protein were measured by image analysis. The positive area rate of COX-2 and p53 protein was analyzed by linear correlation analysis. It was found that COX-2 and p53 proteins were highly expressed in BCC of eyelid, and weakly expressed in paracancerous tissues. Image analysis revealed that the expression of COX-2 and p53 proteins in BCC of eyelid was significantly higher than that in paracancerous tissues (P<0.01). Spearman rank correlation analysis demonstrated a positive correlation between the expression of COX-2 and p53 (r=0.113, P=0.421). It was concluded that COX-2 can increase the expression of p53 protein, therefore suppressing apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ragge NK, Salt A, Collin JR, et al. Gorlin syndrome: the PTCH gene links ocular developmental defects and tumour formation. Br J Ophthalmol, 2005,89(8):988–991
Allali J, D’Hermies F, Renard G. Basal cell carcinomas of the eyelids. Ophthalmologica, 2005,219(2):57–71
Cao Y, Prescott SM. Many actions of cyclooxygenase-2 in cellular dynamics and in cancer. J Cell Physiol, 2002, 190:279–286
Hasturk S, Kemp B, Kalapurakal SK, et al. Expression of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 in bronchial epithelium and non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer, 2002,94:1023–1031
Schuler M, Herrmann R, De Greve JL, et al. Adenovirus mediated p53 gene transfer in patients receiving chemotherapy for advanced non small cell lung cancer: results of a multicenter phase II study. J Clin Oncol, 2001,19(6): 1750–1758
Altorki NK, Keresztes RS, Port JL, et al. Celecoxib, a selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitor, enhances the response to preoperative paclitaxel and carboplatin in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2003,21(14):2645–2650
Allali J, D’Hermies F, Renard G. Basal cell carcinomas of the eyelids. Ophthalmologica, 2005,219(2):57–71
Xu XC. COX-2 inhibitions in cancer treatment and prevention, a recent development. Anticancer Drugs, 2002, 13(2):127–137
Kohno H, Nagasue N, Rahman MA. COX-2 a target for preventing hepatic carcinoma? Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2002,6(4):483–490
Kang S, Kim YB, Kim MH, et a1. Polymorphism in the nuclear factor kappa-B binding promoter region of cyclooxygenase-2 is associated with anincreased risk of bladder cancer. Cancer Lett, 2005,217(1):11–16
Schuler M, Maurer U, Goldstein JC, et a1. P53 triggers apoptosis in oncogene—expression fibroblasts by the induction of Noxa and mitochondrial Bax translocation. Cell Death Differ, 2003,l0(4):457–460
Yuan XM, Li W, Dalen H, et al. Lysosomal destabilization in p53 Induced apoptosis. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA, 2002,99(9):6286–6291
Yuan A, Yu CJ, Luh KT, et al. Aberrant p53 expression correlates with expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-8 mRNA and neoangiogenesis in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 2002,20(4): 900–910
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Yang, J. & Huang, Q. Correlation and expression of COX-2 and P53 protein in basal cell carcinoma of eyelid. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 29, 383–386 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0324-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-009-0324-9