Summary
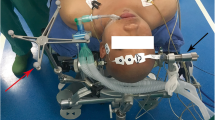
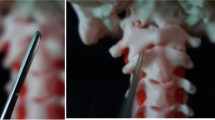
In order to provide anatomical basis for transoral approach (TOA) in dealing with the ventro lesions of craniocervical junction, and the design and application of artificial atlanto-odontoid joint, microsurgical dissecting was performed on 8 fresh craniocervical specimens layer by layer through transoropharyngeal approach. The stratification of posterior pharyngeal wall, course of vertebral artery, adjacent relationship of atlas and axis and correlative anatomical parameters of replacement of artificial atlanto-odontoid joint were observed. Besides, 32 sets of atlanto-axial joint in adults’ fresh bony specimens were measured with a digital caliper and a goniometer, including the width of bony window of anterior arch of atlas, the width of bony window of axis vertebra, the distance between superior and inferior two atlas screw inserting points, the distance between two axis screw inserting points etc. It was found that the width of atlas and axis which could be exposed were 40.2±3.5 mm and 39.3±3.7 mm respectively. The width and height of posterior pharyngeal wall which could be exposed were 40.1±5.2 mm and 50.2±4.6 mm respectively. The distance between superior and inferior two atlas screw inserting points was 28.0±2.9 mm and 24.0±3.5 mm respectively, and the distance of bilateral axis screw inserting points was 18.0±1.2 mm. The operative exposure position through TOA ranged from inferior part of the clivus to the superior part of the C3 vertebral body. Posterior pharyngeal wall consisted of 5 layers and two interspaces: mucosa, submucosa, superficial muscular layer, anterior fascia of vertebrae, anterior muscular layer of vertebrae and posterior interspace of pharynx, anterior interspace of vertebrae. This study revealed that it had the advantages of short operative distance, good exposure and sufficient decompression in dealing with the ventro lesions from the upper cervical to the lower clivus through the TOA. The replacement of artificial atlanto-odontoid joint is suitable and feasible. The design of artificial atlanto-odontoid joint should be based on the above data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yin Q, Ai F, Zhang K et al. Irreducible anterior atlantoxial dislocation: One-stage treatment with a transoral atlantoaxial reduction plate fixation and fusion. Report of 5 cases and review of the literature. Spine, 2005,30:E375–E381
Ji R M, Li R Q, Zhang Y H et al. Applied anatomy of the oropharynx approach to the clivus. Chin J Clin Anat (Chinese), 2003,21:549–551
Wang Z Y, Yin Q S, Wang L J et al. Applied anatomy of transoral approach to the lesion of ventral craniocervical junction. CMINS, 2004,9:499–501
Zhang C Y, Miao J L, Yi X N et al. Feasibility of endoscopic transoral-transpharyngeal approach to atlantoaxis. Chin J Orthop (Chinese), 2004,24:299–303
Ai F, Yin Q, Wang Z et al. Atlantoaxial surgery through transoropharyngeal approach: An anatomic study. Med J Chin PLA, 2004,29:220–222
Ai F, Yin Q, Wang Z et al. Surgical anatomy of transoral atlantoaxial reduction plate internal fixation. Chin J Surg (Chinese), 2004,42:1325–1329
Hu Y, Yang S H, Xie H et al. Quantitative anatomic study of atlanto-odontoid joint and design of an artificial atlanto-odontoid joint for the orthopedics clinic. Chin J Traumatol (Chinese), 2007,10:138–144
Ai F, Yin Q, Wang Z et al. Applied anatomy of transoral atlantoaxial reduction plate internal fixation. Spine, 2006,31:128–132
Yin D, Hong X, Li J Y et al. Quantitative anatomy of the lateral mass of the atlas. Spine, 2003,28:860–863
Hong X, Yin D, Chang Y B et al. Posterior screw placement on the lateral mass of atlas: An anatomic study. Spine, 2004,29:500–503
Resnick D K, Lapsiwala S, Trost G R. Anatomic suitability of the C1–C2 complex for pedicle screw fixation. Spine, 2002,27:1494–1498
Kandziora F, Schulze-Stahl N, Khodadadyan K C et al. Screw placement in transoral atlantoaxial plate systems: an anatomical study. J Neurosurg Spine, 2001,95(Suppl 1):80–87
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Yang, S., Xie, H. et al. The anatomic study on replacement of artificial atlanto-odontoid joint through transoral approach. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 28, 327–332 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-008-0322-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-008-0322-3