Summary
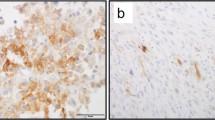
The expression of silience of death domains (SODD) and its clinical significance and relationship with phospho-NF-κB-p65 proteins in bone marrow cells of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) were explored, and the expression of SODD and phospho-NF-κB-p65 in Jurkat cells treated with chemotherapeutic drugs was detected in order to find a new chemotherapeutic target. The expression of SODD and phospho-NF-κB-p65 proteins in bone marrow cells was detected by immunohistochemistry in 25 children with ALL. The apoptosis rate was measured by Annexin-V-Fluorescence/PI double-labeling flow cytometry and the expression of SODD and phospho-NF-κB-p65 proteins determined by Western blotting in the Jurkat cells. It was found that the expression of SODD and active P65 in ALL was significantly higher than that in normal control group (P<0.05). The expression of the SODD and phospho-NF-κB-p65 proteins in the high-risk (HR) group was significantly higher than that in the standard-risk (SR) group (P<0.05). The Pearson rank correlation analysis revealed that there was a positive correlation between SODD and phospho-NF-κB-p65 expression (P<0.01, r=0.69). VCR could effectively induce the apoptosis of Jurkat cells, and down-regulate the expression of SODD and phospho-NF-κB-p65 proteins in a time-dependent manner, but DNR could not down-regulate the expression of SODD effectively. It was concluded that SODD may be closely related to the clinical classification and prognosis of ALL in children. The expression of SODD and phospho-NF-κB-p65 had a definite synergistic relationship with the onset and development of ALL. VCR could down-regulate the expression of SODD and inhibit the NF-κB activation, which could recover the sensibility of apoptosis in leukemic cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takada H, Chen N J, Mirtsos C et al. Role of SODD in regulation of tumor necrosis factor responses. MCB, 2003:23(11):4026–4033
Zhou M, Gu L, Zhu N et al. Transfection of a dominant-negative mutant NF-κB inhibitor (IκBm) represses p53-dependent apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells: interaction of IκBm and p53. Oncogene, 2003:22(50):8137–8144
Suggestions for Diagnosis and Treatment of Children Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (Draft of 2nd Revision). Chin J Pediat, 1999,37:305–307
Jiang Y, Woronicz J D, Goeddel D V et al. Prevention of constitutive TNF receptor 1 signaling by silencer of death domains. Science, 1999:283(5401):543–546
Endres R, Hacker G, Brosch I et al. Apparently normal tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 signaling in the absence of silencer of death domains. MCB, 2003,23(18):6609–6617
Rayet B, Gelinas C. Aberrant Rel/NFκB genes and activity in human cancer. Oncogene, 1999,18:6938–6947
Inada H, Izawa I, Nishizawa M. Keratin attenuates tumor necrosis factor-induced cytotoxicity through association with TRADD. J Cell Biol, 2001, 155(3):415–426
Kiyoshi M, Edward E. Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 is an ATPase by silencer of death domain. MCB, 2002,22:2536–2543
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
TAO Hongfang, female, born in 1979, M.D., Ph.D.
This project was supported by a grant from National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 39970778).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, H., Hu, Q., Fang, J. et al. Expression of SODD and P65 in ALL of children and its relationship with chemotherapeutic drugs. J. Huazhong Univ. Sc. Technol. 27, 326–329 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0328-2
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-007-0328-2