Abstract
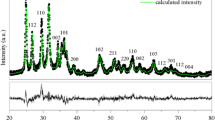
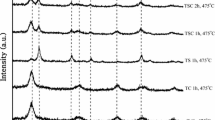
Nitrogen-doped TiO2 nanocrystalline powders were prepared by hydrolysis of tetrachloride titanium (TiCl4) in a mixed solution of ethanol and ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) at ambient temperature and atmosphere followed by calcination at 400 °C for 2 h in air. FTIR spectra demonstrate that amine group in original gel is eliminated by calcination, and the TiO2 powder is liable to absorb water onto its surface and into its capillary pore. XRD and SEM results show that the average size of nanocrystalline TiO2 particles is no more than 60 nm and with increasing the calcination temperature, the size of particles increases. XPS studies indicate the nitrogen atom enters into the TiO2 lattice and occupies the position of oxygen atom. The nitrogen doping not only depresses the grain growth of TiO2 particles, but also reduces the phase transformation temperature of anatase to rutile. The photocatalytic activity of the nitrogen-doped TiO2 powders has been evaluated by experiments of photocatalytic degradation aqueous methylene blue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K Honda, A Fujishima. Electrochemical Photolysis of Water at a Semiconductor Electrode[J]. Nature, 1972, 238(5 358): 37–38
U Diebold. The Surface Science of Titanium Dioxide[J]. Surf. Sci. Rep., 2003, 48(5–8): 53–229
M R Hoffmann, S T Martin, W Y Choi, et al. Environmental Applications of Semiconductor Photocatalysis[J]. Chem. Rev., 1995, 95(1): 69–96
A W Grant, C T Campbell. Cesium Adsorption on TiO2(110)[J]. Phys. Rev. B, 1997, 55(3): 1 844–1 850
J H Wei, X J Zhao, J Xiao, et al. Preparation and Properties of Ag-TiO2 Thin Films on Glass Substrates[J]. J. Wuhan Univ. Tech.-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2002, 17(3): 21–23
R Asahi, T Morikawa, T Ohwaki, et al. Visible-light Photocatalysis in Nitrogen-doped Titanium Oxides[J]. Science, 2001, 293(5 528): 269–271
T Morikawa, R Asahi, T Ohwaki, et al. Band-gap Narrowing of Titanium Dioxide by Nitrogen Doping[J]. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2, 2001, 40(6A): L561–L563
S Yin, H Yamaki, M Komatsu, et al. Preparation of Nitrogen-doped Titania with High Visible Light Induced Photocatalytic Activity by Mechanochemical Reaction of Titania and Hexamethylene-tetramine[J]. J. Mater. Chem., 2003, 13(12): 2 996–3 001
T Ihara, M Miyoshi, Y Iriyama, et al. Visible-light-active Titanium Oxide Photocatalyst Realized by an Oxygen-deficient Structure and by Nitrogen Doping[J]. Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 2003, 42(4): 403–409
J G Yu, J C Yu, X J Zhao. The Effect of SiO2 Addition on the Grain Size and Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2 Thin Films[J]. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn., 2002, 24(2):95–103
J G Yu, J F Xiong, B Cheng, et al. Fabrication and Characterization of Ag-TiO2 Multiphase Nanocomposite Thin Films with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity[J]. Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 2005, 60(3–4): 211–221
H E Chao, Y U Yun, X F Hu, et al. Effect of Silver Doping on the Phase Transformation and Grain Growth of Sol-Gel Titania Powder[J]. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2003, 23(9):1 457–1 464
J G Yu, J C Yu, B Cheng, et al. Photocatalytic Activity and Characterization of the Sol-Gel Derived Pb-Doped TiO2 Thin Films[J]. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Techn., 2002, 24(1):39–48
Y C Hong, C U Bang, D H Shin, et al. Band Gap Narrowing of TiO2 by Nitrogen Doping in Atmospheric Microwave Plasma[J].Chem. Phys. Lett., 2005, 413(4–6):454–457
C D Wagner, W M Riggs, L E Davis, et al. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, Physical Electronics Division[M]. Perkin-Elmer Corporation, Eden Prairie, Minnesota, 1979:68
Z P Wang, W M Cai, X T Hong, et al. Photocatalytic Degradation of Phenol in Aqueous Nitrogen-doped TiO2 Suspensions With Various Light Sources[J]. Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 2005, 57(3):223–231
N P Hua, Z Y Wu, Y K Du, et al. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Codoped with Pt and N for Photodegradation of Cl3CCOOH[J]. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2005, 21(10):1 081–1 085 (in chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20276056) and Shaanxi Natural Science Foundation (No. 2003E225)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Zhou, A. Effects of nitrogen doping on microstructure and photocatalytic activity of nanocrystalline TiO2 powders. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 22, 457–461 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-006-3457-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-006-3457-8