Abstract
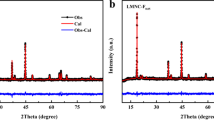
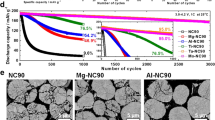
Few studies on two-cations co-doped orthosilicate cathodes have been reported to date. Here, Mn and Ni co-doped Li2Fe0.8-xMn0.2NixSiO4 (x = 0.05 and 0.1) were synthesized using a solid state route. Both Mn and Ni can successfully enter into the Li2FeSiO4 lattice. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) results show some certain evidence about the participation of foreign Mn and Ni in the charge-discharge reaction. Furthermore, at the conduction band minimum, Ni 3d-orbital contribution can reduce the band gap to 1.13 eV. These improvements can promote the Li+ insertion/de-insertion behavior in the co-doped material; consequently, when x = 0.1, Li2Fe0.7Mn0.2Ni0.1SiO4 shows the initial discharge capacities of 164 mAh g−1 and the corresponding Coulombic efficiency of 87.2%. Even at a rate of 80 mA g−1, the first discharge capacity can reach to 71.2 mAh g−1.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ni J, Jiang Y, Bi X, Li L, Lu J (2017) Lithium iron orthosilicate cathode: progress and perspectives. ACS Energy Lett 2:1771–1781
Fujita Y, Iwase H, Shida K, Liao J, Fukui T, Matsuda M (2017) Synthesis of high-performance Li2FeSiO4/C composite powder by spray-freezing/freeze-drying a solution with two carbon sources. J Power Sources 361:115–121
Yang J, Kang X, He D, Zheng A, Pan M, Mu S (2015) Graphene activated 3D hierarchical flower like Li2FeSiO4 for high performance lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 3:16567–16573
Wei H, Lu X, Chiu HC, Wei B, Gauvin R, Arthur Z, Emond V, Jiang DT, Zaghib K, Demopoulos GP (2018) Ethylenediamine-enabled sustainable synthesis of mesoporous nanostructured Li2FeIISiO4 particles from Fe(III) aqueous solution for Li-ion battery application. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:7458–7467
Zhang Q, Yan C, Meng Y, Wang X (2018) Hierarchical mesoporous Li2FeSiO4/C sheaf-rods as a high-performance lithium-ion battery cathode. J Alloys Compd 767:195–203
Zhang Q, Yan C, Guo J, Wang X (2018) Mesoporous Li2FeSiO4/C nanocomposites with enhanced performance synthesized from fumed nano silica. Ionics 24:2555–2563
Qiu H, Jin D, Wang C, Chen G, Wang L, Yue H, Zhang D (2020) Design of Li2FeSiO4 cathode material for enhanced lithium-ion storage performance. Chem Eng J 379:122329
Dhanalakshmi R, Diwakar K, Rajkumar P, Subadevi R, Liu WR, Sivakumar M (2017) Structural and morphological studies on Li2Fe0.5Mn0.5SiO4/C composite synthesized using polyvinyl alcohol for energy storage devices. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 17:1–5
Qu L, Luo D, Fang S, Liu Y, Yang L, Hirano S, Yang CC (2016) Mg-doped Li2FeSiO4/C as high-performance cathode material for lithium-ion battery. J Power Sources 307:69–76
Qu L, Li M, Bian L, Du Q, Luo M, Yang B, Yang L, Fang S, Liu Y (2017) A strontium-doped Li2FeSiO4/C cathode with enhanced performance for the lithium-ion battery. J Solid State Electrochem 21:3659–3673
Qiu H, Yue H, Wang X, Zhang T, Zhang M, Fang Z, Zhao X, Chen G, Wei Y, Wang C, Zhang D (2017) Titanium-doped Li2FeSiO4/C composite as the cathode material for lithium-ion batteries with excellent rate capability and long cycle life. J Alloys Compd 725:860–868
Qiu H, Yue H, Zhang T, Ju Y, Zhang Y, Guo Z, Wang C, Chen G, Wei Y, Zhang D (2016) Enhanced electrochemical performance of Li2FeSiO4/C positive electrodes for lithium-ion batteries via yttrium doping. Electrochim Acta 188:636–644
Li LM, Guo HJ, Li XH, Wang ZX, Peng WJ, Xiang KX, Cao X (2009) Effects of roasting temperature and modification on properties of Li2FeSiO4/C cathode. J Power Sources 189:45–50
Ge YC, Yan XD, Liu J, Zhang XF, Wang JW, He XG, Wang RS, Xie HM (2010) An optimized Ni doped LiFePO4/C nanocomposite with excellent rate performance. Electrochim Acta 55:5886–5890
Zhang WK, Hu Y, Tao XY, Huang H, Gan YP, Wang CT (2010) Synthesis of spherical LiFePO4/C via Ni doping. J Phys Chem Solids 71:1196–1200
Shu HB, Wang XY, Wu Q, Hu BA, Yang XK, Wei QL, Liang QQ, Bai YS, Zhou M, Wu C, Chen MF, Wang AW, Jiang LL (2013) Improved electrochemical performance of LiFePO4/C cathode via Ni and Mn co-doping for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 237:149–155
Li E, Han C, Mi L, Zhu L, Dou YK, Shi (2019) The effect of Ni or Pb substitution on the electrochemical performance of Li2FeSiO4/C cathode materials. Solid State Ionics 330:24–32
Gao K (2014) Effect of Mn doping on electrochemical properties of Li2FeSiO4/C cathode materials based on a vacuum solid-state method. Ionics. 20:809–815
Arroyo-de Dompabloa ME, Armand M, Tarascon JM, Amador U (2006) On-demand design of polyoxianionic cathode materials based on electronegativity correlations: an exploration of the Li2MSiO4 system (M = Fe, Mn, co, Ni). Electrochem Commun 8:1292–1298
Wu XZ, Jiang X, Huo QS, Zhang YX (2012) Facile synthesis of Li2FeSiO4/C composites with triblock copolymer P123 and their application as cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 80:50–55
Lv DP, Bai JY, Zhang P, Wu SQ, Li YX, Wen W, Jiang Z, Mi JX, Zhu ZZ, Yang Y (2013) Understanding the high capacity of Li2FeSiO4: in-situ XRD/XANES study combined with first-principles calculations. Chem Mater 25:2014–2020
Peng G, Zhang LL, Yang XL, Duan S, Liang G, Huang YH (2013) Enhanced electrochemical performance of multi-walled carbonnanotubes modified Li2FeSiO4/C cathode material for lithium-ionbatteries. J Alloys Compd 570:1–6
Liu SK, Xu J, Li DZ, Hu Y, Liu X, Xie K (2013) High capacity Li2MnSiO4/C nanocomposite prepared by sol-gelmethod for lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 232:258–263
Wang F, Wang YM, Sun DM, Wang L, Yang J, Jia HP (2014) Highperformance Li2MnSiO4 prepared in molten KCl-NaCl for rechargeable lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 119:131–137
Chen R, Heinzmann R, Mangold S, Kiran Chakravadhanula VS, Hahn H, Indris S (117, 2013) Structural evolution of Li2Fe1-yMnySiO4 (y = 0, 0.2, 0.5, 1) cathode materials for Li-ion batteries upon electrochemical cycling. J Phys Chem C:884–893
Zhang LL, Duan S, Yang XL, Liang G, Huang YH, Cao XZ, Yang J, Li M, Croft MC, Lewis C (2015) Insight into cobalt-doping in Li2FeSiO4 cathode material for lithium-ion battery. J Power Sources 274:194–202
Rangappa D, Murukanahally KD, Tomai T, Unemoto A, Honma I (2012) Ultrathin Nanosheets of Li2MSiO4 (M = Fe, Mn) as high-capacity Li-ion battery electrode. Nano Lett 12:1146–1151
Deng H, Zhao SX, Wu X, Wei L, Deng YF, Nan CW (2016) Effect of Ni substitution on structural stability, micromorphology, and electrochemical performance of Li2MnSiO4/C cathode materials. RSC Adv 6:111539–111548
Chen L, Li D, Zheng X, Chen L, Zhang Y, Liang Z, Feng J, Si P, Lou J, Ci L (2019) Integrated nanocomposite of LiMn2O4/graphene/carbon nanotubes with pseudocapacitive properties as superior cathode for aqueous hybrid capacitors. J Electroanal Chem 842:74–81
Yang JL, Zheng JX, Kang XC, Teng GF, Hu L, Tan R, Wang K, Song XH, Xu M, Mu SC, Pan F (2016) Tuning structural stability and lithium-storage properties by d-orbital hybridization substitution in full tetrahedron Li2FeSiO4 nanocrystal. Nano Energy 20:117–125
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (No. 201801D121046), Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (No. LH2020B004), and Scientific Research Foundation for Youths of Harbin University (HUDF2019202, HUDF2019203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, SD., Gao, K. Insights into manganese and nickel co-doped Li2FeSiO4 cathodes for lithium-ion battery. Ionics 27, 2345–2352 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04002-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04002-3