Abstract
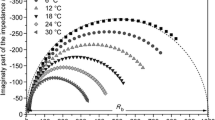
Solid nanocomposite polymer electrolytes based on polyethylene oxide (PEO), AgNO3 as salt, and nanosized Fe2O3 (less than 50 nm size) as filler are prepared by hot press method. In (100-x) PEO:xAgNO3 system (where x = 5 ≤ x ≤ 50 wt%), the solid polymer electrolyte 90PEO:10AgNO3 gives highest ionic conductivity. This composition is further used as host matrix and Fe2O3 as filler for the preparation of solid nanocomposite polymer electrolytes (100-x) (90PEO:10AgNO3):xFe2O3 (where x = 5 ≤ x ≤ 30 wt%). The real impedance (Z') and imaginary impedance (Z") of the samples are analysed using LCR meter. The maximum ionic conductivity is observed for 10 wt% of filler Fe2O3. The optimum conducting composition 90(90PEO:10AgNO3):10Fe2O3 is used for further study. The dielectric response of the samples is analysed using dielectric constant (ε'), dielectric loss (ε"), loss tangent (tanδ), and real and imaginary part of electric modulus (M' and M"). The ionic conductivity and dielectric response of the solid nanocomposite polymer electrolytes are studied within the frequency range of 100 Hz–5 MHz and within the temperature range of 300–323 K. It is observed that the dielectric constant rises sharply towards low frequencies due to electrode polarization effects. The maxima of the loss tangent (tan δ) shift towards higher frequencies with increasing temperature. The enhancement in ionic conductivity is observed when nanosized Fe2O3 filler is added into the solid polymer electrolyte.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jayathilaka PARD, Dissanayake MAKL, Albinsson I, Mellander BE (2002) Effect of nano-porous Al2O3 on thermal, dielectric and transport properties of the (PEO)9LiTFSI polymer electrolyte system. Electrochem Acta 47:3257–3268
Verma ML, Minakshi M, Singh NK (2014) Structural and electrochemical properties of nanocomposite polymer electrolyte for electrochemical devices. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:14993–15001
Rajendran S, Babu RS, Rani MU (2011) Effect of complexing salt on conductivity of PVC/PEO polymer blend electrolytes. Bull Mater Sci 7:1525–1530
Zhang X-W, Wang C, Appleby AJ, Little FE (2002) Characteristics of lithium-ion conducting composite polymer-glass secondary cell electrolytes. J Power Sources 112:209–215
Tominaga Y, Asai S, Sumita M, Panero S, Scrosati B (2005) A novel composite polymer electrolyte: effect of mesoporous SiO2 on ionic conduction in poly(ethylene oxide) –LiCF3SO3 complex. J Power Sources 146:402–405
Kim DG, Shim J, Lee JH, Kwon SJ, Baik JH, Lee JC (2013) Preparation of solid state composite electrolytes based on organic/inorganic hybrid star-shaped polymer and PEG functionalised POSS for all-solid-state lithium battery applications. Polymer 54:5812–5820
Itoh T, Fujita K, Inoue K, Iwama H, Kondoh K, Uno T, Kubo M (2013) Solid polymer electrolytes based on alternating copolymers of vinyl ethers with methoxy oligo(ethleneoxy)ethyl groups and vinylene carbonate. Electrochim Acta 112:221–229
Scrosati B (2000) Recent advances in lithium-ion battery materials. Electrochim Acta 45:2461–2466
Yap YL, You AH, Teo LL, Hanapei H (2013) Inorganic filler sizes effect on ionic conductivity in polyethylene oxide (PEO) composite polymer electrolyte. Int J Electrochem Soc 8:2154
Agrawal RC, Pandey GP (2008) Solid polymer electrolytes: materials designing and all solid-state battery applications: an overview. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:223001 (18pp)
Persi L, Croce F, Scrosati B, Plichta E, Hendrickson MA (2002) Poly(ethylene oxide)-based, nanocomposite electrolytes as improved separators for rechargeable lithium polymer batteries: the Li/LiMn3O6 case. J Electrochem Soc 149:212
Fahmi EM, Ahmad A, Nazeri NNM, Hamzah H, Razali H, Rahman MYA (2012) Effect of LiBF4 salt concentration on the properties of poly(Ethylene Oxide)-based composite polymer electrolyte. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:5798–5804
Johan MF, Ting LM (2011) Structural, thermal and electrical properties of nano manganese-composite polymer electrolytes int. J Electrochem Sci 6:4737–4748
Croce F, Appetecchi GB, Persi L, Scrosati B (1998) Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Nature 394:456–458
Sun JK, Moon HS, Kim JW, Park JW (2003) Role of functional nano-sized inorganic fillers in poly(ethylene) oxide-based polymer electrolytes. J Power Sources 117:124–130
Nan CW, Fan L, Yin Y, Cai Q (2003) Enhanced ionic conductivity of polymer electrolytes containing nanocomposite SiO2 particles. Phys Rev Lett 91:104–108
Yuan A, Zhao J (2006) Composite alkaline polymer electrolytes and its application to nickelmetal hydride batteries. Electrochim Acta 51:2454–2462
Morita M, Noborio H, Yoshimoto N, Ishikawa M (2006) Ionic conductance of composite electrolytes based on network polymer with ceramic powder. Solid State Ionics 177:715–720
Dey A, Karan S, De SK (2008) Thermal and electric properties of CeO2 nanoparticles dispersed in polyethylene oxide: NH4ClO4 complex. Solid State Ionics 178:1963
Teran AA, Tang MH, Mullin SA, Balsara NP (2011) Effect of molecular weight on conductivity of polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 203:18–21
Li YH, Wu XL, Kim JH et al (2013) A novel polymer electrolyte with improved high-temperaturetolerance up to 170 °C for high-temperature lithium-ion batteries. J Power Sources 244:234–239
Verma ML, Minakshi M, Singh NK (2014) Synthesis and characterization of solid polymer electrolyte based on activated carbon for solid state capacitor. Electrochim Acta 137:497–503
Liew CW, Ramesh S, Durairaj R (2012) Impact of low viscosity ionic liquid on PMMA–PVC–LiTFSI polymer electrolytes based on AC -impedance, dielectric behavior, and HATR–FTIR characteristics. J Mater Res 27:2996–3004
Othman L, Chew KW, Osman Z (2007) Impedance spectroscopy studies of poly(methyl methacrylate)-lithium salts polymer electrolyte systems. Ionics 13:337–342
Tripathi SK, Gupta A, Kumari M (2012) Studies on electrical conductivity and dielectric behaviour of PVdF–HFP–PMMA–NaI polymer blend electrolyte. Bull Mater Sci 35:969–975
Liu Y, Lee JY, Hong L (2002) Functionalised SiO2 in poly (ethylene oxide)-based polymer electrolytes. J Power Sources 109:507–514
Arbizzani C, Mastragostino M, Meneghello L (1996) Polymer-based redox supercapacitors: a comparative study. Electrochim Acta 41:21–26
Meng C, Liu C, Chen L, Hu C, Fan S (2010) Highly flexible and all-solid-state paper like polymer supercapacitors. Nano Lett 10:4025–4031
Tan CG, Siew WO, Pang WL, Osman Z, Chew KW (2007) The effects of ceramic fillers on the PMMA-based polymer electrolyte systems. Ionics 13:361–364
Scrosati B, Croce F, Persi L (2000) Impedance spectroscopy study of PEO-based nanocomposite based electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 147:1718–1721
Ataollahi N, Ahmad A, Hamzah H, Rahman MYA, Mohamed NS (2013) Ionic conduction of blend poly (Vinylidene Fluoride-Hexafluoro Propylene) and poly (Methyl Methacrylate)-grafted natural rubber based solid polymer electrolyte. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:7875–7884
Agrawal RC, Mahipal YK (2011) Study of electrical and electrochemical behaviour on hot-press synthesized nano-composite polymer electrolyte (NCPE) membranes: [(70PEO: 30 KNO3) + x SiO2]. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:867–881
Laxmi N, Chandra S (2001) Proton conducting composites of heteropolyacid hydrates (phosphomolybdic and phosphotungstic acids) dispersed with insulating Al2O3. Phys Stat Solidi (a) 186:395
Xu D, Sridhar V, Mahapatra SP, Kim JK (2009) Dielectric properties of exfoliated graphite reinforced flouroelastomer composites. J Appl Polym Sci 111:1358–68
Al-Saleh MH, Al-Anid HK, Husain YA, El-Ghanem HM, Jawad S (2013) Impedance characteristics and conductivity of CNT/ABS nanocomposites. J Phys D Appl Phys 46:385305 (8pp)
Chandra S, Hashmi SA, Saleem M, Agrawal RC (1993) Investigations on poly ethylene oxide based polymer electrolyte complexed with AgNO3. Solid State Ionics 67:1–7
Agrawal RC, Chandra A, Bhatt A, Mahipal YK (2008) Investigations on ion transport properties of and battery discharge characteristic studies on hot-pressed Ag + −ion-conducting nano-composite polymer electrolytes:(1–x) [90PEO : 10AgNO3] : xSiO2. New J Phys 10:043023 (10pp)
Maier J (2004) Ionic transport in nano-sized systems. Solid State Ionics 175:7–12
Sharma JP, Sekhon SS (2007) Nanodispersed polymer gel electrolytes: conductivity modification with the addition of PMMA and fumed silica. Solid State Ionics 178:439–445
Saikia D, Chen-Yang YW, Chen YT, Li YK, Lin SI (2009) Li NMR spectroscopy and ion conduction mechanism of composite gel polymer electrolyte: a comparative study with variation of salt and plasticizer with filler. Electrochim Acta 54:1218–1227
Agrawal RC, Gupta RK (1999) Superionic solids: composite electrolyte phase—an overview. J Mater Sci 34:1131–1162
Croce F, Perse L, Scrosati B, Serraino-Fiory F, Plichta E, Hendrickson MA (2001) Role of the ceramic fillers in enhancing the transport properties of composite polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 46:2457–2461
Chung SH, Wang Y, Persi L, Croce F, Greenbaum SG, Scrosati B, Plichta E (2001) Enhancement of ion transport in polymer electrolytes by addition of nanoscale inorganic oxides. J Power Sources 97:644
Shyly PM, Karuppasamy K, Linda T, Thiravetyan P, Balakumar S, Sahaya Shajan X (2012) Ionic conductivity and dielectric studies of chitin nanofiber (CNF) incorporated PMMA based polymer electrolytes. IOSR J Appl Phys 1:47–51
Zamri SFM, Latif FA et al (2014) Ionic conductivity and dielectric properties of LiBF4 doped PMMA/ENR 50 filled acid modified SiO2 electrolytes. Procedia Technol 15:850–856
Reicha FM, El-Hiti M, El-Sonabati AZ, Diab MA (1991) Conducting polymers. V. Electrical conductivity of polymer complexes of bis-2,6-diaminopyridinesulphoxide-copper halides. J Phys D Appl Phys 24:369
Aziz SB (2013) Li + ion conduction mechanism in poly (e-caprolactone)-based polymer electrolyte. Iran Polym J 22:877–883
Nithya H, Selvasekarapandian S, Kumar DA et al (2011) Thermal and dielectric studies of polymer electrolyte based on P(ECH-EO). Mater Chem Phys 126:404–408
Choudhary S, Sengwa RJ (2011) Dielectric relaxation spectroscopy and ion conduction in poly (ethylene oxide)-blend salts-montmorillonite nanocomposite electrolytes. Indian J Pure Appl Phys 49:204–213
Hassan MF, Yusof SZM (2014) Poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid)-zinc acetate polymer electrolytes: Studies based on structural and morphology and electrical spectroscopy. Microsc Res 2:30–38
Kumar TV, Chary AS, Bhardwaj S, Awasthi AM, Reddy SN (2013) Dielectric relaxation, ionic conduction and Complex impedance studies on NaNO3 fast ion conductor. Int J Mater Sci Appl 2:173–178
Shastry MCR, Rao KJ (1991) Ac conductivity and dielectric relaxation studies in AgI-based fast ion conducting glasses. Solid State Ionics 44:187–198
Ramesh S, Owg Poh Ling (2010) Effect of ethylene carbonate on the ionic conduction in poly (vinylidine fluoride-hexafluorooropylene) based solid polymer electrolytes. Polym Chem 1:702–707
Ramesh S, Chai MF (2007) Conductivity, dielectric behavior and FTIR studies of high molecular weight poly (vinyl chloride)-lithumtriflate polymer electrolytes. Mater Sci Eng B 139:240–245
Aziz SB, Abidin ZHZ, Arof AK (2010) Influence of silver ion reduction on electrical modulus parameters of solid polymer electrolyte based on chitosansilver triflate electrolyte membrane. eXPRESS Polym Lett 4:300–310
Dutta A, Sinha TP, Jena P, Adak S (2008) Ac conductivity and dielectric relaxation in ionically conducting soda-lime-silicate glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 354:3952–3957
Kumar M, Tiwari T, Chauhan JK, Srivastava N (2014) Erratum on ‘Understanding the ion dynamics and relaxation behavior from impedance spectroscopy of NaI doped Zwitterionic polymer system’. Mater Res Express 1:049601
Pradhan DK, Choudhary RNP, Samantaray BK (2009) Studies of dielectric and electrical properties of plasticized polymer nanocomposite electrolytes. Mater Chem Phys 115:557–561
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the kind support of the management of Shri Shankaracharya Technical Campus (SSTC). Helpful discussions with Manickam Minakshi (School of Engineering and Information Technology, Murdoch University, Australia) is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, M.L., Sahu, H.D. Ionic conductivity and dielectric behavior of PEO-based silver ion conducting nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. Ionics 21, 3223–3231 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1517-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1517-9