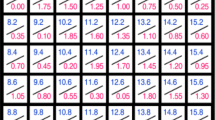
Abstract
Canonical correlation analysis (CCA) method and its extended methods have been widely and successfully applied to the frequency recognition in SSVEP-based BCI systems. As a state-of-the-art extended method, filter bank canonical correlation analysis has higher accuracy and information transmission rate (ITR) than CCA. However, in the CCA method, the temporally local structure of samples has not been well considered. In this correspondence, we proposed termed temporally local canonical correlation analysis (TCCA). In this new method, the original covariance matrix was replaced by the temporally local covariance matrix. Furthermore, we proposed an improved frequency identification method of filter bank based on TCCA, named filter bank temporally local canonical correlation analysis (FBTCCA). In the offline environment, we used a leave-one-subject-out validation strategy on datasets of ten testees to optimize the parameters of TCCA and FBTCCA and evaluate the two algorithms. The experimental results affirm that TCCA markedly outperformed CCA, and FBTCCA obtained the highest accuracy among the four methods. This study corroborates that TCCA-based approaches have great potential for implementing short time window SSVEP-based BCI systems.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakardjian H, Tanaka T, Cichocki A (2010) Optimization of SSVEP brain responses with application to eight-command brain–computer interface. Neurosci Lett 469:34–38
Chang MH, Lee JS, Heo J, Park KS (2016) Eliciting dual-frequency ssvep using a hybrid ssvep-p300 bci. J Neurosci Methods 258:104–113
Chaudhary U, Birbaumer N, Ramos-Murguialday A (2016) Brain–computer interfaces for communication and rehabilitation. Nat Rev Neurol 12:513
Chen X, Wang Y, Gao S, Jung TP, Gao X (2015a) Filter bank canonical correlation analysis for implementing a high-speed SSVEP-based brain–computer interface. J Neural Eng 12:046008
Chen X, Wang Y, Nakanishi M, Gao X, Jung TP, Gao S (2015b) High-speed spelling with a noninvasive brain–computer interface. Proc Nat Acad Sci 112:E6058–E6067
Chen X, Wang ZJ, McKeown M (2016) Joint blind source separation for neurophysiological data analysis: multiset and multimodal methods. IEEE Signal Process Mag 33:86–107
Cheng M, Gao X, Gao S, Xu D (2002) Design and implementation of a brain–computer interface with high transfer rates. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 49:1181–1186
Dai Y, Wang X, Li X, Tan Y (2015) Sparse EEG compressive sensing for web-enabled person identification. Measurement 74:11–20
Feng J, Yin E, Jin J, Saab R, Daly I, Wang X, Hu D, Cichocki A (2018) Towards correlation-based time window selection method for motor imagery BCIS. Neural Netw 102:87–95
Gao S, Wang Y, Gao X, Hong B (2014) Visual and auditory brain–computer interfaces. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61:1436–1447
He B, Baxter B, Edelman BJ, Cline CC, Wenjing WY (2015) Noninvasive brain–computer interfaces based on sensorimotor rhythms. Proc IEEE 103:907–925
Herrmann CS (2001) Human eeg responses to 1–100 hz flicker: resonance phenomena in visual cortex and their potential correlation to cognitive phenomena. Exp Brain Res 137:346–353
Hwang HJ, Lim JH, Jung YJ, Choi H, Lee SW, Im CH (2012) Development of an SSVEP-based BCI spelling system adopting a qwerty-style led keyboard. J Neurosci Methods 208:59–65
Hwang J, Nam K, Jang D, Kim I (2017) Effects of spectral smearing of stimuli on the performance of auditory steady-state response-based brain–computer interface. Cogn Neurodyn 11(6):515–527
Jiao Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wang B, Jin J, Wang X (2018) A novel multilayer correlation maximization model for improving CCA-based frequency recognition in SSVEP brain–computer interface. Int J Neural Syst 28:1750039
Lance BJ, Kerick SE, Ries AJ, Oie KS, McDowell K (2012) Brain–computer interface technologies in the coming decades. Proc IEEE 100:1585–1599
Lay-Ekuakille A, Vergallo P, Griffo G, Conversano F, Casciaro S, Urooj S, Bhateja V, Trabacca A (2013) Entropy index in quantitative EEG measurement for diagnosis accuracy. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 63:1440–1450
Lin Z, Zhang C, Wu W, Gao X (2006) Frequency recognition based on canonical correlation analysis for SSVEP-based bcis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 53:2610–2614
Miao Y, Yin E, Allison BZ, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Dong Y, Wang X, Hu D, Chchocki A, Jin J (2020) An ERP-based BCI with peripheral stimuli: validation with ALS patients. Cogn Neurodyn 14(1):21–33
Muller KR, Anderson CW, Birch GE (2003) Linear and nonlinear methods for brain–computer interfaces. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 11:165–169
Nakanishi M, Wang Y, Wang YT, Jung TP (2015) A comparison study of canonical correlation analysis based methods for detecting steady-state visual evoked potentials. PLoS ONE 10:e0140703
Poryzala P, Materka A (2014) Cluster analysis of CCA coefficients for robust detection of the asynchronous SSVEPS in brain–computer interfaces. Biomed Signal Process Control 10:201–208
Wang H (2010) Temporally local maximum signal fraction analysis for artifact removal from biomedical signals. IEEE Trans Signal Process 58:4919–4925
Wang H, Xu D (2012) Comprehensive common spatial patterns with temporal structure information of EEG data: minimizing nontask related EEG component. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59:2496–2505
Wang H, Zhang Y et al (2016) Detection of motor imagery EEG signals employing naïve bayes based learning process. Measurement 86:148–158
Wang Y, Gao X, Hong B, Jia C, Gao S (2008) Brain–computer interfaces based on visual evoked potentials. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag 27:64–71
Yin E, Zhou Z, Jiang J, Yu Y, Hu D (2014) A dynamically optimized SSVEP brain–computer interface (BCI) speller. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 62:1447–1456
Yuan P, Chen X, Wang Y, Gao X, Gao S (2015) Enhancing performances of SSVEP-based brain–computer interfaces via exploiting inter-subject information. J Neural Eng 12:046006
Zhang R, Xu P, Liu T, Zhang Y, Guo L, Li P, Yao D (2013a) Local temporal correlation common spatial patterns for single trial EEG classification during motor imagery. Comput Math Methods Med 2013:591216
Zhang Y, Zhou G, Jin J, Wang M, Wang X, Cichocki A (2013b) L1-regularized multiway canonical correlation analysis for SSVEP-based BCI. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 21:887–896
Zhang Y, Dong L, Zhang R, Yao D, Zhang Y, Xu P (2014a) An efficient frequency recognition method based on likelihood ratio test for SSVEP-based BCI. Comput Math Methods Med 2014:908719
Zhang Y, Xu P, Cheng K, Yao D (2014b) Multivariate synchronization index for frequency recognition of SSVEP-based brain–computer interface. J Neurosci Methods 221:32–40
Zhang Y, Zhou G, Jin J, Wang X, Cichocki A (2014c) Frequency recognition in SSVEP-based BCI using multiset canonical correlation analysis. Int J Neural Syst 24:1450013
Zhang Y, Zhou G, Jin J, Wang X, Cichocki A (2015) Ssvep recognition using common feature analysis in brain–computer interface. J Neurosci Methods 244:8–15
Zhang Y, Guo D, Xu P, Zhang Y, Yao D (2016) Robust frequency recognition for SSVEP-based BCI with temporally local multivariate synchronization index. Cogn Neurodyn 10:505–511
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Jin J, Wang X (2017) Sparse bayesian learning for obtaining sparsity of EEG frequency bands based feature vectors in motor imagery classification. Int J Neural Syst 27:1650032
Zhang Y, Yin E, Li F, Zhang Y, Tanaka T, Zhao Q, Cui Y, Xu P, Yao D, Guo D (2018) Two-stage frequency recognition method based on correlated component analysis for SSVEP-based BCI. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 26:1314–1323
Acknowledgements
Thanks for the support of science and Technology Department of Shandong Province (2017GGX30103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, X., Lin, M. Filter bank temporally local canonical correlation analysis for short time window SSVEPs classification. Cogn Neurodyn 14, 689–696 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-020-09620-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-020-09620-7