Abstract
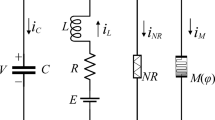
Neuron shows distinct dependence of electrical activities on membrane patch temperature, and the mode transition of electrical activity is induced by the patch temperature through modulating the opening and closing rates of ion channels. In this paper, inspired by the physical effect of memristor, the potassium and sodium ion channels embedded in the membrane patch are updated by using memristor-based voltage gate variables, and an external stimulus is applied to detect the variety of mode selection in electrical activities under different patch temperatures. It is found that each ion channel can be regarded as a physical memristor, and the shape of pinched hysteresis loop of memristor is dependent on both input voltage and patch temperature. The pinched hysteresis loops of two ion-channel memristors are dramatically enlarged by increasing patch temperature, and the hysteresis lobe areas are monotonously reduced with the increasing of excitation frequency if the frequency of external stimulus exceeds certain threshold. However, for the memristive potassium channel, the AREA1 corresponding to the threshold frequency is increased with the increasing of patch temperature. The amplitude of conductance for two ion-channel memristors depends on the variation of patch temperature. The results of this paper might provide insights to modulate the neural activities in appropriate temperature condition completely, and involvement of external stimulus enhance the effect of patch temperature.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari SP, Sah PdM, Kim H, Chua L (2013) Three fingerprints of memristor. IEEE Trans Circuits-I 60(11):3008–3021
Bao B, Hu A, Bao H, Xu Q, Chen M, Wu H (2018) Three-dimensional memristive Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model with hidden coexisting asymmetric behaviors. Complexity. Article ID 3872573
Biolek Z, Biolek D, Biolkova V (2012) Computation of the area of memristor pinched hysteresis loop. IEEE Trans Circuits-II 59(9):670–671
Chua L (2015) Everything you wish to know about memristor but are afraid to ask. Radioengin 24(2):319–368
Chua L, Kang SM (1976) Memristive devices and systems. Proc IEEE 64(2):209
Chua L, Sbitnev V, Kim H (2012) Hodgkin–Huxley axon is made of memristors. Int J Bifurc Chaos 22(3):1230011
Correa AM, Bezanilla F, Latorre R (1992) Gating kinetics of batrachotoxin-modified Na + channels in the squid giant axon voltage and temperature effects. Biophys J 61(5):1332–1352
FitzHugh R (1961) Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys J 1(6):445
Ge M, Jia Y, John BK, Xu Y, Shen J, Lu L, Liu Y, Pei Q, Zhan X, Yang L (2018) Propagation of firing rate by synchronization in a feed-forward multilayer Hindmarsh–Rose neural network. Neurocomputing 320:60–68
Ge M, Jia Y, Xu Y, Lu L, Wang H, Zhao Y (2019) Wave propagation and synchronization induced by chemical autapse in chain feed-forward Hindmarsh–Rose neural network. Appl Math Comput 352:136–145
Guo D, Perc M, Zhang Y (2017) Frequency-difference dependent stochastic resonance in neural systems. Phys Rev E 96(2):022415
Guo D, Gan J, Tan T, Tian X, Wang G, Tak-Pan Ng K (2018) Neonatal exposure of ketamine inhibited the induction of hippocampal long-term potentiation without impairing the spatial memory of adult rats. Cogn Neurodyn 12:377–383
Hindmarsh JL, Rose RM (1982) A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differential equations. Nature 296(5853):162–164
Hindmarsh JL, Rose RM (1984) A model of neuronal bursting using three coupled first order differential equations. Proc R Soc Lond B 221(1222):87–102
Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF (1952) The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol 116(4):497–506
Hyun NG, Hyun KH, Hyun KB, Han JH, Lee K, Kaang BK (2011) A computational model of the temperature-dependent changes in firing patterns in aplysia neurons. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 15(6):371–382
Ji X, Hu X, Zhou Y, Dong Z, Duan S (2019) Adaptive sparse coding based on memristive neural network with applications. Cogn Neurodyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-019-09537-w
Jia B, Gu H, Xue L (2017) A basic bifurcation structure from bursting to spiking of injured nerve fibers in a two-dimensional parameter space. Cogn Neurodyn 11(2):189–200
Lu L, Jia Y, Xu Y, Ge M, Pei Q, Yang L (2019a) Energy dependence on modes of electric activities of neuron driven by different external mixed signals under electromagnetic induction. Sci China Technol Sci 62(3):427–440
Lu L, Jia Y, Kirunda JB, Xu Y, Ge M, Pei Q, Yang L (2019b) Effects of noise and synaptic weight on propagation of subthreshold excitatory postsynaptic current signal in a feed-forward neural network. Nonlinear Dyn 95(2):1673–1686
Ma J, Huang L, Tang J, Ying H, Jin W (2012) Spiral wave death, breakup induced by ion channel poisoning on regular Hodgkin–Huxley neuronal networks. Commun Nonlinear Sci 17(11):4281–4293
Ma J, Zhang G, Hayat T, Ren G (2019) Model electrical activity of neuron under electric field. Nonlinear Dyn 95:1585–1598
Maio VD, Santillo S, Sorgente A, Vanacore P, Ventriglia F (2018) Influence of active synaptic pools on the single synaptic event. Cogn Neurodyn 12:391–402
Micheva KD, Smith SJ (2005) Strong effects of subphysiological temperature on the function and plasticity of mammalian presynaptic terminals. J Neurosci 25(33):7481–7488
Mondal A, Upadhyay RK, Ma J, Yadav BK, Sharma SK, Mondal A (2019) Bifurcation analysis and diverse firing activities of a modified excitable neuron model. Cogn Neurodyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-019-09526-z
Nordenfelt A, Used J, Sanjuán MA (2013) Bursting frequency versus phase synchronization in time-delayed neuron networks. Phys Rev E 87(5):052903
Ozer M, Uzuntarla M, Perc M, Grahamc LJ (2009) Spike latency and jitter of neuronal membrane patches with stochastic Hodgkin–Huxley channels. J Theor Biol 261(1):83–92
Perc M (2007) Effects of small-world connectivity on noise-induced temporal and spatial order in neural media. Chaos 31(2):280–291
Prousalis DA, Volos CK, Stouboulos IN, Kyprianidis IM (2017) Hyperchaotic memristive system with hidden attractors and its adaptive control scheme. Nonlinear Dyn 90(3):1681–1694
Rajamani V, Sah MPD, Mannan ZI, Kim H, Chua L (2017) Third-order memristive Morris–Lecar model of barnacle muscle fiber. Int J Bifurc Chaos 27(4):1730015
Szabo TM, Brookings T, Preuss T, Faber DS (2008) Effects of temperature acclimation on a central neural circuit and its behavioral output. J Neurophysiol 100(6):2997
Thottil SK, Ignatius RP (2016) Nonlinear feedback coupling in Hindmarsh–Rose neurons. Nonlinear Dyn 87(3):1879–1899
Tian C, Cao L, Bi H, Xu K, Liu Z (2018) Chimera states in neuronal networks with time delay and electromagnetic induction. Nonlinear Dyn 93(3):1695–1704
Volkov AG, Reedus J, Mitchell CM, Tucket C, Forde-Tuckett V, Volkova MI, Markin VS, Chua L (2014) Memristors in the electrical network of Aloe vera L. Plant Signal Behav 9(7):e29056
Wang R, Jiao X (2006) Stochastic model and neural coding of large-scale neuronal population with variable coupling strength. Neurocomputing 69(7–9):778–785
Wang C, Ma J (2018) A review and guidance for pattern selection in spatiotemporal system. Int J Mod Phys B 32(6):1830003
Wang YH, Wang R (2017) An improved neuronal energy model that better captures of dynamic property of neuronal activity. Nonlinear Dyn 91(1):319–327
Wang R, Zhang Z (2007) Energy coding in biological neural network. Cogn Neurodyn 1(3):203–212
Wang R, Zhu Y (2016) Can the activities of the large scale cortical network be expressed by neural energy? A brief review. Cogn Neurodyn 10(1):1–5
Wang Q, Perc M, Duan Z, Chen G (2010) Spatial coherence resonance in delayed in delayed Hodgkin–Huxley neuronal networks. Int J Mod Phys B 24(09):1201–1213
Wang Z, Wang R, Fang R (2015) Energy coding in neural network with inhibitory neurons. Cogn Neurodyn 9(2):129–144
Wang C, Lin Q, Yao Y, Yang K, Tian M, Wang Y (2018) Dynamics of a stochastic system driven by cross-correlated sine-Wiener bounded noises. Nonlinear Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4669-0
Wilson HR, Cowan JD (1972) Excitatory and inhibitory interactions in localized populations of model neurons. Biophys J 12(1):1–24
Xu Y, Ying H, Jia Y, Ma J, Hayat T (2017) Autaptic regulation of electrical activities in neuron under electromagnetic induction. Sci Rep 7:43452
Xu Y, Jia Y, Ge M, Lu L, Yang L, Zhan X (2018a) Effects of ion channel blocks on electrical activity of stochastic Hodgkin–Huxley neural network under electromagnetic induction. Neurocomputing 283:196–204
Xu Y, Jia Y, Kirunda JB, Shen J, Ge M, Lu L, Pei Q (2018b) Dynamic behaviors in coupled neurons system with the excitatory and inhibitory autapse under electromagnetic induction. Complexity 2018:3012743
Xu Y, Jia Y, Wang HW, Liu Y, Wang P, Zhao Y (2019) Spiking activities in chain neural network driven by channel noise with field coupling. Nonlinear Dyn 95(4):3237–3247
Yang L, Jia Y (2005) Effects of patch temperature on spontaneous action potential train due to channel fluctuations: coherence resonance. Biosystems 81(3):267–280
Yao Y, Ma J (2018) Weak periodic signal detection by sine-Wiener-noise-induced resonance in the FitzHugh–Nagumo neuron. Cogn Neurodyn 12(3):343–349
Yao C, Zhan M, Shuai J, Ma J, Kurths J (2017) Insensitivity of synchronization to network structure in chaotic pendulum systems with time-delay coupling. Chaos 27:126702
Zhu F, Wang R, Pan X, Zhu Z (2019) Energy expenditure computation of a single bursting neuron. Cogn Neurodyn 13(1):75–78
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Ma, J., Zhan, X. et al. Temperature effect on memristive ion channels. Cogn Neurodyn 13, 601–611 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-019-09547-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-019-09547-8