Abstract
Purpose
This study was performed to determine the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of the normal kidney using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) sequences and to analyse both the changes due to hydration state and results repeatability.
Materials and methods
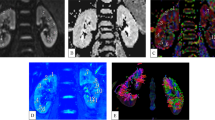
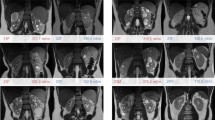
Ten volunteers underwent DW-MRI imaging of the kidneys with a breath-hold single-shot spin-echo planar imaging (SE-EPI) sequence in the axial and coronal planes with b values of 300, 500, 800 s/mm2, in different states of hydration. Urine osmolarity (OsmU) and sodium excretion (NaU) were measured at the time of each examination. ADC maps were created for all b values, and ADC values were calculated and compared between different states of hydration. In five subjects, the protocol was conducted twice to test data repeatability.
Results
ADC values were lower with higher b values (3.00 vs. 2.47 vs. 1.99×10−3 mm2/s with b values of 300, 500, 800 s/mm2, respectively). ADC values in different hydration states were not statistically different. Measurements were reproducible. OsmU and NaU were statistically different in the different states of hydration (p<0.01).
Conclusions
ADC values significantly decrease with higher b values. Average ADC values in the normal kidney are reproducible. Hydration state does not significantly influence mean ADC values.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
Calcolare con RM pesata in diffusione (RM-DW) i valori del coefficiente di diffusione apparente (ADC) del parenchima renale in volontari sani, valutarne le variazioni in relazione allo stato di idratazione e misurare la ripetibilità delle misure.
Materiali e metodi
È stato condotto studio RM-DW renale con sequenza single-shot Echo planare in breath-hold (SE-EPI) assiale e coronale (valori di b di 300, 500, 800 s/mm2) in 10 volontari sani, in differente stato di idratazione, con controllo di osmolarità urinaria (OsmU) e sodiuria (NaU). Sono state create mappe ADC e valutati i valori di ADC per i differenti valori di b ed in relazione allo stato di idratazione. Al fine di verificare la ripetibilità dei dati in 5 soggetti l’esame è stato ripetuto a distanza di 3 mesi, nelle stesse condizioni.
Risultati
I valori di ADC risultavano 3,00 vs 2,47 vs 1,99×10−3 mm2/s con valori di b rispettivamente di 300, 500, 800 s/mm2. Non si sono osservate differenze significative tra valori di ADC nei diversi stati di idratazione e tra esame basale ed esame ripetuto a distanza di tre mesi. OsmU e NaU erano statisticamente differenti nei diversi stati di idratazione (p<0,01).
Conclusioni
Il valori di ADC misurati sono in accordo con i dati riportati in letteratura e decrescono significativamente al crescere di b. Lo stato di idratazione non influenza significativamente i valori di ADC. Le misurazioni sono ripetibili.
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
Steiskal EO, Tanner JE (1965) Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of time dependent field gradient. J Chem Phys 42:28–292
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D et al (1986) MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and pefusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 161:401–407
Laghi A, Catalano C, Assale F et al (2001) Diffusion-weighted echo-planar sequences for the evaluation of the upper abdomen: technique optimization. Radiol Med 101:213–218
Yamashita Y, Tang Y, Takahashi M (1998) Ultrafast MR imaging of the abdomen: echo planar imaging and diffusion weighted imaging. J Magn reson Imaging 8:367–374
Colagrande S, Pallotta S, Vanzulli A et al (2005) Il parametro diffusione in risonanza magnetica: elementi di fisica, tecnica e semeiotica. Radiol Med 109:1–16
Chan JHM, Tsui EYK, Luk SH et al (2001) MR diffusion-weighted imaging of the kidney: differentiation between hydronephrosis and pyonephrosis. J Clin Imaging 25:110–113
Muller MF, Prasad PV, Siewert B et al (1994) Abdominal diffusion mapping with use of a whole-body echo-planar system. Radiology 190:475–478
Muller MF, Prasad PV, Bimmler D et al (1994) Functional imaging of the kidney by means of measurement of the apparent diffusion coefficient. Radiology 193:711–715
Colagrande S, Carbone SF, Carusi LM et al (2006) Magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging: extraneurological applications. Radiol Med 111:392–419
Cova M, Squilaci E, Stacul F et al (2004) Diffusion-weighted MRI in the evaluation of renal lesions: preliminary results. Brit J Radiol 77:851–857
Roy C (2004) Exploration de l’appareil urinaire en IRM: developpements actuels et perspectives futures. J Radiol 85:171–183
Grenier N, Basseau F, Res M et al (2003) Functional MRI of the kidney. Abdominal Imaging 28:164–175
Laissy JP, Menegazzo D, Dumont E et al (2000) Hemodynamic effect of iodinated high-viscosity contrast medium in the rat kidney. Invest Radiol 35:647–652
Fukuda Y, Ohashi I, Hanafusa K et al (2000) Anistropic diffusion in kidney: apparent diffusion coefficient measurements for clinical use. J Magn Reson Imaging 11:156–160
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, Oyen RH et al (2005) Diffusion weighted MR imaging of kidneys in healthy volunteers and patients with parenchymal diseases: initial experience. Radiology 235:911–917
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Damasio, M.B., Tagliafico, A., Capaccio, E. et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI sequences (DW-MRI) of the kidney: normal findings, influence of hydration state and repeatability of results. Radiol med 113, 214–224 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-008-0248-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-008-0248-7