Abstract
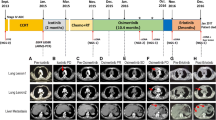
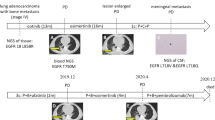
The third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) osimertinib (AZD9291) has shown significant clinical efficacy against the EGFR T790M mutation in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. However, resistance inevitably occurs, and the mechanisms leading to treatment failure need to be further investigated. The B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2)-like 11 (BIM) deletion polymorphism, which occurs at a frequency of 21% in East Asians but is absent in African and European populations, has been associated with resistance to first-generation EGFR TKIs, such as gefitinib and erlotinib; and is a poor prognostic factor for NSCLC patients with EGFR mutations. Nevertheless, the significance of this BIM deletion polymorphism in the resistance to osimertinib has not been reported. Here, we show for the first time that a NSCLC patient harboring the EGFR L858R/T790M mutations, as well as the BIM deletion polymorphism, exhibited poor clinical outcomes with osimertinib treatment. This result suggests that the BIM deletion polymorphism might have prognostic value for determining NSCLC patient outcomes following osimertinib treatment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cross DAE, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S, Eberlein C, Nebhan CA, Spitzler PJ, et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discovery. 2014;4(9):1046–61. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0337.
Mok TS. Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, Kim HR, Ramalingam SS et al. Osimertinib or platinum-Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(7):629–40. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1612674.
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(2):113–25. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1713137.
Thress KS, Paweletz CP, Felip E, Cho BC, Stetson D, Dougherty B, et al. Acquired EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to AZD9291 in non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M. Nat Med. 2015;21(6):560–2. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3854.
Yu HA, Tian SK, Drilon AE, Borsu L, Riely GJ, Arcila ME, et al. Acquired resistance of EGFR-mutant lung Cancer to a T790M-specific EGFR inhibitor: emergence of a third mutation (C797S) in the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain. JAMA Oncol. 2015;1(7):982–4. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.1066.
Niederst MJ, Hu H, Mulvey HE, Lockerman EL, Garcia AR, Piotrowska Z, et al. The allelic context of the C797S mutation acquired upon treatment with third-generation EGFR inhibitors impacts sensitivity to subsequent treatment strategies. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(17):3924–33. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-15-0560.
Yang Z, Yang N, Ou Q, Xiang Y, Jiang T, Wu X, et al. Investigating novel resistance mechanisms to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-17-2310.
Youle RJ, Strasser A. The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(1):47–59. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2308.
Ng KP, Hillmer AM, Chuah CT, Juan WC, Ko TK, Teo AS, et al. A common BIM deletion polymorphism mediates intrinsic resistance and inferior responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Nat Med. 2012;18(4):521–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2713.
Faber AC, Corcoran RB, Ebi H, Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Chung E, et al. BIM expression in treatment-naive cancers predicts responsiveness to kinase inhibitors. Cancer Discovery. 2011;1(4):352–65. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.cd-11-0106.
Adachi M, Zhao X, Imai K. Nomenclature of dynein light chain-linked BH3-only protein Bim isoforms. Cell Death Differ. 2005;12(2):192–3. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401529.
Zou Q, Zhan P, Lv T, Song Y. The relationship between BIM deletion polymorphism and clinical significance of epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy: a meta-analysis. Trans Lung Cancer Res. 2015;4(6):792–6. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2015.12.09.
Cappuzzo F, Ciuleanu T, Stelmakh L, Cicenas S, Szczesna A, Juhasz E, et al. Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(6):521–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(10)70112-1.
Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Akerley W, Bazhenova LA, Borghaei H, Camidge DR, et al. Non-small cell lung Cancer, version 6. J Ntnl Comprehens Cancer Netw. 2015;13(5):515–24.
Yang JC, Ahn MJ, Kim DW, Ramalingam SS, Sequist LV, Su WC, et al. Osimertinib in pretreated T790M-positive advanced non-small-cell lung Cancer: AURA study phase II extension component. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(12):1288–96. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2016.70.3223.
Planchard D, Loriot Y, Andre F, Gobert A, Auger N, Lacroix L, et al. EGFR-independent mechanisms of acquired resistance to AZD9291 in EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC patients. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(10):2073–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdv319.
Ou SI, Agarwal N, Ali SM. High MET amplification level as a resistance mechanism to osimertinib (AZD9291) in a patient that symptomatically responded to crizotinib treatment post-osimertinib progression. Lung Cancer. 2016;98:59–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.05.015.
Cragg MS, Kuroda J, Puthalakath H, Huang DC, Strasser A. Gefitinib-induced killing of NSCLC cell lines expressing mutant EGFR requires BIM and can be enhanced by BH3 mimetics. PLoS Med. 2007;4(10):1681–9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0040316.
Nakagawa T, Takeuchi S, Yamada T, Ebi H, Sano T, Nanjo S, et al. EGFR-TKI resistance due to BIM polymorphism can be circumvented in combination with HDAC inhibition. Cancer Res. 2013;73(8):2428–34. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-12-3479.
Costa DB, Halmos B, Kumar A, Schumer ST, Huberman MS, Boggon TJ, et al. BIM mediates EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in lung cancers with oncogenic EGFR mutations. PLoS Med. 2007;4(10):1669–79. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0040315.
Rosell R, Bivona TG, Karachaliou N. Genetics and biomarkers in personalisation of lung cancer treatment. Lancet. 2013;382(9893):720–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(13)61715-8.
Ebi H, Oze I, Nakagawa T, Ito H, Hosono S, Matsuda F, et al. Lack of association between the BIM deletion polymorphism and the risk of lung cancer with and without EGFR mutations. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10(1):59–66. https://doi.org/10.1097/jto.0000000000000371.
Lee JH, Lin YL, Hsu WH, Chen HY, Chang YC, Yu CJ, et al. Bcl-2-like protein 11 deletion polymorphism predicts survival in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9(9):1385–92. https://doi.org/10.1097/jto.0000000000000238.
Soh SX, Siddiqui FJ, Allen JC, Kim GW, Lee JC, Yatabe Y, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data on the impact of the BIM deletion polymorphism on treatment outcomes in epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(25):41474–86. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17102.
Atsumi J, Shimizu K, Ohtaki Y, Kaira K, Kakegawa S, Nagashima T, et al. Impact of the Bim deletion polymorphism on survival among patients with completely resected non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J Glob Oncol. 2016;2(1):15–25. https://doi.org/10.1200/jgo.2015.000638.
Goldstraw P, Chansky K, Crowley J, Rami-Porta R, Asamura H, Eberhardt WE, et al. The IASLC lung Cancer staging project: proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the TNM classification for lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11(1):39–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2015.09.009.
Isobe K, Hata Y, Tochigi N, Kaburaki K, Kobayashi H, Makino T, et al. Clinical significance of BIM deletion polymorphism in non-small-cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. J Thorac Oncol. 2014;9(4):483–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/jto.0000000000000125.
Zhong J, Li ZX, Zhao J, Duan JC, Bai H, An TT, et al. Analysis of BIM (BCL-2 like 11 gene) deletion polymorphism in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer patients. Thoracic Cancer. 2014;5(6):509–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.12119.
Zhao M, Zhang Y, Cai W, Li J, Zhou F, Cheng N, et al. The Bim deletion polymorphism clinical profile and its relation with tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2014;120(15):2299–307. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.28725.
Tanimoto A, Takeuchi S, Arai S, Fukuda K, Yamada T, Roca X, et al. Histone deacetylase 3 inhibition overcomes BIM deletion polymorphism-mediated Osimertinib resistance in EGFR-mutant lung Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(12):3139–49. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-2271.
Deng J, Shimamura T, Perera S, Carlson NE, Cai D, Shapiro GI, et al. Proapoptotic BH3-only BCL-2 family protein BIM connects death signaling from epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition to the mitochondrion. Cancer Res. 2007;67(24):11867–75. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-07-1961.
Xia J, Bai H, Yan B, Li R, Shao M, Xiong L, et al. Mimicking the BIM BH3 domain overcomes resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(65):108522–33. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19411.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the support from Geneseeq for the NGS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by the Project of Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 2016 M590640), and the Project of Postdoctoral Innovation of Shandong Province (Grant no. 201501010).
Conflict of Interest
Xuanzong Li, Shijiang Wang, Butuo Li, Zhen Wang, Shuheng Shang, Yang Shao, Xindong Sun, and Linlin Wang declare that they have no conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 339 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Wang, S., Li, B. et al. BIM Deletion Polymorphism Confers Resistance to Osimertinib in EGFR T790M Lung Cancer: a Case Report and Literature Review. Targ Oncol 13, 517–523 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-018-0573-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-018-0573-2