Abstract
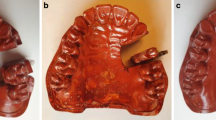
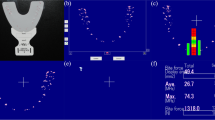
Present dental CAD systems enable us to design functional occlusal tooth surfaces which harmonize with the patient’s stomatognathic function. In order to avoid occlusal interferences during tooth excursions, currently available systems usually use the patient’s functional occlusal impressions for the design of occlusal contact points. Previous interfere-free design, however, has been done on a trial-and-error basis by using visual inspection. To improve this time-consuming procedure, this paper proposes a computer-aided system for assisting in the determination of the occlusal contact points by visualizing the appropriate regions of the opposing surface. The system can designate such regions from data of the opposing occlusal surfaces and their relative movements can be simulated by using a virtual articulator. Experiments for designing the crown of a lower first molar demonstrated that all contact points selected within the designated regions completely satisfied the required contact or separation during tooth excursions, confirming the effectiveness of our computer-aided procedure.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duret F, Preston J, Chapouland E, Duret B (1991) CAD/CAM in the dental office. Quintessence 10(3):449–467
Gysi A (1929) Handbuch der Zahnheilkunde IV. Urban & Schwarzenberg, Berlin
Mörmann WH, Bindl A (2000) The Cerec 3-a quantum leap for computer-aided restorations: initial clinical results. Quintessence Int 31(10):699–712
Mörmann WH, Brandestni M, Lutz F, Barbakow F (1989) Chairside computer-aided direct ceramic inlays. Quintessence Int 20(5):329–339
Reich S, Troeltzsch M, Denekas T, Wichmann M (2004) Generation of functional Cerec 3D occlusal surfaces: a comparison of two production methods relevant in practice. Int J Comput Dent 7(3):229–238
Rekow ED (1987) Computer-aided design and manufacturing in dentistry: a review of the state of the art. J Prosthet Dent 58:512–516
Rekow ED (1991) Dental CAD–CAM systems: what is the state of the art. J Prosthet Dent 122:43–48
Rekow ED, Thompson VP, Yang HS (1991) Margin fit of CAD–CAM produced crowns. J Dent Res 70:715–720
Slavicek R (1984) Die funktionellen Determinanten des Kauorganes. Habilitationsschrift, Munchen
Tinschert J, Natt G, Hassenpflug S, Spiekermann H (2004) Status of current CAD/CAM technology in dental medicine. Int J Comput Dent 7(1):25–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maruyama, T., Nakamura, Y., Hayashi, T. et al. Computer-aided determination of occlusal contact points for dental 3-D CAD. Med Bio Eng Comput 44, 445–450 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-006-0046-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-006-0046-0