Abstract
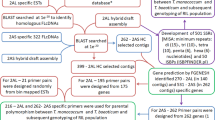
Species containing E genome of Thinopyrum offered potential to increase the genetic variability and desirable characters for wheat improvement. However, E genome specific marker was rare. The objective of the present report was to develop and identify sequenced characterized amplified region (SCAR) markers that can be used in detecting E chromosome in wheat background for breeding purpose. Total 280 random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) primers were amplified for seeking of E genome specific fragments by using the genomic DNA of Thinopyrum elongatum and wheat controls as templates. As a result, six RAPD fragments specific for E genome were found and cloned, and then were converted to SCAR markers. The usability of these markers was validated using a number of Egenome-containing species and wheat as controls. These markers were subsequently located on E chromosomes using specific PCR and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). SCAR markers developed in this research could be used in molecular marker assisted selection of wheat breeding with Thinopyrum chromatin introgressions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brosius J (1991). Retroposons—seeds of evolution. Science, 251(4995): 753
Chen G Y, Dong P, Wei Y M, He K, Li W, Zheng Y L (2007). Development of Ee-chromosome-specific RGAP markers for Lophopyrum elongatum (Host) A. Love in wheat background by using resistance gene analog polymorphism. Acta Agron Sin, 33: 1782–1787
Chen Q (2005). Detection of alien chromatin introgression from Thinopyrum into wheat using S genomic DNA as a probe—a landmark approach for Thinopyrum genome research. Cytogenet Genome Res, 109(1–3): 350–359
Colmer T D, Flowers T J, Munns R (2006). Use of wild relatives to improve salt tolerance in wheat. J Exp Bot, 57(5): 1059–1078
Dewey D R (1984). The genomic system of classification as a guide to intergeneric hybridization with the perennial Triticeae, in Gustafson JP (ed): Gene Manipulation in Plant Improvement. 16: 209–279 (Plenum Press, New York)
Flavell R B, Bennett M D, Smith J B, Smith D B (1974). Genome size and the proportion of repeated nucleotide sequence DNA in plants. Biochem Genet, 12(4): 257–269
Friebe B, Jiang J, Knott D R, Gill B S (1994). Compensation indices of radiation-induced wheat-Agropyron elongatum translocations conferring resistance to leaf rust and stem rust. Crop Sci, 34(2): 400–404
Friebe B, Jiang J, Raupp W J, McIntosh R A, Gill B S (1996). Characterization of wheat-alien translocations conferring resistance to diseases and pests: Current status. Euphytica, 91(1): 59–87
Fu S L, Lv Z L, Qi B, Guo X, Li J, Liu B, Han F P (2012). Molecular cytogenetic characterization of wheat—Thinopyrum elongatum addition, substitution and translocation lines with a novel source of resistance to wheat Fusarium Head Blight. J Genet Genomics, 39(2): 103–110
Han F P, Fedak G (2003). Molecular characterization of partial amphiploids from Triticum durum × tetraploid Thinopyrum elongatum as novel sources of resistance to wheat Fusarium head blight. In: N.E. Pogna, M. Romano, E.A. Pogna, & G. Galterio (Eds.), Proc 10th Int Wheat Genet Symp III. Istituto Sperimentale per la Cerealicoltura, Rome, Italy, 1148–1150
He Z H, Xia X C, Luo J, Xin Z Y, Kong X Y, Jing R L, Wu Z L, Li X P (2006). Trend analysis of international wheat breeding. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 26: 154–156
Hu L J, Zeng Z X, Liu C, Yang Z J, Ren Z L (2008). Production and application of ISSR marker for St genome. Journal of Sichuan University, 45: 143–149
Jia J Q, Yang Z J, Li G R, Liu C, Lei M P, Zhang T, Zhou J P, Ren Z L (2009). Isolation and chromosomal distribution of a Ty1-copia like sequences from Secale allows to identify the wheat-Secale africanum introgression lines. J Appl Genet, 50: 25–28
Ko J M, Do G S, Suh D Y, Seo B B, Shin D C, Moon H P (2002). Identification and chromosomal organization of two rye genomespecific RAPD products useful as introgression markers in wheat. Genome, 45(1): 157–164
Li X M, Lee B S, Mammadov A C, Koo B C, Mott I W, Wang R R C (2007). CAPS markers specific to Eb, Ee, and R genomes in the tribe Triticeae. Genome, 50(4): 400–411
Li Z S, Rong S, Zhong G C, Chen S Y, Mu S M (1985). Wheat wide cross. Beijing: Science Press, 52–83
Liu C, Li G R, Yang Z J, Feng J, Zhou J P, Ren Z L (2006). Isolation and application of specific DNA segments of rye genome. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 26: 2434–2438
Liu C, Yang Z J, Jia J Q, Li G R, Zhou J P, Ren Z L (2009). Genomic distribution of a Long Terminal Repeat (LTR) Sabrina-like retrotransposon in Triticeae species. Cereal Res Commun, 37(3): 363–372
Liu C, Yang Z J, Li G R, Zeng Z X, Zhang Y, Zhou J P, Liu Z H, Ren Z L (2008). Isolation of a new repetitive DNA sequence from Secale africanum enables targeting of Secale chromatin in wheat background. Euphytica, 159(1–2): 249–258
Liu C, Yang Z J, Liu C, Li G R, Ren Z L (2007). Analysis of Stchromosome-containing triticeae polyploids using specific molecular markers. Yi Chuan, 29(10): 1271–1279
Liu S B, Jia J Z, Wang H G, Kong L R, Zhou R H (1998). Special chromosome markers for E genome and DNA polymorphism between Agropyron elongatum (2n = 14) and common wheat detected by RAPD marker. Acta Agron Sin, 24: 687–690
Liu Z W, Biyashev R M, Saghai M M (1996). Development of simple sequence repeat DNA markers and their integration into a barley linkage map. Theor Appl Genet, 93(93): 869–876
Ma J X, Zhou R H, Dong Y S, Jia J Z (2000). Control and inheritance of resistance to yellow rust in Triticum aestivum-Lophopyrum elongatum chromosome substitution lines. Euphytica, 111(1): 57–60
McDonald M P, Galwey N W, Ellneskog-Staam P, Colmer T D (2001). Evaluation of Lophopyrum elongatum as a source of genetic diversity to increase the waterlogging tolerance of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum). New Phytol, 151(2): 369–380
McGuire G E, Dvorak J (1981). High salt tolerance potential in wheatgrasses. Crop Sci, 21(5): 702–705
Mukai Y, Nakahara Y, Yamamoto M (1993). Simultaneous discrimination of the three genomes in hexaploid wheat by multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization using total genomic and highly repeated DNA probes. Genome, 36(3): 489–494
Sharma D, Knott D R (1966). The transfer of leaf rust resistance from Agropyron to Triticum by irradiation. Can J Genet Cytol, 8: 137–143
Sharma H C, Ohm H, Lister R, Foster J E, Shukle R H (1989). Response of wheatgrasses and wheat × wheatgrass hybrids to barley yellow dwarf virus. Theor Appl Genet, 77(3): 369–374
Shen X R, Kong L R, Ohm H (2004). Fusarium head blight resistance in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum)-Lophopyrum genetic lines and tagging of the alien chromatin by PCR markers. Theor Appl Genet, 108(5): 808–813
Shukle R H, Lampe D J, Lister R M, Foster J E (1987). Aphid feeding behavior: relationship to barley yellow dwarf virus resistance in Agropyron species. Phytopathology, 77(5): 725–729
Sun S C (1981). The approach and methods of breeding new varieties and new species from Agrotriticum hybrids. Acta Agron Sin, 7: 51–58
Taeb M, Koebner R M D, Forster B P (1993). Genetic variation for waterlogging tolerance in the Triticeae and the chromosomal location of genes conferring waterlogging tolerance in Thinopyrum elongatum. Genome, 36(5): 825–830
Wang R R C, Zhang X Y (1989). Geneome relationship between Thinopyrum bessarabicum and Th. elongatum: revisited. Genome, 32(5): 802–809
Xu G H, Su W Y, Shu Y J, Cong W W, Wu L, Guo C H (2012). RAPD and ISSR-assisted identification and development of three new SCAR markers specific for the Thinopyrum elongatum E (Poaceae) genome. Genet Mol Res, 11(2): 1741–1751
Yang Z J, Li G R, Chang Z J, Zhou J P, Ren Z L (2006a). Characterization of a partial amphiploid between Triticum aestivum cv. Chinese Spring and Thinopyrum intermedium ssp. trichophorum. Euphytica, 149(1–2): 11–17
Yang Z J, Liu C, Feng J, Li G R, Zhou J P, Deng K J, Ren Z L (2006b). Studies on genome relationship and species-specific PCR marker for Dasypyrum breviaristatum in Triticeae. Hereditas, 143(2006): 47–54
Yang Z J, Ren Z L (2001). Chromosomal distribution and genetic expression of Lophopyrum elongatum (Host) A. Love genes for adult plant resistance to stripe rust in wheat background. Genet Resour Crop Evol, 48(2): 183–187
You M S, Li B Y, Tang Z H, Liu S B, Liu G T (2003). Development of specific SSR markers for Ee-genome of Thinopyrum ssp. by using wheat microsatellites. J Agric Biotechnol, 11: 577–581
You M S, Li B Y, Tang Z H, Liu S B, Song J M, Mao S F, Liu G T (2002). Establishment of E-genome-specific RAPD and SCAR markers for Thinopyrum ssp. Journal of China Agricultural University, 7: 1–6
Zhang WJ, Lukaszewski A J, Kolmer J, Soria MA, Goyal S, Dubcovsky J (2005). Molecular characterization of durum and common wheat recombinant lines carrying leaf rust resistance (Lr19) and yellow pigment (Y) genes from Lophopyrum ponticum. Theor Appl Genet, 111(3): 573–582
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, W., Ran, L., Li, G. et al. Development and utilization of new sequenced characterized amplified region markers specific for E genome of Thinopyrum . Front. Biol. 8, 451–459 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-013-1268-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-013-1268-9