Abstract
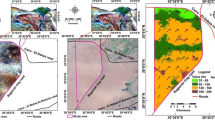
The growth of flue-cured tobacco is sensitive to changes in environmental conditions. Excellent tobacco leaf production is strictly restricted by regional cultivated lands. For the purpose of reasonable utilization and scientific management of Sanmenxia tobacco fields, it is meaningful to evaluate the soil fertility suitability of tobacco crops quantitatively and objectively. In this study, the global positioning system (GPS) technology was used to obtain sample point information automatically. Based on the analysis of fertility properties of soil samples collected from the Sanmenxia tobacco planting regions in Henan Province, we present the index system of soil fertility suitability for tobacco crops. The integrated evaluation of soil fertility suitability was studied with six indices, including organic matter, pH value, available nitrogen (N), available phosphorus (P), available potassium (K), and chlorine (Cl−1) content of surface soil. The subjective grade value was calculated according to S-type and parabola-type functions of the effect of evaluation factors on tobacco crops. Further, the weight value of soil fertility suitability indices was calculated by the method of Hiberarchy analysis. The soil fertility suitability level was evaluated and classified. The suitability map of the Sanmenxia tobacco planting regions in Henan Province was then drawn with the geographic information system (GIS) software mapGIS. It was found that highly suitable fields were mainly distributed in the high mountains in the Southwestern part of the investigated regions where soil pH value and the contents of organic matter were medium, but the contents of available P and available K were higher, accounting for 79.36% of the whole area. Suitable fields were 17% of the whole area, mainly distributed in the middle part of the investigated regions where soil pH value was higher. Unsuitable fields existed in the northern-east and middle part of the Sanmenxia where the contents of soil Cl− was very high, accounting for 3.51% of the whole regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
China Academy Nanjiang Soil Research Institute (1997). Analysis on soil physical and chemical. Shanghai: Shanghai Science Press (in Chinese)
Han X (1991). Crop Ecology. Beijing: China Meteorological Press (in Chinese)
Hu G S, Li Z Y, Wang Z D, Zhao Q B, Zheng W (2000). Nutrition principle of flue-cured tobacco. Beijing: Science Press
Huang H (2004). Suitability evaluation of regional vegetable field by GIS. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 19(2): 108–112 (in Chinese)
Li H, Sun D F, Zhang F R, Zhou L D (2002). Suitability evaluation of fruit trees in Beijing western mountain areas based on DEM and GIS. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 18(5): 250–255
Li X J, Hu Z Q, Liu N, Yu K Q, Ma X Y (2005). Research of soil quality based on 3S in the Yellow River delta. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering. 21(10): 59–63 (in Chinese)
Li Y (1990). Research on China tobacco low fatty acid. Tobacco Journal, 1: 21–28 (in Chinese)
Liu G S (2003). Tobacco Cultivation. Beijing: China Agricultural Press (in Chinese)
Ni S, Huang X (1992). The applied of geography information system to land suitability evaluation. Chinese Science Bulletin, 15: 1403–1404 (in Chinese)
Qiu B W, Chi T H, Wang Q M (2005). Fruit tree suitability assessment using GIS and multi-criteria evaluation. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 21(6): 96–100 (in Chinese)
Seffino L A, Medeiros C B, Rocha J V R, Yi B (1999). Woods-A spatial decision support system based on workflows. Decision Support System, (27): 105–123
Shen H, Zou G (2004). Parameters selection for evaluation of vegetable soil quality and its graduation. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 35(5): 553–557 (in Chinese)
Shi Z, Guan Y L, Wang Y G, Huang M X, Gong J Q, Wang L H (2002). Adjustment of citrus planting structure supported by the integrated remote sensing and GIS. Economic Geography, 22(6): 727–730 (in Chinese)
Sifola M I, Postiglione L (2002). The effect of increasing NaCl in irrigation water on growth, gas exchange and yield of tobacco burley type. Field Crops Research, 74: 81–91
Tang J P, Liu Z (2002). Suitability assessment system for cash crops production based on GIS. System Sciences and Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 18(1): 9–12 (in Chinese)
Wang G (1997). The foundation of tropical crops land suitability evaluation model of three Asia city based on GIS. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2: 23–28 (in Chinese)
Wang R Y, Zhao G X, Li T, Yue Y D (2004). GIS Supported quantitative evaluation of cultivated land fertility. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 20(1): 307–310 (in Chinese)
Xi Z B (2002). Potassium content of flue-cured tobacco from different tobacco production areas. Chinese Tobacco Science, 4: 13–16 (in Chinese)
Xing S H, Huang J, Huang H, Mao Y L (2002). Quality evaluation of regional cultivated land based on GIS. Journal of Fujian Agricultural University (Natural Science), 3: 378–382 (in Chinese)
Zhang H, Zhou Y, Wang S (2003a). Natural productivity evaluation of cultivated land based on GIS and RS date in Houhu farm of Jianghan plain. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 19(2): 219–223 (in Chinese)
Zhang X, Fan Y K, Huang Y J, Guo X F, Sun C H, Ma J M (2003b). Present situation of salinity and chlorine content in irrigation water in tobacco growing areas in Henan. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 22(4): 71–72 (in Chinese)
Zhang Y, Li T F, Zong H, Wen H D, Song Y C, Yang S B, Qu S B (2003c). Analysis on chemical components and flavor substance in oriental tobacco of different producing areas. Chinese Tobacco Science, 4: 12–16 (in Chinese)
Zhang Z P (2002). Discussions on Chlorine contents of tobacco leaves in Luonan county. Journal of Northwest Sci-Tech University of Agriculture and Forestry (Natural Science), 30(4): 33–36 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Yang, Y., Liu, G. et al. Evaluation of tobacco soil fertility suitability of the Sanmenxia area, China, based on geographic information systems. Front. Biol. China 4, 453–459 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-009-0055-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-009-0055-0