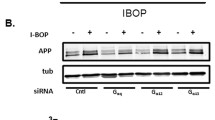
Abstract
Multiple lines of evidence indicate that regional brain eicosanoid signaling is important in initiation and progression of neurodegenerative conditions that have neuroinflammatory pathologic component, such as AD. We hypothesized that PGE2 receptor subtype 1 (EP1) signaling (linked to intracellular Ca2+ release) regulates Aβ peptide neurotoxicity and tested this in two complementary in vitro models: a human neuroblastoma cell line (MC65) producing Aβ1–40 through conditional expression of the APP C-terminal portion, and murine primary cortical neuron cultures exposed to Aβ1–42. In MC65 cells, EP1 receptor antagonist SC-51089 reduced Aβ neurotoxicity ~50 % without altering high molecular weight Aβ immunoreactive species formation. Inositol-3-phosphate receptor antagonist 2-aminoethoxy-diphenyl borate offered similar protection. SC-51089 largely protected the neuron cultures from synthetic Aβ1–42 neurotoxicity. Nimodipine, a Ca2+ channel blocker, was completely neuroprotective in both models. Based on these data, we conclude that suppressing neuronal EP1 signaling may represent a promising therapeutic approach to ameliorate Aβ peptide neurotoxicity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aisen PS, Schafer KA, Grundman M, Pfeiffer E, Sano M, Davis KL, Farlow MR, Jin S, Thomas RG, Thal LJ (2003) Effects of rofecoxib or naproxen vs placebo on Alzheimer disease progression: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 289:2819–2826
Anekonda TS, Quinn JF, Harris C, Frahler K, Wadsworth TL, Woltjer RL (2011) L-type voltage-gated calcium channel blockade with isradipine as a therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis 41:62–70
Bate C, Veerhuis R, Eikelenboom P, Williams A (2003) Neurones treated with cyclo-oxygenase-1 inhibitors are resistant to amyloid-beta1-42. NeuroReport 14:2099–2103
Bate C, Marshall V, Colombo L, Diomede L, Salmona M, Williams A (2008) Docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acids increase neuronal death in response to HuPrP82-146 and Abeta 1–42. Neuropharmacology 54:934–943
Blanco A, Alvarez S, Fresno M, Munoz-Fernandez MA (2010) Amyloid-beta induces cyclooxygenase-2 and PGE2 release in human astrocytes in NF-kappa B dependent manner. J Alzheimers Dis 22:493–505
Carrasco E, Casper D, Werner P (2007) PGE(2) receptor EP1 renders dopaminergic neurons selectively vulnerable to low-level oxidative stress and direct PGE(2) neurotoxicity. J Neurosci Res 85:3109–3117
Combrinck M, Williams J, De Berardinis MA, Warden D, Puopolo M, Smith AD, Minghetti L (2006) Levels of CSF prostaglandin E2, cognitive decline, and survival in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77:85–88
Dargahi L, Nasiraei-Moghadam S, Abdi A, Khalaj L, Moradi F, Ahmadiani A (2011) Cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 activity precedes the COX-2 induction in Abeta-induced neuroinflammation. J Mol Neurosci 45:10–21
Fu H, Li W, Lao Y, Luo J, Lee NT, Kan KK, Tsang HW, Tsim KW, Pang Y, Li Z, Chang DC, Li M, Han Y (2006) Bis(7)-tacrine attenuates beta amyloid-induced neuronal apoptosis by regulating L-type calcium channels. J Neurochem 98:1400–1410
Hanson AJ, Prasad JE, Nahreini P, Andreatta C, Kumar B, Yan XD, Prasad KN (2003) Overexpression of amyloid precursor protein is associated with degeneration, decreased viability, and increased damage caused by neurotoxins (prostaglandins A1 and E2, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide) in differentiated neuroblastoma cells. J Neurosci Res 74:148–159
Hata AN, Breyer RM (2004) Pharmacology and signaling of prostaglandin receptors: multiple roles in inflammation and immune modulation. Pharmacol Ther 103:147–166
Hoshino T, Nakaya T, Homan T, Tanaka K, Sugimoto Y, Araki W, Narita M, Narumiya S, Suzuki T, Mizushima T (2007) Involvement of prostaglandin E2 in production of amyloid-beta peptides both in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 282:32676–32688
Jang JH, Surh YJ (2005) Beta-amyloid-induced apoptosis is associated with cyclooxygenase-2 up-regulation via the mitogen-activated protein kinase-NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 38:1604–1613
Kawano T, Anrather J, Zhou P, Park L, Wang G, Frys KA, Kunz A, Cho S, Orio M, Iadecola C (2006) Prostaglandin E2 EP1 receptors: downstream effectors of COX-2 neurotoxicity. Nat Med 12:225–229
Keene CD, Chang R, Stephen C, Nivison M, Nutt SE, Look A, Breyer RM, Horner PJ, Hevner R, Montine TJ (2009) Protection of hippocampal neurogenesis from toll-like receptor 4-dependent innate immune activation by ablation of prostaglandin E2 receptor subtype EP1 or EP2. Am J Pathol 174:2300–2309
Keene CD, Cudaback E, Li X, Montine KS, Montine TJ (2011) Apolipoprotein E isoforms and regulation of the innate immune response in brain of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol
Li X, Cudaback E, Keene CD, Breyer RM, Montine TJ (2011) Suppressed microglial E prostanoid receptor 1 signaling selectively reduces tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 6 secretion from toll-like receptor 3 activation. Glia 59:569–576
Liang X, Wang Q, Hand T, Wu L, Breyer RM, Montine TJ, Andreasson K (2005) Deletion of the prostaglandin E2 EP2 receptor reduces oxidative damage and amyloid burden in a model of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 25:10180–10187
Lim GP, Yang F, Chu T, Chen P, Beech W, Teter B, Tran T, Ubeda O, Ashe KH, Frautschy SA, Cole GM (2000) Ibuprofen suppresses plaque pathology and inflammation in a mouse model for Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci 20:5709–5714
Lim GP, Yang F, Chu T, Gahtan E, Ubeda O, Beech W, Overmier JB, Hsiao-Ashec K, Frautschy SA, Cole GM (2001) Ibuprofen effects on Alzheimer pathology and open field activity in APPsw transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging 22:983–991
Mawuenyega KG, Sigurdson W, Ovod V, Munsell L, Kasten T, Morris JC, Yarasheski KE, Bateman RJ (2010) Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Science 330:1774
Montine TJ, Sidell KR, Crews BC, Markesbery WR, Marnett LJ, Roberts LJ 2nd, Morrow JD (1999) Elevated CSF prostaglandin E2 levels in patients with probable AD. Neurology 53:1495–1498
Montine TJ, Sonnen JA, Milne G, Baker LD, Breitner JC (2010) Elevated ratio of urinary metabolites of thromboxane and prostacyclin is associated with adverse cardiovascular events in ADAPT. PLoS One 5:e9340
Morihara T, Teter B, Yang F, Lim GP, Boudinot S, Boudinot FD, Frautschy SA, Cole GM (2005) Ibuprofen suppresses interleukin-1beta induction of pro-amyloidogenic alpha1-antichymotrypsin to ameliorate beta-amyloid (Abeta) pathology in Alzheimer's models. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1111–1120
Nagano T, Kimura SH, Takemura M (2010) Prostaglandin E2 reduces amyloid beta-induced phagocytosis in cultured rat microglia. Brain Res 1323:11–17
Quadros A, Patel N, Crescentini R, Crawford F, Paris D, Mullan M (2003) Increased TNFalpha production and Cox-2 activity in organotypic brain slice cultures from APPsw transgenic mice. Neurosci Lett 353:66–68
Resende R, Ferreiro E, Pereira C, Resende de Oliveira C (2008) Neurotoxic effect of oligomeric and fibrillar species of amyloid-beta peptide 1–42: involvement of endoplasmic reticulum calcium release in oligomer-induced cell death. Neuroscience 155:725–737
Shie FS, Breyer RM, Montine TJ (2005a) Microglia lacking E Prostanoid Receptor subtype 2 have enhanced Abeta phagocytosis yet lack Abeta-activated neurotoxicity. Am J Pathol 166:1163–1172
Shie FS, Montine KS, Breyer RM, Montine TJ (2005b) Microglial EP2 as a new target to increase amyloid beta phagocytosis and decrease amyloid beta-induced damage to neurons. Brain Pathol 15:134–138
Shie FS, Montine KS, Breyer RM, Montine TJ (2005c) Microglial EP2 is critical to neurotoxicity from activated cerebral innate immunity. Glia 52:70–77
Sopher BL, Fukuchi K, Smith AC, Leppig KA, Furlong CE, Martin GM (1994) Cytotoxicity mediated by conditional expression of a carboxyl-terminal derivative of the beta-amyloid precursor protein. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 26:207–217
Sugimoto Y, Narumiya S (2007) Prostaglandin E receptors. J Biol Chem 282:11613–11617
Szaingurten-Solodkin I, Hadad N, Levy R (2009) Regulatory role of cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha in NADPH oxidase activity and in inducible nitric oxide synthase induction by aggregated Abeta1–42 in microglia. Glia 57:1727–1740
Szekely CA, Breitner JC, Zandi PP (2007) Prevention of Alzheimer's disease. Int Rev Psychiatr 19:693–706
Ueda K, Shinohara S, Yagami T, Asakura K, Kawasaki K (1997) Amyloid beta protein potentiates Ca2+ influx through L-type voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels: a possible involvement of free radicals. J Neurochem 68:265–271
Vlad SC, Miller DR, Kowall NW, Felson DT (2008) Protective effects of NSAIDs on the development of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 70:1672–1677
Woltjer RL, Maezawa I, Ou JJ, Montine KS, Montine TJ (2003) Advanced glycation endproduct precursor alters intracellular amyloid-beta/A beta PP carboxy-terminal fragment aggregation and cytotoxicity. J Alzheimers Dis 5:467–476
Woltjer RL, McMahan W, Milatovic D, Kjerulf JD, Shie FS, Rung LG, Montine KS, Montine TJ (2007) Effects of chemical chaperones on oxidative stress and detergent-insoluble species formation following conditional expression of amyloid precursor protein carboxy-terminal fragment. Neurobiol Dis 25:427–437
Yang H, Zhang J, Breyer RM, Chen C (2009) Altered hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity in mice deficient in the PGE2 EP2 receptor. J Neurochem 108:295–304
Zhen G, Kim YT, Li RC, Yocum J, Kapoor N, Langer J, Dobrowolski P, Maruyama T, Narumiya S, Dore S (2011) PGE(2) EP1 receptor exacerbated neurotoxicity in a mouse model of cerebral ischemia and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging epub ahead of print
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by ES016754, AG005136, NS062684 and the Nancy and Buster Alvord Endowment. We thank Ms. Amy Look for administrative support and Ms. Carol Arnold for managerial support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Rose, S.E., Montine, K.S. et al. Antagonism of Neuronal Prostaglandin E2 Receptor Subtype 1 Mitigates Amyloid β Neurotoxicity In Vitro. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 8, 87–93 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-012-9380-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-012-9380-1