Abstract
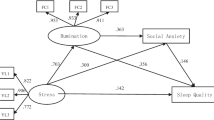
Along with its economic prosperity, China faces a fast increasing rate of drug use. This study aimed to explore the relationship between perceived stress and sleep quality among Chinese drug users while considering rumination as a mediator and resilience as a moderator. Measuring scales, including the Connor–Davidson Resilience Scale, the Ruminative Response Scale, the Perceived Stress Scale, and the Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index, were used to collect information from 104 Chinese drug users. The mediating analysis documented that the effect of perceived stress on sleep quality was mediated via rumination significantly. Resilience acts as a significant moderator on the relationship between perceived stress and poor sleep quality. Simple slope analysis further suggests that participants with a low level of resilience experienced more sleep disturbances given the same level of perceived stress compared to those with a high level of resilience. These findings indicated that psychological intervention that improves drug users’ resilience and reduces their rumination is helpful to release their stress and improve their sleep quality.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, S. H. (2011). Toward an evolutionary basis for resilience to drug addiction. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 34(6), 310–311.
Alim, T. N., Feder, A., Graves, R. E., Wang, Y., Weaver, J., Westphal, M., Alonso, A., Aigbogun, N. U., Smith, B. W., Doucette, J. T., Mellman, T. A., Lawson, W. B., & Charney, D. S. (2008). Trauma, resilience, and recovery in a highrisk African-American population. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 165, 1566–1575.
Alvaro, P. K., Roberts, R. M., & Harris, J. K. (2013). A systematic review assessing bidirectionality between sleep disturbances, anxiety, and depression. Sleep, 36(7), 1059–1068.
Aiken, L. S., West, S. G., & Reno, R. R. (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. New York: Sage.
Anglin, M. D., Burke, C., Perrochet, B., Stamper, E., & Dawud-Noursi, S. (2000). History of the methamphetamine problem. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 32, 137–141.
Anthony, E. J. (1987). Risk, vulnerability, and resilience: An overview. The Invulnerable Child (pp. 3–48). New York: Guilford.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51(6), 1173.
Berset, M., Elfering, A., Lüthy, S., Lüthi, S., & Semmer, N. K. (2011). Work stressors and impaired sleep: Rumination as a mediator. Stress and Health, 27, e71–e82.
Bolla, K. I., Lesage, S. R., Gamaldo, C. E., Neubauer, D. N., Funderburk, F. R., Cadet, J. L., David, P. M., Verdejo-Garcia, A., & Benbrook, A. R. (2008). Sleep disturbance in heavy marijuana users. Sleep, 31, 901–908.
Borkovec, T. D. (1982). Insomnia. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 50, 880–895.
Brand, S., Gerber, M., Kalak, N., Kirov, R., Lemola, S., Clough, P. J., Pühse, U., & Holsboer-Trachsler, E. (2014). Adolescents with greater mental toughness show higher sleep efficiency, more deep sleep and fewer awakenings after sleep onset. Journal of Adolescent Health, 54(1), 109–113.
Burke, C. K., Peirce, J. M., Kidorf, M. S., Neubauer, D., Punjabi, N. M., Stoller, K. B., Hursh, S., & Brooner, R. K. (2008). Sleep problems reported by patients entering opioid agonist treatment. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 35, 328–333.
Buysse, D. J., Reynolds, C. F., Monk, T. H., Berman, S. R., & Kupfer, D. J. (1989). The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Research, 28(2), 193–213.
Cao, Q., & Liang, Y. (2017). Perceived social support and life satisfaction in drug addicts: Self-esteem and loneliness as mediators. Journal of Health Psychology, 25(7), 976–985.
Carney, C. E., Edinger, J. D., Meyer, B., Lindman, L., & Istre, T. (2006). Symptom-focused rumination and sleep disturbance. Behavioral Sleep Medicine, 4(4), 228–241.
Carney, C. E., Harris, A. L., Moss, T. G., & Edinger, J. D. (2010). Distinguishing rumination from worry in clinical insomnia. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 48(6), 540–546.
Chatburn, A., Coussens, S., & Kohler, M. J. (2014). Resiliency as a mediator of the impact of sleep on child and adolescent behavior. Nature and science of sleep, 6, 1–9.
Cicchetti, D., & Blender, J. A. (2006). A multiple-levels-of-analysis perspective on resilience: Implications for the developing brain, neural plasticity, and preventive interventions. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1094, 248–258.
Cohen, S., & Kessler, R. C. (1997). Measuring stress: A guide for health and social scientists. New York: Oxford University Press.
Cohen, S., Kamarck, T., & Mermelstein, R. (1983). A global measure of perceived stress. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 24, 385–396.
Cohen, S., & Williamson, G. (1988). Perceived stress in a probability sample of the US. In S. Spacapam & S. Oskamp (Eds.), The social psychology of health: Claremont symposium on applied social psychology (pp. 31–67).
Cohen-Zion, M., Drummond, S. P. A., Padula, C. B., Winward, J., Kanady, J., Medina, K. L., & Tapert, S. F. (2009). Sleep architecture in adolescent marijuana and alcohol users during acute and extended abstinence. Addictive Behaviors, 34, 976–979.
Collishaw, S., Pickles, A., Messer, J., Rutter, M., Shearer, C., & Maughan, B. (2007). Resilience to adult psychopathology following childhood maltreatment: Evidence from a community sample. Child Abuse & Neglect, 31, 211–229.
Connor, K. M., & Davidson, J. R. (2003). Development of a new resilience scale: The Connor-Davidson resilience scale (CD-RISC). Depression and Anxiety, 18(2), 76–82.
Deeken, F., Häusler, A., Nordheim, J., Rapp, M., Knoll, N., & Rieckmann, N. (2018). Psychometric properties of the perceived stress scale in a sample of German dementia patients and their caregivers. International Psychogeriatrics, 30(1), 39–47.
Ding, H., Han, J., Zhang, M., Wang, K., Gong, J., & Yang, S. (2017). Moderating and mediating effects of resilience between childhood trauma and depressive symptoms in Chinese children. Journal of Affective Disorders, 211, 130–135.
Diestel, S., & Schmidt, K. H. (2009). Mediator and moderator effects of demands on self-control in the relationship between work load and indicators of job strain. Work & Stress, 23(1), 60–79.
Dissel, S., Seugnet, L., Thimgan, M. S., Silverman, N., Angadi, V., Thacher, P. V., Burnham, M. M., & Shaw, P. J. (2015). Differential activation of immune factors in neurons and glia contribute to individual differences in resilience/vulnerability to sleep disruption. Brain Behavior and Immunity, 47, 75–85.
Feder, A., Nestler, E. J., & Charney, D. S. (2009). Psychobiology and molecular genetics of resilience. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 10, 446–457.
Fletcher, F. E., Conduit, R., Foster-Owens, M. D., Rinehart, N. J., Rajaratnam, S. M., & Cornish, K. M. (2018). The association between anxiety symptoms and sleep in school-aged children: A combined insight from the Children’s sleep habits questionnaire and actigraphy. Behavioral Sleep Medicine, 16(2), 169–184.
Frazier, P. A., Tix, A. P., & Barron, K. E. (2004). Testing moderator and mediator effects in counseling psychology research. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 51(1), 115.
Gao, W., Ping, S., & Liu, X. (2020). Gender differences in depression, anxiety, and stress among college students: A longitudinal study from China. Journal of Affective Disorders, 263, 292–300.
Grebner, S., Semmer, N. K., & Elfering, A. (2005). Working conditions and three types of well-being: A longitudinal study with self-report and rating data. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 10(1), 31–43.
Grella, C. E., & Lovinger, K. (2012). Gender differences in physical and mental health outcomes among an aging cohort of individuals with a history of heroin dependence. Addictive Behaviors, 37(3), 306–312.
Han, B., Gfroerer, J. C., & Colliver, J. D. (2010). Associations between duration of illicit drug use and health conditions: Results from the 2005-2007 National Surveys on drug use and health. Annals of Epidemiology, 20(4), 289–297.
Harvey, A. G., & Greenall, E. (2003). Catastrophic worry in primary insomnia. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 34, 11–23.
Hodder, R. K., Freund, M., Bowman, J., Wolfenden, L., Gillham, K., Dray, J., & Wiggers, J. (2016). Association between adolescent tobacco, alcohol and illicit drug use and individual and environmental resilience protective factors. BMJ Open, 6(11), e012688.
Johnson, E. O., & Breslau, N. (2001). Sleep problems and substance use in adolescence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 64(1), 1–7.
Kemper, K. J., Mo, X., & Khayat, R. (2015). Are mindfulness and self-compassion associated with sleep and resilience in health professionals? The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 21, 496–503.
Kopp, M. S., Thega, B. K., Balog, P., Stauder, A., Salaveez, G., Rózsa, S., Purebl, G., & Ádám, S. (2010). Measures of stress in epidemiological research. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 69, 211–225.
Hayes, A. F. (2012). PROCESS: A versatile computational tool for observed variable mediation, moderation, and conditional process modeling. Retrieved from http://www.afhayes.com/public/process2012.pdf
Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. New York: The Guilford Press.
Lee, E.-H. (2012). Review of the psychometric evidence of the perceived stress scale. Asian Nursing Research, 6, 121–127.
Lee, E.-H., Chung, B. Y., Suh, C. H., & Jung, J. Y. (2015a). Korean versions of the perceived stress scale (PSS-14, 10 and 4): Psychometric evaluation in patients with chronic disease. Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences, 29(1), 183–192.
Lee, S.-J., Park, C.-S., Kim, B.-J., Lee, C.-S., Cha, B., & Lee, D. (2015b). Sleep and resilience. Sleep Medicine and Psychophysiology, 22(2), 53–56.
Lemola, S., Räikkönen, K., Scheier, M. F., Matthews, K. A., Pesonen, A. k., Heinonen, K., Lahti, J., Komsi, N., Paavonen, E. J., & Kajantie, E. (2011). Sleep quantity, quality and optimism in children. Journal of Sleep Research, 20, 12–20.
Li, G., Kong, L., Zhou, H., Kang, X., Fang, Y., & Li, P. (2016). Relationship between prenatal maternal stress and sleep quality in Chinese pregnant women: The mediation effect of resilience. Sleep Medicine, 25, 8–12.
Liu, D. W., Fairweather-Schmidt, A. K., Burns, R. A., & Roberts, R. M. (2015). The Connor-Davidson resilience scale: Establishing invariance between gender across the lifespan in a large community based study. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 37(2), 340–348.
Liu, L., & Hsiao, S. C. (2018). Chinese female drug users’ experiences and attitudes with institutional drug treatment. International Journal of Offender Therapy and Comparative Criminology, 62(13), 4221–4235.
Liu, X. C., Tang, M. Q., Hu, L., Wang, A. L., Wu, X. G., Zhao, G. F., et al. (1996). The study on the reliability and validity of Pittsburgh sleep quality index. Chinese Journal of Psychiatry, 29(2), 103–107.
Luthar, S. S., & Brown, P. J. (2007). Maximizing resilience through diverse levels of inquiry: Prevailing paradigms, possibilities, and priorities for the future. Development and Psychopathology, 19(3), 931–955.
Luthar, S. S., Cicchetti, D., & Becker, B. (2000). The construct of resilience: A critical evaluation and guidelines for future work. Child Development, 71(3), 543–562.
Mednick, S. C., Christakis, N. A., & Fowler, J. H. (2010). The spread of sleep loss influences drug use in adolescent social networks. PLoS One, 5(3), e9775.
National Narcotics Control Commission of China. (2017). Annual report on drug-using situation in China. Beijing: Ministry of Public Security.
Ni, C., Chow, M. C. M., Jiang, X., Li, S., & Pang, S. M. C. (2015). Factors associated with resilience of adult survivors five years after the 2008 Sichuan earthquake in China. PLoS One, 10, e0121033.
Nicassio, P. M., Mendlowitz, D. R., Fussell, J. J., & Petras, L. (1985). The phenomenology of the pre-sleep state: The development of the pre-sleep arousal scale. Behabiour Research and Therapy, 23, 263–271.
NIDA. (2007). Marijuana: Facts parents need to know. NIH Publication No. 07–4036 ed: National Institute of Health.
Nolen-hoeksema, S., & Morrow, J. (1991). A prospective study of depression and posttraumatic stress symptoms after a natural disaster. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 61(1), 115–121.
Norris, F. H., Stevens, S. P., Pfefferbaum, B., Wyche, K. F., & Pfefferbaum, R. L. (2008). Community resilience as a metaphor, theory, set of capacities, and strategy for disaster readiness. American Journal of Community Psychology, 41, 127–150.
Ong, A. D., Bergeman, C. S., Bisconti, T. L., & Wallace, K. A. (2006). Psychological resilience, positive emotions, and successful adaptation to stress in later life. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 91(4), 730.
Pasch, K. E., Laska, M. N., Lytle, L. A., & Moe, S. G. (2010). Adolescent sleep, risk behaviors, and depressive symptoms: Are they linked? American Journal of Health Behavior, 34(2), 237–248.
Pasch, K. E., Latimer, L. A., Cance, J. D., Moe, S. G., & Lytle, L. A. (2012). Longitudinal bi-directional relationships between sleep and youth substance use. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 41, 1184–1196.
Preacher, K. J., & Hayes, A. F. (2004). SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers, 36(4), 717–731.
Richardson, G. E. (2002). The metatheory of resilience and resiliency. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 58(3), 307–321.
Richardson, G. E., & Waite, P. J. (2001). Mental health promotion through resilience and resiliency education. International Journal of Emergency Mental Health, 4(1), 65–75.
Ruisoto, P., & Contador, I. (2019). The role of stress in drug addiction: An integrative review. Physiology & Behavior, 202, 62–68.
Schiffrin, H. H., & Nelson, S. K. (2010). Stressed and happy? Investigating the relationship between happiness and perceived stress. Journal of Happiness Studies, 11, 33–39.
Sherman, S. G., German, D., Sirirojn, B., Thompson, N., Aramrattana, A., & Celentano, D. D. (2008). Initiation of methamphetamine use among young Thai drug users: A qualitative study. Journal of Adolescent Health, 42, 36–42.
Sinha, R. (2008). Chronic stress, drug use, and vulnerability to addiction. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1141, 105–130.
Southwick, S. M., & Charney, D. S. (2012). The science of resilience: Implications for the prevention and treatment of depression. Science, 338, 79–82.
Stoia-Caraballo, R., Rye, M. S., Pan, W., Kirschman, K. J. B., Lutz-Zois, C., & Lyons, A. M. (2008). Negative affect and anger rumination as mediators between forgiveness and sleep quality. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 31, 478–488.
Tang, J., Liao, Y., He, H., Deng, Q., Zhang, G., Qi, C., et al. (2015). Sleeping problems in Chinese illicit drug dependent subjects. BMC Psychiatry, 15, 28.
Tang, Y.-L., & Hao, W. (2007). Improving drug addiction treatment in China. Addiction, 102, 1057–1063.
Thomsen, D. K., Mehlsen, M. Y., Christensen, S., & Zachariae, R. (2003). Rumination–relationship with negative mood and sleep quality. Personality and Individual Differences, 34, 1293–1301.
Tournous, N. L., & Bagwell-Adams, G. (2016). The association of stress with anxiety and depression: Evidence from a community health needs assessment. Journal of the Georgia Public Health Association, 6, 236–245.
van Boekel, L. C., Brouwers, E. P. M., van Weeghel, J., & Garretsen, H. F. L. (2013). Stigma among health professionals towards patients with substance use disorders and its consequences for healthcare delivery: Systematic review. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 131, 23–35.
WHO. (2017). World drug report. New York: UN. https://doi.org/10.18356/c595e10f-en.
Wong, M. M., Brower, K. J., Fitzgerald, H. E., & Zucker, R. A. (2004). Sleep problems in early childhood and early onset of alcohol and other drug use in adolescence. Alcoholism-Clinical and Experimental Research, 28(4), 578–587.
Yang, J., Ling, Y., Xiao, J., & Yao, S. Q. (2009). The Chinese version of ruminative responses scale in high school students: Its reliability and validity. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 17(1), 27–28.
Yang, M., Mamy, J., Gao, P., & Xiao, S. (2015). From abstinence to relapse: A preliminary qualitative study of drug users in a compulsory drug rehabilitation center in Changsha, China. PLoS One, 10(6), e0130711.
Zoccola, P. M., Dickerson, S. S., & Lam, S. (2009). Rumination predicts longer sleep onset latency after an acute psychosocial stressor. Psychosomatic Medicine, 71, 771–775.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Ms. Xuemeng Li from the City University of New York for consulting during the preparation of the article.
Funding
Funding was provided by The National Social Science Fund of the People’s Republic of China (19BSH029), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018 M632285), Postdoctoral Research Funding Program of Jiangsu Province (1701078C), and the Jiangsu Province Social Science Fund Project (18SHC006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Cao, Q. Perceived Stress and Sleep Quality among Chinese Drug Users: Analysis of Rumination as a Mediator and Resilience as a Moderator. Int J Ment Health Addiction 20, 569–580 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-020-00388-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-020-00388-9