Abstract
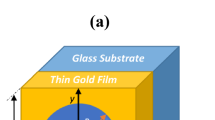
We report on the novel fabrication and characterisation of plasmonic arrays of elliptical nanohole, and their use for refractive index based sensing. The substrates were fabricated using nanoimprint lithography into a chromium hard mask followed by transfer of the patterns into the underlying gold layer by dry etching—a combination of processes amendable to mass manufacturing. 3D-FDTD simulations were undertaken and showed the transmission spectrum was dependant upon the polarisation of the incident light, with a series of minima that can be attributed to plasmonic effects on the gold/water or gold/substrate interfaces. Each polarisation showed two peaks on the gold/water interface, one in the visible and one in the near-infrared part of the spectrum. Simulated electric field profiles showed that the electric field in the infrared propagates deep in the bulk while the one in the visible was more tightly bound to the surface. Experimental transmission spectra of the fabricated samples showed good agreement with the simulated ones. Bulk refractive index experiments were carried out and sensitivities of 293 nm/RIU and 414 nm/RIU were obtained for the two spectral features of interest when the polarisation was along the long axis of the elliptical nanohole for the visible and infrared features, respectively, and 293 nm/RIU and 323 nm/RIU measured when the polarisation was along the short axis of the nanohole.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebbesen TW, Lezec HJ, Ghaemi HF, Thio T, Wolff PA (1998) Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays. Nature 391:667–669
Blanchard-Dionne A-P, Meunier M (2017) Sensing with periodic nanohole arrays. Adv Opt Photon 9(4):891–940
Escobedo C (2013) On-chip nanohole array based sensing: a review. Lab Chip 13(13):2445–2463
Lovera P, Creedon N, Alatawi H, Mitchell M, Burke M, Quinn AJ, O’Riordan A (2014) Low-cost silver capped polystyrene nanotube arrays as super-hydrophobic substrates for SERS applications. Nanotechnology 25(17):175502
Wong CL, Olivo M (2014) Surface plasmon resonance imaging sensors: a review. Plasmonics 9(4):809–824
Brolo AG, Gordon R, Leathem B, Kavanagh KL (2004) Surface plasmon sensor based on the enhanced light transmission through arrays of nanoholes in gold films. Langmuir 20(12):4813–4815
Wright JB, Cicotte KN, Subramania G, Dirk SM, Brener I (2012) Chemoselective gas sensors based on plasmonic nanohole arrays. Opt Mater Express 2(11):1655–1662
Lindquist NC, Turner MA, Heppner BP (2014) Template fabricated plasmonic nanoholes on analyte-sensitive substrates for real-time vapor sensing. RSC Adv 4(29):15115–15121
Le AP et al (2012) Functional nanoimprinted plasmonic crystals for chemical sensing and imaging. In: Dmitriev A (ed) Nanoplasmonic sensors, pp 199–227
Chuo Y, Hohertz D, Landrock C, Omrane B, Kavanagh KL, Kaminska B (2013) Large-area low-cost flexible plastic nanohole arrays for integrated bio-chemical sensing. IEEE Sensors J 13(10):3982–3990
Barrios CA, Canalejas-Tejero V, Herranz S, Moreno-Bondi MC, Avella-Oliver M, Puchades R, Maquieira A (2014) Aluminum nanohole arrays fabricated on polycarbonate for compact disc-based label-free optical biosensing. Plasmonics 9(3):645–649
Bottazzi B, Fornasari L, Frangolho A, Giudicatti S, Mantovani A, Marabelli F, Marchesini G, Pellacani P, Therisod R, Valsesia A (2014) Multiplexed label-free optical biosensor for medical diagnostics. J Biomed Opt 19(1):017006
Im H, Shao H, Park YI, Peterson VM, Castro CM, Weissleder R, Lee H (2014) Label-free detection and molecular profiling of exosomes with a nano-plasmonic sensor. Nat Biotechnol 32(5):490–U219
Cetin AE, Etezadi D, Galarreta BC, Busson MP, Eksioglu Y, Altug H (2015) Plasmonic nanohole arrays on a robust hybrid substrate for highly sensitive label-free biosensing. Acs Photonics 2(8):1167–1174
Ding T et al (2015) Quantification of a cardiac biomarker in human serum using extraordinary optical transmission (EOT). PLoS One 10(3)
Li X, Soler M, Özdemir CI, Belushkin A, Yesilköy F, Altug H (2017) Plasmonic nanohole array biosensor for label-free and real-time analysis of live cell secretion. Lab Chip 17(13):2208–2217
Cetin AE, Iyidogan P, Hayashi Y, Wallen M, Vijayan K, Tu E, Nguyen M, Oliphant A (2018) Plasmonic sensor could enable label-free DNA sequencing. Acs Sensors 3(3):561–568
Soler M, Belushkin A, Cavallini A, Kebbi-Beghdadi C, Greub G, Altug H (2017) Multiplexed nanoplasmonic biosensor for one-step simultaneous detection of Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae in urine. Biosens Bioelectron 94:560–567
Yanik AA, Cetin AE, Huang M, Artar A, Mousavi SH, Khanikaev A, Connor JH, Shvets G, Altug H (2011) Seeing protein monolayers with naked eye through plasmonic Fano resonances. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(29):11784–11789
Gordon R, Sinton D, Kavanagh KL, Brolo AG (2008) A new generation of sensors based on extraordinary optical transmission. Acc Chem Res 41(8):1049–1057
Yanik AA, Huang M, Kamohara O, Artar A, Geisbert TW, Connor JH, Altug H (2010) An optofluidic nanoplasmonic biosensor for direct detection of live viruses from biological media. Nano Lett 10(12):4962–4969
Niu LF et al (2015) Integrating plasmonic diagnostics and microfluidics. Biomicrofluidics 9(5):052611
Monteiro JP, de Oliveira JH, Radovanovic E, Brolo AG, Girotto EM (2016) Microfluidic plasmonic biosensor for breast cancer antigen detection. Plasmonics 11(1):45–51
Escobedo C, Brolo AG, Gordon R, Sinton D (2010) Flow-through vs flow-over: analysis of transport and binding in nanohole array plasmonic biosensors. Anal Chem 82(24):10015–10020
Zehtabi-Oskuie A, Bergeron JG, Gordon R (2012) Flow-dependent double-nanohole optical trapping of 20 nm polystyrene nanospheres. Sci Rep 2:966
Yoshikawa T, Tamura M, Tokonami S, Iida T (2017) Optical trap-mediated high-sensitivity nanohole array biosensors with random nanospikes. J Phys Chem Lett 8(2):370–374
Atighilorestani M, dos Santos DP, Jaimes RFVV, Rahman MM, Temperini MLA, Brolo AG (2016) Electrochemical control of light transmission through nanohole electrode arrays. ACS Photonics 3(12):2375–2382
Galvan DD, Špačková B, Slabý J, Sun F, Ho YH, Homola J, Yu Q (2016) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering on gold nanohole arrays in symmetrical dielectric environments exhibiting electric field extension. J Phys Chem C 120(44):25519–25529
Zheng P, Cushing SK, Suri S, Wu N (2015) Tailoring plasmonic properties of gold nanohole arrays for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17(33):21211–21219
Lee SH, Bantz KC, Lindquist NC, Oh SH, Haynes CL (2009) Self-assembled plasmonic nanohole arrays. Langmuir 25(23):13685–13693
Brolo AG, Arctander E, Gordon R, Leathem B, Kavanagh KL (2004) Nanohole-enhanced Raman scattering. Nano Lett 4(10):2015–2018
Skehan C, Ai B, Larson SR, Stone KM, Dennis WM, Zhao Y (2018) Plasmonic and SERS performances of compound nanohole arrays fabricated by shadow sphere lithography. Nanotechnology 29(9):095301
Yesilkoy F et al (2018) Phase-sensitive plasmonic biosensor using a portable and large field-of-view interferometric microarray imager. Light-Sci Appl:7
Coskun AF et al (2014) Lensfree optofluidic plasmonic sensor for real-time and label-free monitoring of molecular binding events over a wide field-of-view. Sci Rep 4
Cetin AE et al (2014) Handheld high-throughput plasmonic biosensor using computational on-chip imaging. Light-Sci Appl:3
Guyot L, Blanchard-Dionne AP, Patskovsky S, Meunier M (2011) Integrated silicon-based nanoplasmonic sensor. Opt Express 19(10):9962–9967
Seiler ST, Rich IS, Lindquist NC (2016) Direct spectral imaging of plasmonic nanohole arrays for real-time sensing. Nanotechnology 27(18):184001
Blanchard-Dionne AP, Guyot L, Patskovsky S, Gordon R, Meunier M (2011) Intensity based surface plasmon resonance sensor using a nanohole rectangular array. Opt Express 19(16):15041–15046
Lesuffleur A, Im H, Lindquist NC, Oh SH (2007) Periodic nanohole arrays with shape-enhanced plasmon resonance as real-time biosensors. Appl Phys Lett 90(24):243110
Gordon R, Brolo AG, McKinnon A, Rajora A, Leathem B, Kavanagh KL (2004) Strong polarization in the optical transmission through elliptical nanohole arrays. Phys Rev Lett 92(3)
Tellez GAC et al (2013) Atomically flat symmetric elliptical nanohole arrays in a gold film for ultrasensitive refractive index sensing. Lab Chip 13(13):2541–2546
Ai B, Basnet P, Larson S, Ingram W, Zhao Y (2017) Plasmonic sensor with high figure of merit based on differential polarization spectra of elliptical nanohole array. Nanoscale 9(38):14710–14721
Nishiguchi K, Sueyoshi K, Hisamoto H, Endo T (2016) Fabrication of gold-deposited plasmonic crystal based on nanoimprint lithography for label-free biosensing application. Jpn J Appl Phys 55(8):08RE02
Mona JKK et al (2010) Inexpensive and fast wafer-scale fabrication of nanohole arrays in thin gold films for plasmonics. Nanotechnology 21(20):205301
Md Nazmul H et al (2014) High aspect ratio nano-fabrication of photonic crystal structures on glass wafers using chrome as hard mask. Nanotechnology 25(35):355301
JDFTD3D, www.thecomputationalphysicist.com
Lovera P, Jones D, Corbett B, O’Riordan A (2012) Polarization tunable transmission through plasmonic arrays of elliptical nanopores. Opt Express 20(23):25325–25332
Ghaemi HF, Thio T, Grupp DE, Ebbesen TW, Lezec HJ (1998) Surface plasmons enhance optical transmission through subwavelength holes. Phys Rev B 58(11):6779–6782
Gao H, Henzie J, Odom TW (2006) Direct evidence for surface plasmon-mediated enhanced light transmission through metallic nanohole arrays. Nano Lett 6(9):2104–2108
Chang S-H, Gray SK, Schatz GC (2005) Surface plasmon generation and light transmission by isolated nanoholes and arrays of nanoholes in thin metal films. Opt Express 13(8):3150–3165
Hossain MN, Justice J, Lovera P, O’Riordan A, Corbett B (2014) Dual resonance approach to decoupling surface and bulk attributes in photonic crystal biosensor. Opt Lett 39(21):6213–6216
Funding
This work was supported by the EU-funded project Phast-ID (FP7-ICT-2009-5-258238) and the EPA project UisceSense (2015-W-MS-21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, C., Justice, J., Petäjä, J. et al. Nanoimprint Lithography–Based Fabrication of Plasmonic Array of Elliptical Nanoholes for Dual-Wavelength, Dual-Polarisation Refractive Index Sensing. Plasmonics 14, 951–959 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-018-0879-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-018-0879-z