Abstract
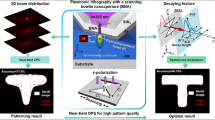
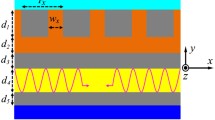
Surface plasmon lithography is potentially an alternative technique for high resolution patterning. However, implementation involves high cost and challenging fabrication steps. Here, we report nano-patterning assisted by surface plasmons with a perfectly contacted mask using colloidal lithography. A nano-scaled aluminum mask was fabricated using closed packed polystyrene spheres with a simple, fast, and low-cost method, and the loss of surface plasmon waves was reduced by the perfect contact between the mask and the photoresist. A photoresist pattern of two-dimensional hexagonal annular ring arrays was produced by illuminating light of 436 nm wavelength, and the width of the obtained annular ring was approximately λ/6. The simulation results showed that the proposed structure had a sufficiently high contrast value for lithography, and the fabrication patterns and the simulation results presented good agreement.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ito T, Okazaki S (2000) Pushing the limits of lithography. Nature 406(6799):1027–1031
Choksi N, Pickard DS, McCord M, Pease RFW, Shroff Y, Chen Y, Oldham W, Markle D (1999) Maskless extreme ultraviolet lithography. J Vac Sci Technol B Microelectron Nanometer Struct 17(6):3047. doi:10.1116/1.590952
Vieu C, Carcenac F, Pépin A, Chen Y, Mejias M, Lebib A, Manin-Ferlazzo L, Couraud L, Launois H (2000) Electron beam lithography: resolution limits and applications. Appl Surf Sci 164(1–4):111–117. doi:10.1016/S0169-4332(00)00352-4
Steve R, Robert P (2001) A review of focused ion beam applications in microsystem technology. J Micromech Microeng 11(4):287
Ouk Kim S, Solak HH, Stoykovich MP, Ferrier NJ, de Pablo JJ, Nealey PF (2003) Epitaxial self-assembly of block copolymers on lithographically defined nanopatterned substrates. Nature 424(6947):411–414
Black CT (2007) Polymer self-assembly as a novel extension to optical lithography. ACS Nano 1(3):147–150. doi:10.1021/nn7002663
Maier SA (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and applications. Springer, US
Xiong W, Du J, Fang L, Luo X, Deng Q, Du C (2008) 193 nm interference nanolithography based on SPP. Microelectron Eng 85(5–6):754–757. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2008.01.057
Sreekanth KV, Murukeshan VM (2010) Effect of metals on UV-excited plasmonic lithography for sub-50 nm periodic feature fabrication. Applied Physics A 101(1):117–120. doi:10.1007/s00339-010-5769-y
Guo X, Du J, Guo Y, Yao J (2006) Large-area surface-plasmon polariton interference lithography. Opt Lett 31(17):2613–2615. doi:10.1364/ol.31.002613
Luo X, Ishihara T (2004) Surface plasmon resonant interference nanolithography technique. Appl Phys Lett 84(23):4780. doi:10.1063/1.1760221
Srituravanich W, Fang N, Durant S, Ambati M, Sun C, Zhang X (2004) Sub-100 nm lithography using ultrashort wavelength of surface plasmons. J Vac Sci Technol B 22(6):3475–3478. doi:10.1116/1.1823437
Srituravanich W, Fang N, Sun C, Luo Q, Zhang X (2004) Plasmonic nanolithography. Nano Lett 4(6):1085–1088. doi:10.1021/nl049573q
Blaikie RJ, McNab SJ (2001) Evanescent interferometric lithography. Appl Opt 40(10):1692–1698. doi:10.1364/AO.40.001692
Dong J, Liu J, Kang G, Xie J, Wang Y (2014) Pushing the resolution of photolithography down to 15nm by surface plasmon interference. Sci Rep 4:5618. doi:10.1038/srep05618
Fan Y, Xi C, Eun-Hyoung C, Chang Seung L, Peng J, Guo LJ (2015) Period reduction lithography in normal UV range with surface plasmon polaritons interference and hyperbolic metamaterial multilayer structure. Appl Phys Express 8(6):062004
Gao P, Yao N, Wang C, Zhao Z, Luo Y, Wang Y, Gao G, Liu K, Zhao C, Luo X (2015) Enhancing aspect profile of half-pitch 32 nm and 22 nm lithography with plasmonic cavity lens. Appl Phys Lett 106(9):093110. doi:10.1063/1.4914000
Prabhathan P, Murukeshan VM (2015) Dielectric supported bimetal layer configuration for long-range surface plasmon polariton interference-based subwavelength lithography. Opt Eng 54(9):097107–097107. doi:10.1117/1.OE.54.9.097107
Luo X, Ishihara T (2004) Subwavelength photolithography based on surface-plasmon polariton resonance. Opt Express 12(14):3055–3065. doi:10.1364/OPEX.12.003055
Wei X, Luo X, Dong X, Du C (2007) Localized surface plasmon nanolithography with ultrahigh resolution. Opt Express 15(21):14177–14183. doi:10.1364/OE.15.014177
Doskolovich LL, Kadomina EA, Kadomin II (2007) Nanoscale photolithography by means of surface plasmon interference. J Opt A Pure Appl Opt 9(10):854
Mehrotra P, Mack CA, Blaikie RJ (2013) A detailed study of resonance-assisted evanescent interference lithography to create high aspect ratio, super-resolved structures. Opt Express 21(11):13710–13725. doi:10.1364/OE.21.013710
Palik ED (1998) Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids: Index, vol 3. Access Online via Elsevier
Ctistis G, Papaioannou E, Patoka P, Gutek J, Fumagalli P, Giersig M (2008) Optical and magnetic properties of hexagonal arrays of subwavelength holes in optically thin cobalt films. Nano Lett 9(1):1–6. doi:10.1021/nl801811t
Ctistis G, Patoka P, Wang X, Kempa K, Giersig M (2007) Optical transmission through hexagonal arrays of subwavelength holes in thin metal films. Nano Lett 7(9):2926–2930. doi:10.1021/nl0712973
Goodberlet JG, Kavak H (2002) Patterning sub-50 nm features with near-field embedded-amplitude masks. Appl Phys Lett 81(7):1315–1317. doi:10.1063/1.1495538
Yang X, Zeng B, Wang C, Luo X (2009) Breaking the feature sizes down to sub-22 nm by plasmonic interference lithography using dielectric-metal multilayer. Opt Express 17(24):21560–21565. doi:10.1364/OE.17.021560
Lee E, Hahn JW (2008) The effect of photoresist contrast on the exposure profiles obtained with evanescent fields of nanoapertures. J Appl Phys 103(8):083550. doi:10.1063/1.2907971
Meliorisz B, Partel S, Schnattinger T, Fühner T, Erdmann A, Hudek P (2008) Investigation of high-resolution contact printing. Microelectron Eng 85(5–6):744–748. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2007.12.012
Lee S, Teshima K, Fujisawa M, Fujii S, Endo M, Oishi S (2009) Fabrication of highly ordered, macroporous Na2W4O13 arrays by spray pyrolysis using polystyrene colloidal crystals as templates. Phys Chem Chem Phys 11(19):3628–3633. doi:10.1039/B821209K
Darling SB (2007) Directing the self-assembly of block copolymers. Prog Polym Sci 32(10):1152–1204. doi:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2007.05.004
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean Government (MSIP) (No. NRF-2014R1A2A2A01005770).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 758 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, E.S., Kim, Y.M. & Choi, K.C. Surface plasmon-assisted nano-lithography with a perfect contact aluminum mask of a hexagonal dot array. Plasmonics 11, 1337–1342 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0180-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0180-y