Abstract
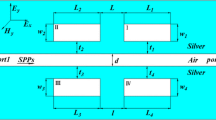
Dynamically tunable multichannel filter based on plasmon-induced transparencies (PITs) is proposed in a plasmonic waveguide side-coupled to slot and rectangle resonators system at optical communication range. The slot and rectangle resonators in this system can be regarded as radiative or dark resonators as same as the radiative or dark elements in the metamaterial structure with the help of the evanescent coupling. The multiple PIT responses which can enable the realization of nanoscale filter with four channels are originated from the direct near-field coupling and indirect phase couple through a plasmonic waveguide simultaneously. Moreover, the magnitudes and bandwidths of the filter can be efficiently tuned by controlling of the geometric parameters such as the coupling distances and the pump light-induced refractive index change of the Kerr material which is embedded into the metal-dielectric-metal waveguide between the radiative resonators.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pitarke JM, Silkin VM, Chulkov EV, Echenique PM (2007) Theory of surface plasmons and surface-plasmon polaritons. Rep Prog Phys 70:1–87
Gramotnev DK, Bozhevolnyi SI (2010) Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit. Nat Photonics 4:83–91
Yun B, Hu G, Cui Y (2010) Theoretical analysis of a nanoscale plasmonic filter based on a rectangular metal-insulator-metal waveguide. J Phys D Appl Phys 43:385102
Yun B, Hu G, Cui Y (2013) Resonant mode analysis of the nanoscale surface plasmon polaritons waveguide filter with rectangle cavity. Plasmonics 8:267–275
Wen K, Yan L, Pan W, Luo B, Guo Z, Guo Y, Luo X (2013) Design of plasmonic comb-like filters using loop-based resonators. Plasmonics 8:1017–1022
Lu H, Liu X, Mao D, Wang L, Gong Y (2010) Tunable band-pass plasmonic waveguide filters with nanodisk resonators. Opt Express 18:17922–17927
Setayesh A, Mirnaziry SR, Abrishamian MS (2011) Numerical investigation of a tunable band-pass plasmonics filter with a hollow-core ring resonator. J Opt 13:035004
Lu H, Liu X, Wang G, Mao D (2011) Tunable high-channel-count bandpass plasmonic filters based on an analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency. Nanotechnology 23:444003
Zhou X, Zhou L (2012) Analysis of subwavelength bandpass plasmonic filters based on single and coupled slot nanocavities. Appl Opt 52:480–488
Zhang Z, Shi F, Chen Y (2015) Tunable multichannel plasmonic filter based on coulpling-induced mode splitting. Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s11468-014-9787-z
Zheng G, Su W, Chen Y, Zhang C, Lai M, Liu Y (2012) Band-stop filters based on a coupled circular ring metal-insulator-metal resonator containing nonlinear material. J Opt 14:055001
Peng X, Li H, Wu C, Cao G, Liu Z (2013) Research on transmission characteristics of aperture-coupled square-ring resonator based filters. Opt Commun 294:368–371
Zand I, Mahigir A, Pakizeh T, Abrishamian MS (2012) Selective-mode optical nanofilters based on plasmonic complementary split-ring resonators. Opt Express 20:7516–7525
Ma F, Lee C (2013) Optical nanofilters based on meta-atom side-coupled plasmonics metal-insulator-metal waveguide. J Lightwave Technol 31:2876–2880
Zhang H, Shen D, Zhang Y (2014) Circular split-ring core resonators used in nanoscale metal-insulator-metal band-stop filters. Laser Phys Lett 11:115902
Wang G, Lu H, Liu X, Mao D, Duan L (2011) Tunable multi-channel wavelength demultiplexer based on MIM plasmonic nanodisk resonators at telecommunication regime. Opt Express 19:3513–3518
Pu M, Yao N, Hu C, Xin X, Zhao Z, Wang C, Luo X (2010) Directional coupler and nonlinear Mach-Zehnder interferometer based on metal-insulator-metal plasmonic waveguide. Opt Express 18:21030–21037
Lu H, Liu X, Wang L, Gong Y, Mao D (2011) Ultrafast all-optical switching in nanoplasmonic waveguide with Kerr nonlinear resonator. Opt Express 19:2910–2914
Wen K, Hu Y, Chen L, Zhou J, Lei L, Guo Z (2015) Fano resonance with ultra-high figure of merits based on plasmonic metal-insulator-metal waveguide. Plasmonics 10:27–32
Bian Y, Gong Q (2014) Compact all-optical interferometric logic gates based on one-dimensional meal-insulator-metal structures. Opt Commun 313:27–35
Cao G, Li H, Deng Y, Zhang S, He Z, Li B (2014) Systematic theoretical analysis of selective-mode plasmonic filter based on aperture-side-coupled slot cavity. Plasmonics 9:1163–1169
Yang X, Hu X, Chai Z, Lu C, Yang H, Gong Q (2014) Tunable ultracompact chip-integrated multichannel filter based on plasmon-induced transparencies. Appl Phys Lett 104:221114
Chen J, Wang C, Zhang R, He S, Xiao J (2012) Multiple plasmon-induced transparencies in coupled-resonator system. Opt Lett 37:5133–5135
Han X, Wang T, Wang B, Liu B, He Y, Zhu Y (2015) Low-power and ultrafast all-optical tunable plasmon induced transparency in metal-dielectric-metal waveguide side-coupled Fabry-Perot resonators system. J Appl Phys 117:103105
Han X, Wang T, Li X, Liu B, He Y, Tang J (2015) Dynamically tunable slow light on plasmon induced transparency in disk resonators coupled MDM waveguide system (2015). J Phys D Appl Phys 48:235102
Zhang Z, Zhang L, Li H, Chen H (2014) Plasmon induced transparency in a surface plasmon polariton waveguide with a comb line slot and rectangele cavity. Appl Phys Lett 104:231114
Wang T, Zhang Y, Hong Z, Han Z (2014) Analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency in integrated plasmonics with radiative and subradiant resonators. Opt Express 22:21529–21534
Xia X, Wang J, Zhang F, Hu Z, Liu C, Yan X, Yuan L (2015) Multi-mode plasmonically induced transparency in dual coupled graphene-integrated ring resonators. Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s11468-015-9955-9
Kim M, Lee S, Kim S (2015) Plasmon-induced transparency in coupled graphene gratings. Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s11468-015-9965-7
Zhu Y, Hu X, Yang H, Gong Q (2014) On-chip plasmon-induced transparency based on plasmonic coupled nanocavities. Sci Rep 4:3752
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61376055 and 61006045), and the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2010CB923204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, X., Wang, T., Li, X. et al. Dynamically Tunable by Kerr Effect Multichannel Filter Based on Plasmon Induced Transparencies at Optical Communication Range. Plasmonics 11, 729–733 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0102-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0102-4