Abstract
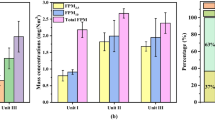
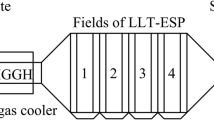
Measurements of the characteristics of particulate matter (PM) were performed at the inlet and outlet of the electrostatic precipitators (ESP) of four boilers in two full-scale pulverized coal power plants. PM was collected with a 13-stages low-pressure-impactor (LPI) having aerodynamic cut-off diameter ranging from 10.0 to 0.03 μm for a size-segregated collection. The properties of PM including its concentration, mass size distribution, emission characteristics, percent penetration of PM through ESP and elemental composition were investigated. The experimental results indicate that, in all the cases the mass size distribution of PM10 had typical bimodal. PM1 contained up to 1.15 wt% of the total particle (TP) generated in the boilers. PM2.5 contained about 2 wt%–7 wt% of the TP and PM10 contained about 4 wt%–19 wt% of the TP. When additive limestone used for desulphurization as sorbent besides PM generated from coal combustion, there was new PM generated from limestone. Penetration as a function of particle diameter had a clear peak in particle size ranging from 0.2 to 0.6 μm. Particles in the submicrometer size range were much more difficult to be collected with ESP than larger particles. Distributions of individual elements within PM10 were different.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McElroy M W, Carr R C, Ensor D S, et al. Size distribution of fine particles from coal combustion. Science, 1982, 215(4528): 13–19
Mohr M, Ylatalo S, Klippel N, et al. Submicron fly ash penetration through electrostatic precipitators at two coal power plants. Aerosol Sci Tech, 1996, 24(3): 191–204
Flagan R C, Taylor D D. Laboratory studies of submicron particles from coal combustion. P combust Inst, 1981, 18(1): 1227–1237
Quann R J, Sarofim A F. Vaporization of refractory oxides during pulverized coal combustion. P combust Inst, 1982, 19(1): 1429–1440
Buhre B J P, Hinkley J T, Gupta R P, et al. Submicron ash formation from coal combustion. Fuel, 2005, 84(10): 1206–1214
Lockwood F C, Yousif S. A model for the particulate matter enrichment with toxic metals in solid fuel flames. Fuel Process Tech, 2000, 65–66(6): 439–457
Zhang L A, Ninomiya Y, Yamashita T. Formation of submicron particulate matter (PM1) during coal combustion and influence of reaction temperature. Fuel, 2006, 85(10–11): 1446–1457
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 50720145604, 50721005, 90610017), the Programme of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities of China (“111” Project) (Grant No. B06019)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Xu, M., Yao, H. et al. Characteristics and composition of particulate matter from coal-fired power plants. Sci. China Ser. E-Technol. Sci. 52, 1521–1526 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-009-0174-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-009-0174-5