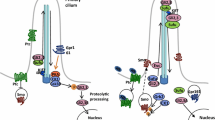
Abstract
The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling is one of the essential signaling pathways during embryogenesis and in adults. Hh signal transduction relies on primary cilium, a specialized cell surface organelle viewed as the hub of cell signaling. Protein kinase A (PKA) has been recognized as a potent negative regulator of the Hh pathway, raising the question of how such a ubiquitous kinase specifically regulates one signaling pathway. We reviewed recent genetic, molecular and biochemical studies that have advanced our mechanistic understanding of PKA’s role in Hh signaling in vertebrates, focusing on the compartmentalized PKA at the centrosome and in the primary cilium. We outlined the recently developed genetic and optical tools that can be harvested to study PKA activities during the course of Hh signal transduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, M.D., and Zhang, J. (2006). Subcellular dynamics of protein kinase A activity visualized by FRET-based reporters. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348, 716–721.
Arveseth, C.D., Happ, J.T., Hedeen, D.S., Zhu, J.F., Capener, J.L., Klatt Shaw, D., Deshpande, I., Liang, J., Xu, J., Stubben, S.L., et al. (2021). Smoothened transduces hedgehog signals via activity-dependent sequestration of PKA catalytic subunits. PLoS Biol 19, e3001191.
Ayers, K.L., and Thérond, P.P. (2010). Evaluating Smoothened as a G-protein-coupled receptor for Hedgehog signalling. Trends Cell Biol 20, 287–298.
Bachmann, V.A., Mayrhofer, J.E., Ilouz, R., Tschaikner, P., Raffeiner, P., Röck, R., Courcelles, M., Apelt, F., Lu, T.W., Baillie, G.S., et al. (2016). Gpr161 anchoring of PKA consolidates GPCR and cAMP signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 7786–7791.
Badgandi, H.B., Hwang, S.H., Shimada, I.S., Loriot, E., and Mukhopadhyay, S. (2017). Tubby family proteins are adapters for ciliary trafficking of integral membrane proteins. J Cell Biol 216, 743–760.
Bai, C.B., Auerbach, W., Lee, J.S., Stephen, D., and Joyner, A.L. (2002). Gli2, but not Gli1, is required for initial Shh signaling and ectopic activation of the Shh pathway. Development 129, 4753–4761.
Bai, C.B., and Joyner, A.L. (2001). Gli1 can rescue the in vivo function of Gli2. Development 128, 5161–5172.
Baillie, G.S., Scott, J.D., and Houslay, M.D. (2005). Compartmentalisation of phosphodiesterases and protein kinase A: Opposites attract. FEBS Lett 579, 3264–3270.
Bangs, F., and Anderson, K.V. (2017). Primary cilia and mammalian Hedgehog signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 9, a028175.
Barr, M.M., and Sternberg, P.W. (1999). A polycystic kidney-disease gene homologue required for male mating behaviour in C. elegans. Nature 401, 386–389.
Barzi, M., Berenguer, J., Menendez, A., Alvarez-Rodriguez, R., and Pons, S. (2010). Sonic-hedgehog-mediated proliferation requires the localization of PKA to the cilium base. J Cell Sci 123, 62–69.
Basto, R., Lau, J., Vinogradova, T., Gardiol, A., Woods, C.G., Khodjakov, A., and Raff, J.W. (2006). Flies without centrioles. Cell 125, 1375–1386.
Beavo, J.A., and Brunton, L.L. (2002). Cyclic nucleotide research–still expanding after half a century. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3, 710–717.
Bitgood, M.J., and McMahon, A.P. (1995). Hedgehog and Bmp genes are coexpressed at many diverse sites of cell-cell interaction in the mouse embryo. Dev Biol 172, 126–138.
Cadd, G., and McKnight, G.S. (1989). Distinct patterns of cAMP-dependent protein kinase gene expression in mouse brain. Neuron 3, 71–79.
Chen, M.H., Wilson, C.W., Li, Y.J., Law, K.K.L., Lu, C.S., Gacayan, R., Zhang, X., Hui, C., and Chuang, P.T. (2009). Cilium-independent regulation of Gli protein function by SuFu in Hedgehog signaling is evolutionarily conserved. Genes Dev 23, 1910–1928.
Cheung, H.O.L., Zhang, X., Ribeiro, A., Mo, R., Makino, S., Puviindran, V., Law, K.K.L., Briscoe, J., and Hui, C.C. (2009). The kinesin protein Kif7 is a critical regulator of Gli transcription factors in mammalian Hedgehog signaling. Sci Signal 2, ra29.
Choi, Y.H., Suzuki, A., Hajarnis, S., Ma, Z., Chapin, H.C., Caplan, M.J., Pontoglio, M., Somlo, S., and Igarashi, P. (2011). Polycystin-2 and phosphodiesterase 4C are components of a ciliary A-kinase anchoring protein complex that is disrupted in cystic kidney diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108, 10679–10684.
Concordet, J.P., Lewis, K.E., Moore, J.W., Goodrich, L.V., Johnson, R.L., Scott, M.P., and Ingham, P.W. (1996). Spatial regulation of a zebrafish patched homologue reflects the roles of sonic hedgehog and protein kinase A in neural tube and somite patterning. Development 122, 2835–2846.
Cooper, A.F., Yu, K.P., Brueckner, M., Brailey, L.L., Johnson, L., McGrath, J.M., and Bale, A.E. (2005). Cardiac and CNS defects in a mouse with targeted disruption of suppressor of fused. Development 132, 4407–4417.
Corcoran, R.B., and Scott, M.P. (2006). Oxysterols stimulate Sonic hedgehog signal transduction and proliferation of medulloblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 8408–8413.
Dahmane, N., and Ruiz-i-Altaba, A. (1999). Sonic hedgehog regulates the growth and patterning of the cerebellum. Development 126, 3089–3100.
DeCaen, P.G., Delling, M., Vien, T.N., and Clapham, D.E. (2013). Direct recording and molecular identification of the calcium channel of primary cilia. Nature 504, 315–318.
DeCamp, D.L., Thompson, T.M., de Sauvage, F.J., and Lerner, M.R. (2000). Smoothened activates Gαi-mediated signaling in frog melanophores. J Biol Chem 275, 26322–26327.
Delling, M., DeCaen, P.G., Doerner, J.F., Febvay, S., and Clapham, D.E. (2013). Primary cilia are specialized calcium signalling organelles. Nature 504, 311–314.
Deshpande, I., Liang, J., Hedeen, D., Roberts, K.J., Zhang, Y., Ha, B., Latorraca, N.R., Faust, B., Dror, R.O., Beachy, P.A., et al. (2019). Smoothened stimulation by membrane sterols drives Hedgehog pathway activity. Nature 571, 284–288.
Ding, Q., Motoyama, J., Gasca, S., Mo, R., Sasaki, H., Rossant, J., and Hui, C.C. (1998). Diminished Sonic hedgehog signaling and lack of floor plate differentiation in Gli2 mutant mice. Development 125, 2533–2543.
Eccles, R.L., Czajkowski, M.T., Barth, C., Müller, P.M., McShane, E., Grunwald, S., Beaudette, P., Mecklenburg, N., Volkmer, R., Zühlke, K., et al. (2016). Bimodal antagonism of PKA signalling by ARHGAP36. Nat Commun 7, 12963.
Eguether, T., Cordelieres, F.P., and Pazour, G.J. (2018). Intraflagellar transport is deeply integrated in hedgehog signaling. Mol Biol Cell 29, 1178–1189.
Endoh-Yamagami, S., Evangelista, M., Wilson, D., Wen, X., Theunissen, J. W., Phamluong, K., Davis, M., Scales, S.J., Solloway, M.J., de Sauvage, F.J., et al. (2009). The mammalian Cos2 Homolog Kif7 plays an essential role in modulating Hh signal transduction during development. Curr Biol 19, 1320–1326.
Epstein, D. J., Marti, E., Scott, M.P., and McMahon, A.P. (1996). Antagonizing cAMP-dependent protein kinase A in the dorsal CNS activates a conserved Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Development 122, 2885–2894.
Fan, C.M., Porter, J.A., Chiang, C., Chang, D.T., Beachy, P.A., and Tessier-Lavigne, M. (1995). Long-range sclerotome induction by sonic hedgehog: Direct role of the amino-terminal cleavage product and modulation by the cyclic AMP signaling pathway. Cell 81, 457–465.
Fuccillo, M., Joyner, A.L., and Fishell, G. (2006). Morphogen to mitogen: The multiple roles of hedgehog signalling in vertebrate neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 7, 772–783.
Ge, X., Milenkovic, L., Suyama, K., Hartl, T., Purzner, T., Winans, A., Meyer, T., and Scott, M.P. (2015). Phosphodiesterase 4D acts downstream of Neuropilin to control Hedgehog signal transduction and the growth of medulloblastoma. eLife 4, e07068.
Goetz, S.C., and Anderson, K.V. (2010). The primary cilium: a signalling centre during vertebrate development. Nat Rev Genet 11, 331–344.
Gold, M.G., Gonen, T., and Scott, J.D. (2013). Local cAMP signaling in disease at a glance. J Cell Sci 126, 4537–4543.
Goodrich, L.V., Johnson, R.L., Milenkovic, L., McMahon, J.A., and Scott, M.P. (1996). Conservation of the hedgehog/patched signaling pathway from flies to mice: induction of a mouse patched gene by Hedgehog. Genes Dev 10, 301–312.
Goodrich, L.V., Milenković, L., Higgins, K.M., and Scott, M.P. (1997). Altered neural cell fates and medulloblastoma in mouse patched mutants. Science 277, 1109–1113.
Guthrie, C.R., Skålhegg, B.S., and McKnight, G.S. (1997). Two novel brain-specific splice variants of the murine Cβ gene of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 272, 29560–29565.
Hammerschmidt, M., Bitgood, M.J., and McMahon, A.P. (1996). Protein kinase A is a common negative regulator of Hedgehog signaling in the vertebrate embryo. Genes Dev 10, 647–658.
Hammerschmidt, M., and McMahon, A.P. (1998). The effect of pertussis toxin on zebrafish development: A possible role for inhibitory G-proteins in Hedgehog signaling. Dev Biol 194, 166–171.
Han, Y.G., Spassky, N., Romaguera-Ros, M., Garcia-Verdugo, J.M., Aguilar, A., Schneider-Maunoury, S., and Alvarez-Buylla, A. (2008). Hedgehog signaling and primary cilia are required for the formation of adult neural stem cells. Nat Neurosci 11, 277–284.
Hansen, J.N., Kaiser, F., Klausen, C., Stüven, B., Chong, R., Bönigk, W., Mick, D.U., Möglich, A., Jurisch-Yaksi, N., Schmidt, F.I., et al. (2020). Nanobody-directed targeting of optogenetic tools to study signaling in the primary cilium. eLife 9, e57907.
Haycraft, C.J., Banizs, B., Aydin-Son, Y., Zhang, Q., Michaud, E.J., and Yoder, B.K. (2005). Gli2 and Gli3 localize to cilia and require the intraflagellar transport protein polaris for processing and function. PLoS Genet preprint, e53.
Hayden Gephart, M.G., Su, Y.R.S., Bandara, S., Tsai, F.C., Hong, J., Conley, N., Rayburn, H., Milenkovic, L., Meyer, T., and Scott, M.P. (2013). Neuropilin-2 contributes to tumorigenicity in a mouse model of Hedgehog pathway medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol 115, 161–168.
Hayes, J.S., Brunton, L.L., and Mayer, S.E. (1980). Selective activation of particulate cAMP-dependent protein kinase by isoproterenol and prostaglandin E1. J Biol Chem 255, 5113–5119.
Hillman, R.T., Feng, B.Y., Ni, J., Woo, W.M., Milenkovic, L., Hayden Gephart, M.G., Teruel, M.N., Oro, A.E., Chen, J.K., and Scott, M.P. (2011). Neuropilins are positive regulators of Hedgehog signal transduction. Genes Dev 25, 2333–2346.
Houslay, M.D. (2010). Underpinning compartmentalised cAMP signalling through targeted cAMP breakdown. Trends Biochem Sci 35, 91–100.
Houslay, M.D., and Adams, D.R. (2003). PDE4 cAMP phosphodiesterases: Modular enzymes that orchestrate signalling cross-talk, desensitization and compartmentalization. Biochem J 370, 1–18.
Huang, P., Nedelcu, D., Watanabe, M., Jao, C., Kim, Y., Liu, J., and Salic, A. (2016). Cellular cholesterol directly activates smoothened in Hedgehog signaling. Cell 166, 1176–1187.e14.
Huang, P., Zheng, S., Wierbowski, B.M., Kim, Y., Nedelcu, D., Aravena, L., Liu, J., Kruse, A.C., and Salic, A. (2018). Structural basis of smoothened activation in Hedgehog signaling. Cell 174, 312–324.e16.
Huang, Y., Roelink, H., and McKnight, G.S. (2002). Protein kinase A deficiency causes axially localized neural tube defects in mice. J Biol Chem 277, 19889–19896.
Huangfu, D., Liu, A., Rakeman, A.S., Murcia, N.S., Niswander, L., and Anderson, K.V. (2003). Hedgehog signalling in the mouse requires intraflagellar transport proteins. Nature 426, 83–87.
Humke, E.W., Dorn, K.V., Milenkovic, L., Scott, M.P., and Rohatgi, R. (2010). The output of Hedgehog signaling is controlled by the dynamic association between Suppressor of Fused and the Gli proteins. Genes Dev 24, 670–682.
Hwang, S.H., White, K.A., Somatilaka, B.N., Shelton, J.M., Richardson, J. A., and Mukhopadhyay, S. (2018). The G-protein-coupled receptor Gpr161 regulates forelimb formation, limb patterning and skeletal morphogenesis in a primary cilium-dependent manner. Development 145.
Hynes, M., Porter, J.A., Chiang, C., Chang, D., Tessier-Lavigne, M., Beachy, P.A., and Rosenthal, A. (1995). Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons by Sonic hedgehog. Neuron 15, 35–44.
Ilouz, R., Lev-Ram, V., Bushong, E.A., Stiles, T.L., Friedmann-Morvinski, D., Douglas, C., Goldberg, J.L., Ellisman, M.H., and Taylor, S.S. (2017). Isoform-specific subcellular localization and function of protein kinase a identified by mosaic imaging of mouse brain. eLife 6, e17681.
Ingham, P.W. (2018). From Drosophila segmentation to human cancer therapy. Development 145.
Ishikawa, H., Thompson, J., Yates Iii, J.R., and Marshall, W.F. (2012). Proteomic analysis of mammalian primary cilia. Curr Biol 22, 414–419.
Jacob, L.S., Wu, X., Dodge, M.E., Fan, C.W., Kulak, O., Chen, B., Tang, W., Wang, B., Amatruda, J.F., and Lum, L. (2011). Genome-wide RNAi screen reveals disease-associated genes that are common to Hedgehog and Wnt signaling. Sci Signal 4, ra4.
Jiang, J., and Struhl, G. (1995). Protein kinase A and hedgehog signaling in Drosophila limb development. Cell 80, 563–572.
Johnson, R.L., Rothman, A.L., Xie, J., Goodrich, L.V., Bare, J.W., Bonifas, J.M., Quinn, A.G., Myers, R.M., Cox, D.R., Epstein Ervin H. J., et al. (1996). Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus syndrome. Science 272, 1668–1671.
Keady, B.T., Samtani, R., Tobita, K., Tsuchya, M., San Agustin, J.T., Follit, J.A., Jonassen, J.A., Subramanian, R., Lo, C.W., and Pazour, G.J. (2012). IFT25 links the signal-dependent movement of Hedgehog components to intraflagellar transport. Dev Cell 22, 940–951.
Keshwani, M.M., Klammt, C., von Daake, S., Ma, Y., Kornev, A.P., Choe, S., Insel, P.A., and Taylor, S.S. (2012). Cotranslational cis-phosphorylation of the COOH-terminal tail is a key priming step in the maturation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109, E1221–E1229.
Kim, J., Kato, M., and Beachy, P.A. (2009). Gli2 trafficking links Hedgehog-dependent activation of Smoothened in the primary cilium to transcriptional activation in the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 21666–21671.
Kong, J.H., Siebold, C., and Rohatgi, R. (2019). Biochemical mechanisms of vertebrate hedgehog signaling. Development 146.
Lechtreck, K.F. (2015). IFT-cargo interactions and protein transport in cilia. Trends Biochem Sci 40, 765–778.
Lee, R.T.H., Zhao, Z., and Ingham, P.W. (2016). Hedgehog signalling. Development 143, 367–372.
Lefkowitz, R.J., Pierce, K.L., and Luttrell, L.M. (2002). Dancing with different partners: protein kinase a phosphorylation of seven membrane-spanning receptors regulates their G protein-coupling specificity. Mol Pharmacol 62, 971–974.
Lepage, T., Cohen, S.M., Diaz-Benjumea, F.J., and Parkhurst, S.M. (1995). Signal transduction by cAMP-dependent protein kinase A in Drosophila limb patterning. Nature 373, 711–715.
Li, J., Wang, C., Wu, C., Cao, T., Xu, G., Meng, Q., and Wang, B. (2017). PKA-mediated Gli2 and Gli3 phosphorylation is inhibited by Hedgehog signaling in cilia and reduced in Talpid3 mutant. Dev Biol 429, 147–157.
Li, S., Ma, G., Wang, B., and Jiang, J. (2014). Hedgehog induces formation of PKA-smoothened complexes to promote smoothened phosphorylation and pathway activation. Sci Signal 7, ra62.
Li, S., Li, S., Han, Y., Tong, C., Wang, B., Chen, Y., and Jiang, J. (2016). Regulation of smoothened phosphorylation and high-level Hedgehog signaling activity by a plasma membrane associated kinase. PLoS Biol 14, e1002481.
Li, W., Ohlmeyer, J.T., Lane, M.E., and Kalderon, D. (1995). Function of protein kinase A in hedgehog signal transduction and Drosophila imaginal disc development. Cell 80, 553–562.
Liem, K.F., He, M., Ocbina, P.J.R., and Anderson, K.V. (2009). Mouse Kif7/Costal2 is a cilia-associated protein that regulates Sonic hedgehog signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106, 13377–13382.
Liu, J., Zeng, H., and Liu, A. (2015). The loss of Hh responsiveness by a non-ciliary Gli2 variant. Development 142, 1651–1660.
Low, W.C., Wang, C., Pan, Y., Huang, X.Y., Chen, J.K., and Wang, B. (2008). The decoupling of Smoothened from Gαi proteins has little effect on Gli3 protein processing and Hedgehog-regulated chick neural tube patterning. Dev Biol 321, 188–196.
Lynch, M.J., Hill, E.V., and Houslay, M.D. (2006). Intracellular targeting of phosphodiesterase-4 underpins compartmentalized cAMP signaling. In: Current Topics in Developmental Biology. New York: Academic Press. 225–259.
Marley, A., Choy, R.W.Y., and von Zastrow, M. (2013). GPR88 reveals a discrete function of primary cilia as selective insulators of GPCR crosstalk. PLoS ONE 8, e70857.
Matise, M.P., Epstein, D.J., Park, H.L., Platt, K.A., and Joyner, A.L. (1998). Gli2 is required for induction of floor plate and adjacent cells, but not most ventral neurons in the mouse central nervous system. Development 125, 2759–2770.
May, E.A., Kalocsay, M., D’Auriac, I.G., Schuster, P.S., Gygi, S.P., Nachury, M.V., and Mick, D.U. (2021). Time-resolved proteomics profiling of the ciliary Hedgehog response. J Cell Biol 220.
May, S.R., Ashique, A.M., Karlen, M., Wang, B., Shen, Y., Zarbalis, K., Reiter, J., Ericson, J., and Peterson, A.S. (2005). Loss of the retrograde motor for IFT disrupts localization of Smo to cilia and prevents the expression of both activator and repressor functions of Gli. Dev Biol 287, 378–389.
McCormick, K., and Baillie, G.S. (2014). Compartmentalisation of second messenger signalling pathways. Curr Opin Genets Dev 27, 20–25.
McMahon, A.P., Ingham, P.W., and Tabin, C.J. (2003). Developmental roles and clinical significance of Hedgehog signaling. In: Current Topics in Developmental Biology. New York: Academic Press. 1–114.
Mehta, S., Zhang, Y., Roth, R.H., Zhang, J.F., Mo, A., Tenner, B., Huganir, R.L., and Zhang, J. (2018). Single-fluorophore biosensors for sensitive and multiplexed detection of signalling activities. Nat Cell Biol 20, 1215–1225.
Mick, D.U., Rodrigues, R.B., Leib, R.D., Adams, C.M., Chien, A.S., Gygi, S.P., and Nachury, M.V. (2015). Proteomics of primary cilia by proximity labeling. Dev Cell 35, 497–512.
Milenkovic, L., Weiss, L.E., Yoon, J., Roth, T.L., Su, Y.R.S., Sahl, S.J., Scott, M.P., and Moerner, W.E. (2015). Single-molecule imaging of Hedgehog pathway protein Smoothened in primary cilia reveals binding events regulated by Patched1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112, 8320–8325.
Moore, B.S., Stepanchick, A.N., Tewson, P.H., Hartle, C.M., Zhang, J., Quinn, A.M., Hughes, T.E., and Mirshahi, T. (2016). Cilia have high cAMP levels that are inhibited by Sonic Hedgehog-regulated calcium dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113, 13069–13074.
Mukherjee, S., Jansen, V., Jikeli, J.F., Hamzeh, H., Alvarez, L., Dombrowski, M., Balbach, M., Strünker, T., Seifert, R., Kaupp, U.B., et al. (2016). A novel biosensor to study camp dynamics in cilia and flagella. eLife 5, e14052.
Mukhopadhyay, S., Wen, X., Chih, B., Nelson, C.D., Lane, W.S., Scales, S. J., and Jackson, P.K. (2010). TULP3 bridges the IFT-A complex and membrane phosphoinositides to promote trafficking of G proteincoupled receptors into primary cilia. Genes Dev 24, 2180–2193.
Mukhopadhyay, S., Wen, X., Ratti, N., Loktev, A., Rangell, L., Scales, S.J., and Jackson, P.K. (2013). The ciliary G-protein-coupled receptor Gpr161 negatively regulates the sonic hedgehog pathway via cAMP signaling. Cell 152, 210–223.
Nieuwenhuis, E., and Hui, C. (2005). Hedgehog signaling and congenital malformations. Clin Genets 67, 193–208.
Niewiadomski, P., Zhujiang, A., Youssef, M., and Waschek, J.A. (2013). Interaction of PACAP with Sonic hedgehog reveals complex regulation of the Hedgehog pathway by PKA. Cell Signal 25, 2222–2230.
Niewiadomski, P., Kong, J.H., Ahrends, R., Ma, Y., Humke, E.W., Khan, S., Teruel, M.N., Novitch, B.G., and Rohatgi, R. (2014). Gli protein activity is controlled by multisite phosphorylation in vertebrate hedgehog signaling. Cell Rep 6, 168–181.
Nikolaev, V.O., Bünemann, M., Hein, L., Hannawacker, A., and Lohse, M. J. (2004). Novel single chain cAMP sensors for receptor-induced signal propagation. J Biol Chem 279, 37215–37218.
Nüsslein-Volhard, C., and Wieschaus, E. (1980). Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature 287, 795–801.
Ogden, S.K., Fei, D.L., Schilling, N.S., Ahmed, Y.F., Hwa, J., and Robbins, D.J. (2008). G protein Gαi functions immediately downstream of Smoothened in Hedgehog signalling. Nature 456, 967–970.
Page, C.P., and Spina, D. (2012). Selective PDE inhibitors as novel treatments for respiratory diseases. Curr Opin Pharmacol 12, 275–286.
Pal, K., Hwang, S.H., Somatilaka, B., Badgandi, H., Jackson, P.K., DeFea, K., and Mukhopadhyay, S. (2016). Smoothened determines β-arrestin-mediated removal of the G protein-coupled receptor Gpr161 from the primary cilium. J Cell Biol 212, 861–875.
Pan, D., and Rubin, G.M. (1995). cAMP-dependent protein kinase and hedgehog act antagonistically in regulating decapentaplegic transcription in Drosophila imaginal discs. Cell 80, 543–552.
Pan, Y., Bai, C.B., Joyner, A.L., and Wang, B. (2006). Sonic hedgehog signaling regulates Gli2 transcriptional activity by suppressing its processing and degradation. Mol Cell Biol 26, 3365–3377.
Pan, Y., and Wang, B. (2007). A novel protein-processing domain in Gli2 and Gli3 differentially blocks complete protein degradation by the proteasome. J Biol Chem 282, 10846–10852.
Pan, Y., Wang, C., and Wang, B. (2009). Phosphorylation of Gli2 by protein kinase A is required for Gli2 processing and degradation and the Sonic Hedgehog-regulated mouse development. Dev Biol 326, 177–189.
Park, H.L., Bai, C., Platt, K.A., Matise, M.P., Beeghly, A., Hui, C.C., Nakashima, M., and Joyner, A.L. (2000). Mouse Gli1 mutants are viable but have defects in SHH signaling in combination with a Gli2 mutation. Development 127, 1593–1605.
Pathi, S., Pagan-Westphal, S., Baker, D.P., Garber, E.A., Rayhorn, P., Bumcrot, D., Tabin, C.J., Blake Pepinsky, R., and Williams, K.P. (2001). Comparative biological responses to human Sonic, Indian, and Desert hedgehog. Mech Dev 106, 107–117.
Pazour, G.J., and Witman, G.B. (2003). The vertebrate primary cilium is a sensory organelle. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15, 105–110.
Peng, H., Zhang, J., Ya, A., Ma, W., Villa, S., Sukenik, S., and Ge, X. (2021). Myomegalin regulates Hedgehog pathway by controlling PDE4D at the centrosome. Mol Biol Cell doi: https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E21-02-0064.
Persson, M., Stamataki, D., te Welscher, P., Andersson, E., Böse, J., Rüther, U., Ericson, J., and Briscoe, J. (2002). Dorsal-ventral patterning of the spinal cord requires Gli3 transcriptional repressor activity. Genes Dev 16, 2865–2878.
Pinskey, J.M., Franks, N.E., McMellen, A.N., Giger, R.J., and Allen, B.L. (2017). Neuropilin-1 promotes Hedgehog signaling through a novel cytoplasmic motif. J Biol Chem 292, 15192–15204.
Ponsioen, B., Zhao, J., Riedl, J., Zwartkruis, F., van der Krogt, G., Zaccolo, M., Moolenaar, W.H., Bos, J.L., and Jalink, K. (2004). Detecting cAMP-induced Epac activation by fluorescence resonance energy transfer: Epac as a novel cAMP indicator. EMBO Rep 5, 1176–1180.
Pugh, T.J., Weeraratne, S.D., Archer, T.C., Pomeranz Krummel, D.A., Auclair, D., Bochicchio, J., Carneiro, M.O., Carter, S.L., Cibulskis, K., Erlich, R.L., et al. (2012). Medulloblastoma exome sequencing uncovers subtype-specific somatic mutations. Nature 488, 106–110.
Pusapati, G.V., Kong, J.H., Patel, B.B., Gouti, M., Sagner, A., Sircar, R., Luchetti, G., Ingham, P.W., Briscoe, J., and Rohatgi, R. (2018). G protein-coupled receptors control the sensitivity of cells to the morphogen Sonic Hedgehog. Sci Signal 11, eaao5749.
Qi, X., Schmiege, P., Coutavas, E., and Li, X. (2018a). Two patched molecules engage distinct sites on hedgehog yielding a signaling-competent complex. Science 362, eaas8843.
Qi, X., Schmiege, P., Coutavas, E., Wang, J., and Li, X. (2018b). Structures of human Patched and its complex with native palmitoylated sonic hedgehog. Nature 560, 128–132.
Qi, X., Liu, H., Thompson, B., McDonald, J., Zhang, C., and Li, X. (2019). Cryo-EM structure of oxysterol-bound human Smoothened coupled to a heterotrimeric Gi. Nature 571, 279–283.
Rack, P.G., Ni, J., Payumo, A.Y., Nguyen, V., Crapster, J.A., Hovestadt, V., Kool, M., Jones, D.T.W., Mich, J.K., Firestone, A.J., et al. (2014). Arhgap36-dependent activation of Gli transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111, 11061–11066.
Raleigh, D.R., Sever, N., Choksi, P.K., Sigg, M.A., Hines, K.M., Thompson, B.M., Elnatan, D., Jaishankar, P., Bisignano, P., Garcia-Gonzalo, F.R., et al. (2018). Cilia-associated oxysterols activate smoothened. Mol Cell 72, 316–327.e5.
Raleigh, D.R., and Reiter, J.F. (2019). Misactivation of Hedgehog signaling causes inherited and sporadic cancers. J Clin Invest 129, 465–475.
Rallu, M., Machold, R., Gaiano, N., Corbin, J.G., McMahon, A.P., and Fishell, G. (2002). Dorsoventral patterning is established in the telencephalon of mutants lacking both Gli3 and hedgehog signaling. Development 129, 4963–4974.
Regard, J.B., Malhotra, D., Gvozdenovic-Jeremic, J., Josey, M., Chen, M., Weinstein, L.S., Lu, J., Shore, E.M., Kaplan, F.S., and Yang, Y. (2013). Activation of hedgehog signaling by loss of GNAS causes heterotopic ossification. Nat Med 19, 1505–1512.
Rich, T.C., Fagan, K.A., Tse, T.E., Schaack, J., Cooper, D.M.F., and Karpen, J.W. (2001). A uniform extracellular stimulus triggers distinct cAMP signals in different compartments of a simple cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 13049–13054.
Riobo, N.A., Saucy, B., Dilizio, C., and Manning, D.R. (2006). Activation of heterotrimeric G proteins by Smoothened. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 12607–12612.
Robbins, D.J., Nybakken, K.E., Kobayashi, R., Sisson, J.C., Bishop, J.M., and Thérond, P.P. (1997). Hedgehog elicits signal transduction by means of a large complex containing the kinesin-related protein costal2. Cell 90, 225–234.
Röck, R., Mayrhofer, J.E., Bachmann, V., and Stefan, E. (2015). Impact of kinase activating and inactivating patient mutations on binary PKA interactions. Front Pharmacol 6.
Rosenbaum, J.L., and Witman, G.B. (2002). Intraflagellar transport. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3, 813–825.
Rudolf, A.F., Kinnebrew, M., Kowatsch, C., Ansell, T.B., El Omari, K., Bishop, B., Pardon, E., Schwab, R.A., Malinauskas, T., Qian, M., et al. (2019). The morphogen Sonic hedgehog inhibits its receptor Patched by a pincer grasp mechanism. Nat Chem Biol 15, 975–982.
Ruel, L., Rodriguez, R., Gallet, A., Lavenant-Staccini, L., and Thérond, P.P. (2003). Stability and association of Smoothened, Costal2 and fused with Cubitus interruptus are regulated by Hedgehog. Nat Cell Biol 5, 907–913.
Ruiz i Altaba, A., Palma, V., and Dahmane, N. (2002). Hedgehog-GLI signaling and the growth of the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 3, 24–33.
Ruppert, J.M., Kinzler, K.W., Wong, A.J., Bigner, S.H., Kao, F.T., Law, M. L., Seuanez, H.N., O’Brien, S.J., and Vogelstein, B. (1988). The GLI-Kruppel family of human genes. Mol Cell Biol 8, 3104–3113.
Sagner, A., and Briscoe, J. (2019). Establishing neuronal diversity in the spinal cord: A time and a place. Development 146.
Satir, P., and Christensen, S.T. (2007). Overview of structure and function of mammalian cilia. Annu Rev Physiol 69, 377–400.
Scotland, G., Beard, M., Erdogan, S., Huston, E., McCallum, F., MacKenzie, S.J., Peden, A.H., Pooley, L., Rena, N.G., Ross, A.H., et al. (1998). Intracellular compartmentalization of PDE4 cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterases. Methods 14, 65–79.
Scott, J.D., and Pawson, T. (2009). Cell signaling in space and time: Where proteins come together and when they’re apart. Science 326, 1220–1224.
Shen, F., Cheng, L., Douglas, A.E., Riobo, N.A., and Manning, D.R. (2013). Smoothened is a fully competent activator of the heterotrimeric G protein Gi. Mol Pharmacol 83, 691–697.
Shimada, I.S., Hwang, S.H., Somatilaka, B.N., Wang, X., Skowron, P., Kim, J., Kim, M., Shelton, J.M., Rajaram, V., Xuan, Z., et al. (2018). Basal suppression of the Sonic Hedgehog pathway by the G-protein-coupled receptor Gpr161 restricts medulloblastoma pathogenesis. Cell Rep 22, 1169–1184.
Singh, J., Wen, X., and Scales, S.J. (2015). The orphan G protein-coupled receptor Gpr175 (Tpra40) enhances Hedgehog signaling by modulating cAMP levels. J Biol Chem 290, 29663–29675.
Sisson, J.C., Ho, K.S., Suyama, K., and Scott, M.P. (1997). Costal2, a novel kinesin-related protein in the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Cell 90, 235–245.
Snuderl, M., Batista, A., Kirkpatrick, N.D., Ruiz de Almodovar, C., Riedemann, L., Walsh, E.C., Anolik, R., Huang, Y., Martin, J.D., Kamoun, W., et al. (2013). Targeting placental growth factor/neuropilin 1 pathway inhibits growth and spread of medulloblastoma. Cell 152, 1065–1076.
Somatilaka, B.N., Hwang, S.H., Palicharla, V.R., White, K.A., Badgandi, H., Shelton, J.M., and Mukhopadhyay, S. (2020). Ankmy2 prevents smoothened-independent hyperactivation of the Hedgehog pathway via cilia-regulated adenylyl cyclase signaling. Dev Cell 54, 710–726.e8.
Spina, D. (2008). PDE4 inhibitors: Current status. British J Pharmacol 155, 308–315.
Stone, D.M., Hynes, M., Armanini, M., Swanson, T.A., Gu, Q., Johnson, R. L., Scott, M.P., Pennica, D., Goddard, A., Phillips, H., et al. (1996). The tumour-suppressor gene patched encodes a candidate receptor for Sonic hedgehog. Nature 384, 129–134.
Stoufflet, J., Chaulet, M., Doulazmi, M., Fouquet, C., Dubacq, C., Métin, C., Schneider-Maunoury, S., Trembleau, A., Vincent, P., and Caillé, I. (2020). Primary cilium-dependent cAMP/PKA signaling at the centrosome regulates neuronal migration. Sci Adv 6, eaba3992.
Strutt, D.I., Wiersdorff, V., and Mlodzik, M. (1995). Regulation of furrow progression in the Drosophila eye by cAMP-dependent protein kinase A. Nature 373, 705–709.
Su, S., Phua, S.C., DeRose, R., Chiba, S., Narita, K., Kalugin, P.N., Katada, T., Kontani, K., Takeda, S., and Inoue, T. (2013). Genetically encoded calcium indicator illuminates calcium dynamics in primary cilia. Nat Methods 10, 1105–1107.
Svärd, J., Heby-Henricson, K., Henricson, K.H., Persson-Lek, M., Rozell, B., Lauth, M., Bergström, A., Ericson, J., Toftgård, R., and Teglund, S. (2006). Genetic elimination of suppressor of fused reveals an essential repressor function in the mammalian Hedgehog signaling pathway. Dev Cell 10, 187–197.
Taylor, S.S., Buechler, J.A., and Yonemoto, W. (1990). cAMP-dependent protein kinase: Framework for a diverse family of regulatory enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 59, 971–1005.
Taylor, S.S., Zhang, P., Steichen, J.M., Keshwani, M.M., and Kornev, A.P. (2013). PKA: Lessons learned after twenty years. Biochim Biophys Acta 1834, 1271–1278.
Tempe, D., Casas, M., Karaz, S., Blanchet-Tournier, M.F., and Concordet, J.P. (2006). Multisite protein kinase A and glycogen synthase kinase 3β phosphorylation leads to Gli3 ubiquitination by SCFβTiCP. Mol Cell Biol 26, 4316–4326.
Terrin, A., Monterisi, S., Stangherlin, A., Zoccarato, A., Koschinski, A., Surdo, N.C., Mongillo, M., Sawa, A., Jordanides, N.E., Mountford, J. C., et al. (2012). PKA and PDE4D3 anchoring to AKAP9 provides distinct regulation of cAMP signals at the centrosome. J Cell Biol 198, 607–621.
Tian, L., Hires, S.A., Mao, T., Huber, D., Chiappe, M.E., Chalasani, S.H., Petreanu, L., Akerboom, J., McKinney, S.A., Schreiter, E.R., et al. (2009). Imaging neural activity in worms, flies and mice with improved GCaMP calcium indicators. Nat Methods 6, 875–881.
Torres-Quesada, O., Mayrhofer, J.E., and Stefan, E. (2017). The many faces of compartmentalized PKA signalosomes. Cell Signal 37, 1–11.
Truong, M.E., Bilekova, S., Choksi, S.P., Li, W., Bugaj, L.J., Xu, K., and Reiter, J.F. (2021). Vertebrate cells differentially interpret ciliary and extraciliary cAMP. Cell 184, 2911–2926.e18.
Tukachinsky, H., Lopez, L.V., and Salic, A. (2010). A mechanism for vertebrate Hedgehog signaling: recruitment to cilia and dissociation of SuFu-Gli protein complexes. J Cell Biol 191, 415–428.
Turnham, R.E., and Scott, J.D. (2016). Protein kinase A catalytic subunit isoform PRKACA; History, function and physiology. Gene 577, 101–108.
Tuson, M., He, M., and Anderson, K.V. (2011). Protein kinase A acts at the basal body of the primary cilium to prevent Gli2 activation and ventralization of the mouse neural tube. Development 138, 4921–4930.
Uys, G.M., Ramburan, A., Loos, B., Kinnear, C.J., Korkie, L.J., Mouton, J., Riedemann, J., and Moolman-Smook, J.C. (2011). Myomegalin is a novel A-kinase anchoring protein involved in the phosphorylation of cardiac myosin binding protein C. BMC Cell Biol 12, 18.
Verde, I., Pahlke, G., Salanova, M., Zhang, G., Wang, S., Coletti, D., Onuffer, J., Jin, S.L.C., and Conti, M. (2001). Myomegalin is a novel protein of the Golgi/centrosome that interacts with a cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem 276, 11189–11198.
Vuolo, L., Herrera, A., Torroba, B., Menendez, A., and Pons, S. (2015). Ciliary adenylyl cyclases control the Hedgehog pathway. J Cell Sci 128, 2928.
Wallace, V.A. (1999). Purkinje-cell-derived Sonic hedgehog regulates granule neuron precursor cell proliferation in the developing mouse cerebellum. Curr Biol 9, 445–448.
Wang, B., Fallon, J.F., and Beachy, P.A. (2000). Hedgehog-regulated processing of Gli3 produces an anterior/posterior repressor gradient in the developing vertebrate limb. Cell 100, 423–434.
Wang, B., and Li, Y. (2006). Evidence for the direct involvement of TrCP in Gli3 protein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103, 33–38.
Wechsler-Reya, R.J., and Scott, M.P. (1999). Control of neuronal precursor proliferation in the cerebellum by sonic hedgehog. Neuron 22, 103–114.
Wen, X., Lai, C.K., Evangelista, M., Hongo, J.A., de Sauvage, F.J., and Scales, S.J. (2010). Kinetics of hedgehog-dependent full-length Gli3 accumulation in primary cilia and subsequent degradation. Mol Cell Biol 30, 1910–1922.
Williams, C.H., Hempel, J.E., Hao, J., Frist, A.Y., Williams, M.M., Fleming, J.T., Sulikowski, G.A., Cooper, M.K., Chiang, C., and Hong, C.C. (2015). An in vivo chemical genetic screen identifies phosphodiesterase 4 as a pharmacological target for Hedgehog signaling inhibition. Cell Rep 11, 43–50.
Wong, W., and Scott, J.D. (2004). AKAP signalling complexes: focal points in space and time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5, 959–970.
Xie, J., Murone, M., Luoh, S.M., Ryan, A., Gu, Q., Zhang, C., Bonifas, J. M., Lam, C.W., Hynes, M., Goddard, A., et al. (1998). Activating Smoothened mutations in sporadic basal-cell carcinoma. Nature 391, 90–92.
Yang, T.T., Tran, M.N.T., Chong, W.M., Huang, C.E., and Liao, J.C. (2019). Single-particle tracking localization microscopy reveals nonaxonemal dynamics of intraflagellar transport proteins at the base of mammalian primary cilia. Mol Biol Cell 30, 828–837.
Zaccolo, M., and Pozzan, T. (2002). Discrete microdomains with high concentration of cAMP in stimulated rat neonatal cardiac myocytes. Science 295, 1711–1715.
Zaccolo, M., Zerio, A., and Lobo, M.J. (2021). Subcellular organization of the camp signaling pathway. Pharmacol Rev 73, 278–309.
Zhang, B., Zhuang, T., Lin, Q., Yang, B., Xu, X., Xin, G., Zhu, S., Wang, G., Yu, B., Zhang, T., et al. (2019). Patched1-ArhGAP36-PKA-Inversin axis determines the ciliary translocation of smoothened for sonic hedgehog pathway activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116, 874–879.
Zhang, J., Ma, Y., Taylor, S.S., and Tsien, R.Y. (2001). Genetically encoded reporters of protein kinase A activity reveal impact of substrate tethering. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98, 14997–15002.
Zhang, J.F., Liu, B., Hong, I., Mo, A., Roth, R.H., Tenner, B., Lin, W., Zhang, J.Z., Molina, R.S., Drobizhev, M., et al. (2021). An ultrasensitive biosensor for high-resolution kinase activity imaging in awake mice. Nat Chem Biol 17, 39–46.
Zhang, P., Knape, M.J., Ahuja, L.G., Keshwani, M.M., King, C.C., Sastri, M., Herberg, F.W., and Taylor, S.S. (2015). Single turnover autophosphorylation cycle of the PKA RIIβ holoenzyme. PLoS Biol 13, e1002192.
Zhang, W., Zhao, Y., Tong, C., Wang, G., Wang, B., Jia, J., and Jiang, J. (2005). Hedgehog-regulated Costal2-kinase complexes control phosphorylation and proteolytic processing of cubitus interruptus. Dev Cell 8, 267–278.
Zhang, Y., Bulkley, D.P., Xin, Y., Roberts, K.J., Asarnow, D.E., Sharma, A., Myers, B.R., Cho, W., Cheng, Y., and Beachy, P.A. (2018). Structural basis for cholesterol transport-like activity of the Hedgehog receptor patched. Cell 175, 1352–1364.e14.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (CA235749). We apologize to the investigators whose work we were unable to cite owing to space constraints and the investigators working in the many important areas of Hh signaling we were unable to cover. We thank Dr. Aaron Gitler for comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Compliance and ethics The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, E., Zhang, J. & Ge, X. Control of the Hedgehog pathway by compartmentalized PKA in the primary cilium. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 500–514 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-1975-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-1975-9