Abstract
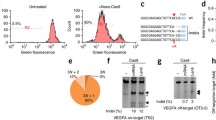
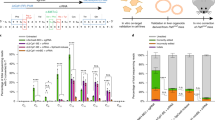
Genome editing through adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors is a promising gene therapy strategy for various diseases, especially genetic disorders. However, homologous recombination (HR) efficiency is extremely low in adult animal models. We assumed that increasing AAV transduction efficiency could increase genome editing activity, especially HR efficiency, for in vivo gene therapy. Firstly, a mouse phenylketonuria (PKU) model carrying a pathogenic R408W mutation in phenylalanine hydroxylase (Pah) was generated. Through co-delivery of the general AAV receptor (AAVR), we found that AAVR could dramatically increase AAV transduction efficiency in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, co-delivery of SaCas9/sgRNA/donor templates with AAVR via AAV8 vectors increased indel rate over 2-fold and HR rate over 15-fold for the correction of the single mutation in PahR408W mice. Moreover, AAVR co-injection successfully increased the site-specific insertion rate of a 1.4 kb Pah cDNA by 11-fold, bringing the HR rate up to 7.3% without detectable global off-target effects. Insertion of Pah cDNA significantly decreased the Phe level and ameliorated PKU symptoms. This study demonstrates a novel strategy to dramatically increase AAV transduction which substantially enhanced in vivo genome editing efficiency in adult animal models, showing clinical potential for both conventional and genome editing-based gene therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barzel, A., Paulk, N.K., Shi, Y., Huang, Y., Chu, K., Zhang, F., Valdmanis, P.N., Spector, L. P., Porteus, M.H., Gaensler, K.M., et al. (2015). Promoterless gene targeting without nucleases ameliorates haemophilia B in mice. Nature 517, 360–364.
Blau, N., Bélanger-Quintana, A., Demirkol, M., Feillet, F., Giovannini, M., MacDonald, A., Trefz, F.K., and van Spronsen, F. (2010a). Management of phenylketonuria in Europe: survey results from 19 countries. Mol Genet Metab 99, 109–115.
Blau, N., van Spronsen, F.J., and Levy, H.L. (2010b). Phenylketonuria. Lancet 376, 1417–1427.
Chen, X., Liu, J., Janssen, J.M., and Gonçalves, M.A.F.V. (2017). The chromatin structure differentially impacts high-specificity CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease strategies. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 8, 558–563.
Dilella, A.G., Marvi, J., Brayton, K., and Woo, S.L.C. (1987). An ammo-acid substitution involved in phenylketonuria is in linkage disequilibrium with DNA haplotype 2. Nature 327, 333–336.
Ding, Z., Georgiev, P., and Thöny, B. (2006). Administration-route and gender-independent long-term therapeutic correction of phenylketonuria (PKU) in a mouse model by recombinant adenoassociated virus 8 pseudotyped vector-mediated gene transfer. Gene Ther 13, 587–593.
Ding, Z., Harding, C.O., Rebuffat, A., Elzaouk, L., Wolff, J.A., and Thöny, B. (2008). Correction of murine PKU following AAV-mediated intramuscular expression of a complete phenylalanine hydroxylating system. Mol Ther 16, 673–681.
Duan, D. (2016). Systemic delivery of adeno-associated viral vectors. Curr Opin Virol 21, 16–25.
Dunbar, C.E., High, K.A., Joung, J.K., Kohn, D.B., Ozawa, K., and Sadelain, M. (2018). Gene therapy comes of age. Science 359, eaan4672.
Graham, T., McIntosh, J., Work, L.M., Nathwani, A., and Baker, A.H. (2008). Performance of AAV8 vectors expressing human factor IX from a hepatic-selective promoter following intravenous injection into rats. Genet Vaccines Ther 6, 9.
Grisch-Chan, H.M., Schlegel, A., Scherer, T., Allegri, G., Heidelberger, R., Tsikrika, P., Schmeer, M., Schleef, M., Harding, C.O., Haberle, J., et al. (2017). Low-dose gene therapy for murine PKU using episomal naked DNA vectors expressing PAH from its endogenous liver promoter. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 7, 339–349.
Grünewald, J., Zhou, R., Garcia, S.P., Iyer, S., Lareau, C.A., Aryee, M.J., and Joung, J.K. (2019). Transcriptome-wide off-target RNA editing induced by CRISPR-guided DNA base editors. Nature 569, 433–437.
Guan, Y., Ma, Y., Li, Q., Sun, Z., Ma, L., Wu, L., Wang, L., Zeng, L., Shao, Y., Chen, Y., et al. (2016). CRISPR/Cas9-mediated somatic correction of a novel coagulator factor IX gene mutation ameliorates hemophilia in mouse. EMBO Mol Med 8, 477–488.
Hamman, K., Clark, H., Montini, E., Al-Dhalimy, M., Grompe, M., Finegold, M., and Harding, C.O. (2005). Low therapeutic threshold for hepatocyte replacement in murine phenylketonuria. Mol Ther 12, 337–344.
Harding, C.O., Gillingham, M.B., Hamman, K., Clark, H., Goebel-Daghighi, E., Bird, A., and Koeberl, D.D. (2006). Complete correction of hyperphenylalaninemia following liver-directed, recombinant AAV2/8 vector-mediated gene therapy in murine phenylketonuria. Gene Ther 13, 457–462.
Jin, S., Zong, Y., Gao, Q., Zhu, Z., Wang, Y., Qin, P., Liang, C., Wang, D., Qiu, J.L., Zhang, F., et al. (2019). Cytosine, but not adenine, base editors induce genome-wide off-target mutations in rice. Science 364, 292–295.
Komor, A.C., Kim, Y.B., Packer, M.S., Zuris, J.A., and Liu, D.R. (2016). Programmable editing of a target base in genomic DNAwithout double-stranded DNA cleavage. Nature 533, 420–424.
Li, H., Haurigot, V., Doyon, Y., Li, T., Wong, S.Y., Bhagwat, A.S., Malani, N., Anguela, X.M., Sharma, R., Ivanciu, L., et al. (2011). In vivo genome editing restores haemostasis in a mouse model of haemophilia. Nature 475, 217–221.
Manno, C.S., Pierce, G.F., Arruda, V.R., Glader, B., Ragni, M., Rasko, J.J. E., Ozelo, M.C., Hoots, K., Blatt, P., Konkle, B., et al. (2006). Successful transduction of liver in hemophilia by AAV-Factor IX and limitations imposed by the host immune response. Nat Med 12, 342–347.
Mendell, J.R., Al-Zaidy, S., Shell, R., Arnold, W.D., Rodino-Klapac, L.R., Prior, T.W., Lowes, L., Alfano, L., Berry, K., Church, K., et al. (2017). Single-dose gene-replacement therapy for spinal muscular atrophy. N Engl J Med 377, 1713–1722.
Mingozzi, F., and High, K.A. (2011). Therapeutic in vivo gene transfer for genetic disease using AAV: progress and challenges. Nat Rev Genet 12, 341–355.
Mochizuki, S., Mizukami, H., Ogura, T., Kure, S., Ichinohe, A., Kojima, K., Matsubara, Y., Kobayahi, E., Okada, T., Hoshika, A., et al. (2004). Long-term correction ofhyperphenylalaninemia by AAV-mediated gene transfer leads to behavioral recovery in phenylketonuria mice. Gene Ther 11, 1081–1086.
Nathwani, A.C., Gray, J.T., Ng, C.Y.C., Zhou, J., Spence, Y., Waddington, S.N., Tuddenham, E.G.D., Kemball-Cook, G., McIntosh, J., Boon-Spijker, M., et al. (2006). Self-complementary adeno-associated virus vectors containing a novel liver-specific human factor IX expression cassette enable highly efficient transduction of murine and nonhuman primate liver. Blood 107, 2653–2661.
Nathwani, A.C., Reiss, U.M., Tuddenham, E.G.D., Rosales, C., Chowdary, P., McIntosh, J., Della Peruta, M., Lheriteau, E., Patel, N., Raj, D., et al. (2014). Long-term safety and efficacy of factor IX gene therapy in hemophilia B. N Engl J Med 371, 1994–2004.
Nygaard, S., Barzel, A., Haft, A., Major, A., Finegold, M., Kay, M.A., and Grompe, M. (2016). A universal system to select gene-modified hepatocytes in vivo. Sci Transl Med 8, 342ra79.
Pillay, S., Meyer, N.L., Puschnik, A.S., Davulcu, O., Diep, J., Ishikawa, Y., Jae, L.T., Wosen, J.E., Nagamine, C.M., Chapman, M.S., et al. (2016). An essential receptor for adeno-associated virus infection. Nature 530, 108–112.
Ran, F.A., Cong, L., Yan, W.X., Scott, D.A., Gootenberg, J.S., Kriz, A.J., Zetsche, B., Shalem, O., Wu, X., Makarova, K.S., et al. (2015). In vivo genome editing using Staphylococcus aureus Cas9. Nature 520, 186–191.
Rangarajan, S., Walsh, L., Lester, W., Perry, D., Madan, B., Laffan, M., Yu, H., Vettermann, C., Pierce, G.F., Wong, W.Y., et al. (2017). AAV5-factor VIII gene transfer in severe hemophilia A. N Engl J Med 377, 2519–2530.
Rees, H.A., Wilson, C., Doman, J.L., and Liu, D.R. (2019). Analysis and minimization of cellular RNA editing by DNA adenine base editors. Sci Adv 5, eaax5717.
Russell, S., Bennett, J., Wellman, J.A., Chung, D.C., Yu, Z.F., Tillman, A., Wittes, J., Pappas, J., Elci, O., McCague, S., et al. (2017). Efficacy and safety of voretigene neparvovec (AAV2-hRPE65v2) in patients with RPE65-mediated inherited retinal dystrophy: a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 390, 849–860.
Scriver, C.R., and Clow, C.L. (1980). Phenylketonuria: epitome of human biochemical genetics. N Engl J Med 303, 1336–1342.
Shao, Y., Guan, Y., Wang, L., Qiu, Z., Liu, M., Chen, Y., Wu, L., Li, Y., Ma, X., Liu, M., et al. (2014). CRISPR/Cas-mediated genome editing in the rat via direct injection of one-cell embryos. Nat Protoc 9, 2493–2512.
Shao, Y., Wang, L., Guo, N., Wang, S., Yang, L., Li, Y., Wang, M., Yin, S., Han, H., Zeng, L., et al. (2018). Cas9-nickase-mediated genome editing corrects hereditary tyrosinemia in rats. J Biol Chem 293, 6883–6892.
van Spronsen, F.J., Ahring, K.K., and Gizewska M. (2009). PKU—What is daily practice in various centres in Europe? J Inherit Metab Dis 32, 58–64.
van Wegberg, A.M.J., MacDonald, A., Ahring, K., Bélanger-Quintana, A., Blau, N., Bosch, A.M., Burlina, A., Campistol, J., Feillet, F., Gizewska, M., et al. (2017). The complete European guidelines on phenylketonuria: diagnosis and treatment. Orphanet J Rare Dis 12, 162.
Viecelli, H.M., Harbottle, R.P., Wong, S.P., Schlegel, A., Chuah, M.K., VandenDriessche, T., Harding, C.O., and Thöny, B. (2014). Treatment of phenylketonuria using minicircle-based naked-DNA gene transfer to murine liver. Hepatology 60, 1035–1043.
Villiger, L., Grisch-Chan, H.M., Lindsay, H., Ringnalda, F., Pogliano, C.B., Allegri, G., Fingerhut, R., Haberle, J., Matos, J., Robinson, M.D., et al. (2018). Treatment of a metabolic liver disease by in vivo genome base editing in adult mice. Nat Med 24, 1519–1525.
Wang, D., Tai, P.W.L., and Gao, G. (2019). Adeno-associated virus vector as a platform for gene therapy delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18, 358–378.
Wang, L., Shao, Y., Guan, Y., Li, L., Wu, L., Chen, F., Liu, M., Chen, H., Ma, Y., Ma, X., et al. (2015). Large genomic fragment deletion and functional gene cassette knock-in via Cas9 protein mediated genome editing in one-cell rodent embryos. Sci Rep 5, 17517.
Wang, L., Wang, H., Bell, P., McMenamin, D., and Wilson, J.M. (2012). Hepatic gene transfer in neonatal mice by adeno-associated virus serotype 8 vector. Hum Gene Ther 23, 533–539.
Yagi, H., Ogura, T., Mizukami, H., Urabe, M., Hamada, H., Yoshikawa, H., Ozawa, K., and Kume, A. (2011). Complete restoration of phenylalanine oxidation in phenylketonuria mouse by a self-complementary adeno-associated virus vector. J Gene Med 13, 114–122.
Yang, Y., Wang, L., Bell, P., McMenamin, D., He, Z., White, J., Yu, H., Xu, C., Morizono, H., Musunuru, K., et al. (2016). A dual AAV system enables the Cas9-mediated correction of a metabolic liver disease in newborn mice. Nat Biotechnol 34, 334–338.
Yarrington, R.M., Verma, S., Schwartz, S., Trautman, J.K., and Carroll, D. (2018). Nucleosomes inhibit target cleavage by CRISPR-Cas9 in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115, 9351–9358.
Yin, H., Song, C.Q., Dorkin, J.R., Zhu, L.J., Li, Y., Wu, Q., Park, A., Yang, J., Suresh, S., Bizhanova, A., et al. (2016). Therapeutic genome editing by combined viral and non-viral delivery of CRISPR system components in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 34, 328–333.
Yuen, G., Khan, F.J., Gao, S., Stommel, J.M., Batchelor, E., Wu, X., and Luo, J. (2017). CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene knockout is insensitive to target copy number but is dependent on guide RNA potency and Cas9/sgRNA threshold expression level. Nucleic Acids Res 45, 12039–12053.
Zhong, L., Li, B., Mah, C.S., Govindasamy, L., Agbandje-McKenna, M., Cooper, M., Herzog, R.W., Zolotukhin, I., Warrington Kenneth H. J., Weigel-Van Aken, K.A., et al. (2008). Next generation of adeno-associated virus 2 vectors: point mutations in tyrosines lead to high-efficiency transduction at lower doses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 7827–7832.
Zincarelli, C., Soltys, S., Rengo, G., and Rabinowitz, J.E. (2008). Analysis of AAV serotypes 1–9 mediated gene expression and tropism in mice after systemic injection. Mol Ther 16, 1073–1080.
Zuo, E., Sun, Y., Wei, W., Yuan, T., Ying, W., Sun, H., Yuan, L., Steinmetz, L.M., Li, Y., and Yang, H. (2019). Cytosine base editor generates substantial off-target single-nucleotide variants in mouse embryos. Science 364, 289–292.
Acknowledgements
We thank Meizhen Liu from East China Normal University for microinjection and generation of the PKU mouse model, the ECNU Public Platform for innovation(011) for its support, and Dr Stefan Siwko for proof reading of this manuscript. This work was partially supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFA0110802), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81670470 and 81873685), grants from the Shanghai Municipal Commission for Science and Technology (18411953500 and 20140900201), a grant from the Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (2019-01-07-00-05-E00054), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Compliance and ethics
The author(s) declare that they have no conflict of interest. All animal work conformed to the regulations of the animal ethics committee and was approved by the East China Normal University Center for Animal Research.
Supporting Information
11427_2020_1744_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Enhanced genome editing to ameliorate a genetic metabolic liver disease through co-delivery of adeno-associated virus receptor
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, S., Ma, L., Shao, T. et al. Enhanced genome editing to ameliorate a genetic metabolic liver disease through co-delivery of adeno-associated virus receptor. Sci. China Life Sci. 65, 718–730 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1744-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1744-6