Abstract
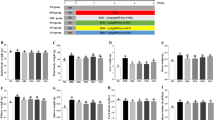
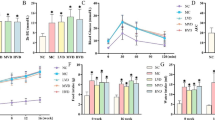
In this study, treatment of C57BL/6J (wild type, WT) mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD) with retinoic acid (RA) decreased body weight and subcutaneous and visceral fat content, reversed the apparent hepatosteatosis, and reduced hepatic intracellular triglyceride and serum alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) concentrations. Moreover, RA treatment improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in WT mice fed a HFD. However, these RA-induced effects in WT mice fed a HFD were alleviated in liver specific Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) deficient (LKO) mice fed a HFD. Furthermore, RA also could not improve glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in LKO mice fed a HFD. The mechanism studies indicated that RA indeed increased the expression of hepatic Sirt1 and superoxide dismutase 2 (Sod2), and inhibited the expression of sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c (Srebp-1c) in WT mice in vivo and in vitro. RA decreased mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in WT primary hepatocytes and increased mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number in WT mice liver. However, these RA-mediated molecular effects were also abolished in the liver and primary hepatocytes from LKO mice. In summary, RA protected against HFD-induced hepatosteatosis by decreasing Srebp-1c expression and improving antioxidant capacity through a Sirt1-mediated mechanism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, M.H., and Byrne, C.D. (2007). Modulation of sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs) as potential treatments for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Drug Discov Today 12, 740–747.
Alvarez, R., de Andres, J., Yubero, P., Vinas, O., Mampel, T., Iglesias, R., Giralt, M., and Villarroya, F. (1995). A novel regulatory pathway of brown fat thermogenesis: retinoic acid is a transcriptional activator of the mitochondrial uncoupling protein gene. J Biol Chem 270, 5666–5673.
Asrih, M., and Jornayvaz, F.R. (2013). Inflammation as a potential link between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. J Endocrinol 218, R25–R36.
Berry, D.C., and Noy, N. (2009). All-trans-retinoic acid represses obesity and insulin resistance by activating both peroxisome proliferation-activated receptor beta/delta and retinoic acid receptor. Mol Cell Biol 29, 3286–3296.
Bradbury, M.W. (2006). Lipid Metabolism and Liver Inflammation. I. Hepatic fatty acid uptake: possible role in steatosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290, G194–G198.
Brookes, P.S., Levonen, A.L., Shiva, S., Sarti, P., and Darley-Usmar, V.M. (2002). Mitochondria: regulators of signal transduction by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Free Radical Biol Med 33, 755–764.
Brunt, E.M. (2010). Pathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7, 195–203.
Brunt, E.M., Kleiner, D.E., Wilson, L.A., Belt, P., Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A., and Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. (2011). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) activity score and the histopathologic diagnosis in NAFLD: distinct clinicopathologic meanings. Hepatology 53, 810–820.
Caron, A.Z., He, X., Mottawea, W., Seifert, E.L., Jardine, K., Dewar-Darch, D., Cron, G.O., Harper, M.E., Stintzi, A., and McBurney, M.W. (2014). The SIRT1 deacetylase protects mice against the symptoms of metabolic syndrome. FASEB J 28, 1306–1316.
Cave, M., Deaciuc, I., Mendez, C., Song, Z., Joshi-Barve, S., Barve, S., and McClain, C. (2007). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: predisposing factors and the role of nutrition. J Nutr Biochem 18, 184–195.
Chambon, P. (1996). A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J 10, 940–954.
Cheng, H.L., Mostoslavsky, R., Saito, S., Manis, J.P., Gu, Y., Patel, P., Bronson, R., Appella, E., Alt, F.W., and Chua, K.F. (2003). Developmental defects and p53 hyperacetylation in Sir2 homolog (SIRT1)-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100, 10794–10799.
Chiang, D.J., Pritchard, M.T., and Nagy, L.E. (2011). Obesity, diabetes mellitus, and liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 300, G697–G702.
Cohen, H.Y., Miller, C., Bitterman, K.J., Wall, N.R., Hekking, B., Kessler, B., Howitz, K.T., Gorospe, M., de Cabo, R., and Sinclair, D.A. (2004). Calorie restriction promotes mammalian cell survival by inducing the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 305, 390–392.
Day, C.P., and James, O.F. (1998). Steatohepatitis: a tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology 114, 842–845.
Diez, J., and Iglesias, P. (2003). The role of the novel adipocyte-derived hormone adiponectin in human disease. Eur J Endocrinol 148, 293–300.
Gerhart-Hines, Z., Rodgers, J.T., Bare, O., Lerin, C., Kim, S.H., Mostoslavsky, R., Alt, F.W., Wu, Z., and Puigserver, P. (2007). Metabolic control of muscle mitochondrial function and fatty acid oxidation through SIRT1/PGC-1α. EMBO J 26, 1913–1923.
Goodpaster, B.H. (2013). Mitochondrial deficiency is associated with insulin resistance. Diabetes 62, 1032–1035.
Heliövaara, M.K., Remitz, A., Reitamo, S., Teppo, A.M., Karonen, S.L., and Ebeling, P. (2007). 13-Retinoic acid therapy induces insulin resistance, regulates inflammatory parameters, and paradoxically increases serum adiponectin concentration. Metabolism 56, 786–791.
Hou, X., Xu, S., Maitland-Toolan, K.A., Sato, K., Jiang, B., Ido, Y., Lan, F., Walsh, K., Wierzbicki, M., Verbeuren, T.J., Cohen, R.A., and Zang, M. (2008). SIRT1 regulates hepatocyte lipid metabolism through activating AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 283, 20015–20026.
Koistinen, H.A., Remitz, A., Koivisto, V.A., and Ebeling, P. (2006). Paradoxical rise in serum adiponectin concentration in the face of acid-induced insulin resistance 13-cis-retinoic. Diabetologia 49, 383–386.
Krawczyk, M., Bonfrate, L., and Portincasa, P. (2010). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 24, 695–708.
Li, Y., Wong, K., Walsh, K., Gao, B., and Zang, M. (2013). Retinoic acid receptor beta stimulates hepatic induction of fibroblast growth factor 21 to promote fatty acid oxidation and control whole-body energy homeostasis in mice. J Biol Chem 288, 10490–10504.
Liang, F., Kume, S., and Koya, D. (2009). SIRT1 and insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol 5, 367–373.
Lin, J., Yang, R., Tarr, P.T., Wu, P.H., Handschin, C., Li, S., Yang, W., Pei, L., Uldry, M., Tontonoz, P., Newgard, C.B., and Spiegelman, B.M. (2005). Hyperlipidemic effects of dietary saturated fats mediated through PGC-1β coactivation of SREBP. Cell 120, 261–273.
Liu, X., Gao, Y., Li, M., Geng, C., Xu, H., Yang, Y., Guo, Y., Jiao, T., Fang, F., and Chang, Y. (2015). Sirt1 mediates the effect of the heme oxygenase inducer, cobalt protoporphyrin, on ameliorating liver metabolic damage caused by a high-fat diet. J Hepatol 63, 713–721.
Maiese, K. (2015). New insights for oxidative stress and diabetes mellitus. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015, 1–17.
Matsumoto, M., Ogawa, W., Teshigawara, K., Inoue, H., Miyake, K., Sakaue, H., and Kasuga, M. (2002). Role of the insulin receptor substrate 1 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway in insulin-induced expression of sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c and glucokinase genes in rat hepatocytes. Diabetes 51, 1672–1680.
Mercader, J., Ribot, J., Murano, I., Felipe, F., Cinti, S., Bonet, M.L., and Palou, A. (2006). Remodeling of white adipose tissue after retinoic acid administration in mice. Endocrinology 147, 5325–5332.
Milne, J.C., Lambert, P.D., Schenk, S., Carney, D.P., Smith, J.J., Gagne, D.J., Jin, L., Boss, O., Perni, R.B., Vu, C.B., Bemis, J.E., Xie, R., Disch, J.S., Ng, P.Y., Nunes, J.J., Lynch, A.V., Yang, H., Galonek, H., Israelian, K., Choy, W., Iffland, A., Lavu, S., Medvedik, O., Sinclair, D.A., Olefsky, J.M., Jirousek, M.R., Elliott, P.J., and Westphal, C.H. (2007). Small molecule activators of SIRT1 as therapeutics for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Nature 450, 712–716.
Mukhopadhyay, P., Rajesh, M., Haskó, G., Hawkins, B.J., Madesh, M., and Pacher, P. (2007). Simultaneous detection of apoptosis and mitochondrial superoxide production in live cells by flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. Nat Protoc 2, 2295–2301.
Murphy, M.P. (2009). How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem J 417, 1–13.
Pfluger, P.T., Herranz, D., Velasco-Miguel, S., Serrano, M., and Tschöp, M.H. (2008). Sirt1 protects against high-fat diet-induced metabolic damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105, 9793–9798.
Ponugoti, B., Kim, D.H., Xiao, Z., Smith, Z., Miao, J., Zang, M., Wu, S.Y., Chiang, C.M., Veenstra, T.D., and Kemper, J.K. (2010). SIRT1 deacetylates and inhibits SREBP-1C activity in regulation of hepatic lipid metabolism. J Biol Chem 285, 33959–33970.
Rahimi, R.S., and Landaverde, C. (2013). Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the metabolic syndrome: clinical implications and treatment. Nutr Clin Pract 28, 40–51.
Sato, D., Itami, N., Tasaki, H., Takeo, S., Kuwayama, T., and Iwata, H. (2014). Relationship between mitochondrial DNA copy number and SIRT1 expression in porcine oocytes. PLoS ONE 9, e94488.
Takeda, Y., Kang, H.S., Freudenberg, J., DeGraff, L.M., Jothi, R., and Jetten, A.M. (2014). Retinoic acid-related orphan receptor γ (RORγ): a novel participant in the diurnal regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and insulin sensitivity. PLoS Genet 10, e1004331.
Tsuchiya, H., Ikeda, Y., Ebata, Y., Kojima, C., Katsuma, R., Tsuruyama, T., Sakabe, T., Shomori, K., Komeda, N., Oshiro, S., Okamoto, H., Takubo, K., Hama, S., Shudo, K., Kogure, K., and Shiota, G. (2012). Retinoids ameliorate insulin resistance in a leptin-dependent manner in mice. Hepatology 56, 1319–1330.
Yang, H., Jin, X., Kei Lam, C.W., and Yan, S.K. (2011). Oxidative stress and diabetes mellitus. Clin Chem Lab Med 49, 1773–1782.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371191).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, C., Xu, H., Zhang, Y. et al. Retinoic acid ameliorates high-fat diet-induced liver steatosis through sirt1. Sci. China Life Sci. 60, 1234–1241 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-016-9027-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-016-9027-6