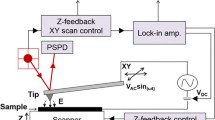
Abstract
The kesterite-structured semiconductor Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 (CZTSSe) is prepared by spin coating a non-hydrazine precursor and annealing at Se atmosphere. Local electrical and optoelectronic properties of the CZTSSe thin-film are explored by Kelvin probe force microscopy and conductive atomic force microscopy. Before and after irradiation, no marked potential bending and very low current flow are observed at GBs, suggesting that GBs behave as a charge recombination site and an obstacle for charge transport. Furthermore, CdS nano-islands are synthesized via successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) method on the surface of CZTSSe. By comparing the work function and current flow change of CZTSSe and CdS in dark and under illumination, we demonstrate photo-induced electrons and holes are separated at the interface of p-n junction and transferred in CdS and CZTSSe, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitzi DB, Gunawan O, Todorov TK, Wang K, Guha S. The path towards a high-performance solution-processed kesterite solar cell. Sol Energ Mat Sol C, 2011, 95: 1421–1436
Green MA, Emery K, Hishikawa Y, Warta W, Dunlop ED. Solar cell efficiency tables (Version 42). Prog Photovolt: Res Appl, 2013, 21: 827–837
Jackson P, Hariskos D, Wuerz R, Wischmann W, Powalla M. Compositional investigation of potassium doped Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells with efficiencies up to 20.8%. Phs Status Solidi RRL, 2014, 8: 219–222
Wang W, Winkler MT, Gunawan O, Gokmen T, Todorov TK, Zhu Y, Mitzi DB. Device characteristics of CZTSSe thin-film solar cells with 12.6% efficienc. Adv Energy Mater, 2014, 4: 1301465
Katagiri H, Sasaguchi N, Hando S, Hoshino S, Ohashi J, Yokota T. Preparation films by and evaluation of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin sulfurization of E-B evaporated precursors. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells, 1997, 49: 407–414
Zoppi G, Forbes I, Miles RW, Dale PJ, Scragg JJ, Peter M. Cu2ZnSnSe4 thin film solar cells produced by selenisation of magnetron sputtered precursors. Prog Photovolt: Res Appl, 2009, 17: 315–319
Wang K, Gunawan O, Todorov T, Shin B, Chey SJ, Bojarczuk NA, Mitzi D, Guha S. Thermally evaporated Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cells. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 97: 143508
Scragg JJ, Dale PJ, Peter LM, Zoppi G, Forbes I. New routes to sustainable photovoltaics: evaluation of Cu2ZnSnS4 as an alternative absorber material. Phys Status Solidi B, 2008, 245: 1772–1778
Moriya K, Tanaka K, Uchiki H. Characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films prepared by photo-chemical deposition. J Appl Phys, 2005, 44: 715–717
Moriya K, Watabe J, Tanaka K, Uchiki H. Characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films prepared by photo-chemical deposition. Phys Status Solidi C, 2006, 3: 2848–2852
Nakayama N, Ito K. Sprayed films of stannite Cu2ZnSnS4. Surf Sci, 1996, 92: 171–175
Todorov T, Kita M, Carda J, Escribano P. Cu2ZnSnS4 films deposited by a soft-chemistry method. Thin Solid Films, 2009, 517: 2541–2544
Steinhagen C, Panthani MG, Akhavan V, Goodfellow B, Koo B, Korgel BA. Synthesis of Cu2ZnSnS4 Nanocrystals for use in low-cost photovoltaics. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131: 12554–12555
Haight R, Barkhouse A, Gunawan O, Shin B, Copel M, Hopstaken M, Mitzi DB. Band alignment at the Cu2ZnSn(SxSe1-x )4/CdS interface. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98: 253502
Chen S, Yang JH, Gong XG, Walsh A, Wei SH. Intrinsic point defects and complexes in the quaternary kesterite semiconductor Cu2ZnSnS4. Phys Rev B, 2010, 81: 245204
Nagoya A, Asahi R, Kresse G. First-principles study of Cu2ZnSnS4 and the related band offsets for photovoltaic applications. J Phys Condens Matter, 2011, 23: 404203
Gloeckler M, Sites JR. Efficiency limitations for wide-band-gap chalcopyrite solar cells. Thin Solid Films, 2005, 480: 241–245
Bär M, Schubert BA, Marsen B, Wilks RG, Pookpanratana S, Blum M, Krause S, Unold T, Yang W, Weinhardt L, Heske C, Schock HW. Liff-like conduction band offset and KCN-induced recombination barrier enhancement at the CdS/Cu2ZnSnS4 thin-film solar cell heterojunction. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 99: 222105
Dong ZY, Li YF, Yao B, Ding ZH, Yang G, Deng R, Fang X, Wei ZP, Liu L. An experimental and first-principles study on band alignments at interfaces of Cu2ZnSnS4/CdS/ZnO heterojunctions. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2014, 47: 075304
Xin H, Reid OG, Ren G, Kim FS, Ginger DS, Jenekhe SA. Polymer nanowire/fullerene bulk heterojunction solar cells: how nanostructure determines photovoltaic properties. ACS Nano, 2010, 4: 1861–1872
Kamkar DA, Wang M, Wudl F, Nguyen TQ. Single nanowire OPV properties of a fullerene-capped P3HT dyad investigated using conductive and photoconductive AFM. ACS Nano, 2012, 6: 1149–1157
Hamadani BH, Jung SY, Haney PM, Richter LJ, Zhitenev NB. Origin of nanoscale variations in photoresponse of an organic solar cell. Nano Lett, 2010, 10: 1611–1617
Ellison DJ, Kim JY, Derek M, Stevens C, Frisbie D. Determination of quasi-fermi levels across illuminated organic donor/acceptor heterojunctions by Kelvin probe force microscopy. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 13802–13805
Douhéret O, Lutsen L, Swinnen A, Breselge M, Vandewal K, Goris L, Manca J. Nanoscale electrical characterization of organic photovoltaic blends by conductive atomic force microscopy. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89: 032107
Spadafora EJ, Demadrille R, Ratier B, Grévin B. Imaging the carrier photogeneration in nanoscale phase segregated organic heterojunctions by Kelvin probe force microscopy. Nano Lett, 2010, 10: 3337–3342
Zeng TW, Ho CC, Tu YC, Tu GY, Wang LY, Su WF. Correlating interface heterostructure, charge recombination, and device efficiency of poly(3-hexyl thiophene)/TiO2 nanorod solar cell. Langmuir, 2011, 27: 15255–15260
Kong J, Lee J, Jeong Y, Kim M, Kang SO, Lee K. Biased internal potential distributions in a bulk-heterojunction organic solar cell incorporated with a TiOx interlayer. Appl Phys Lett, 2012, 100: 213305
Visoly-Fisher I, Cohen SR, Cahen D, Ferekides CS. Electronically active layers and interfaces in polycrystalline devices: cross-section mapping of CdS/CdTe solar cells. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 83: 4924–4926
Lee J, Kong J, Kim H, Kang SO, Lee K. Direct observation of internal potential distributions in a bulk heterojunction solar cell. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 99: 243301
Bergmann VW, Weber SAL, Ramos FJ, Nazeeruddin MK, Grätzel M, Li D, Domanski AL, Lieberwirth I, Ahmad S, Berger R. Real-space observation of unbalanced charge distribution inside a perovskite-sensitized solar cell. Nat Commun, 2014, 5: 5001
Koren E, Berkovitch N, Azriel O, Boag A, Rosenwaks Y, Hemesath ER, Lauhon LJ. Direct measurement of nanowire Schottky junction depletion region. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 99: 223511
Ishii H, Hayashi N, Ito E, Washizu Y, Sugi K, Kimura Y, Niwano M, Ouchi Y, Seki K. Kelvin probe study of band bending at organic semiconductor/metal interfaces: examination of Fermi level alignment. Phys Status Solidi A, 2004, 201: 1075–1094
Wu MC, Liao HC, Cho YC, Hsu CP, Lin TH, Su WF, Spi A, Kukovecz A, Konya Z, Shchukarev A, Sarkar A, Larsson W, Mikkola JP, Mohl M, Toth G, Jantunen H, Valtanen A, Huuhtanen M, Keiski RL, Kordas KJ. Photocatalytic activity of nitrogen-doped TiO2-based nanowires: a photo-assisted Kelvin probe force microscopy study. J Nanopart Res 2013, 16: 1–11
Wang G, Yan Y, Yang X, Li J, Qiao L. Investigation of hydrogen evolution and enrichment by scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy. Electrochem Commun, 2013, 35: 100–103
Palermo V, Palma M, Samorì P. Electronic characterization of organic thin films by kelvin probe force microscopy. Adv Mater, 2006, 18: 145–164
Dominik Z, Andreas S. Force gradient sensitive detection in lift-mode Kelvin probe force microscopy. Nanotechnol, 2011, 22: 075501
Jiang CS, Noufi R, Ramanathan K, AbuShama J, Moutinho H, Al- Jassim M. Electrical modification in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films by chemical bath deposition process of CdS films. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85: 2625–2627
Dang XD, Tamayo AB, Seo J, Hoven CV, Walker B, Nguyen TQ. Nanostructure and optoelectronic characterization of small molecule bulk heterojunction solar cells by photoconductive atomic force microscopy. Adv Funct Mater, 2010, 20: 3314–3321
Chen HY, Lo MKF, Yang G, Monbouquette HG, Yang Y. Nanoparticle- assisted high photoconductive gain in composites of polymer and fullerene. Nat Nanotechnol., 2008, 3: 543–547
Li JB, Chawla V, Clemens BM. Investigating the role of grain boundaries in CZTS and CZTSSe thin film solar cells with scanning probe microscopy. Adv Mater, 2012, 24: 720–723
Shin RH, Jo W, Kim DW, Yun J, Ahn S. Local current-voltage behaviors of preferentially and randomly textured Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin films investigated by conductive atomic force microscopy. Appl Phys A, 2011, 104: 1189–1194
Kim GY, Kim JR, Jo W, Son DH, Kim DH, Kang JK. Nanoscale observation of surface potential and carrier transport in Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 thin films grown by sputtering-based two-step process. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2004, 9: 10
Li J, Mitzi DB, Shenoy VB. Structure and electronic properties of grain boundaries in earth-abundant photovoltaic absorber Cu2ZnSnSe4. ACS Nano, 2011, 5: 8613–8619
Yin WJ, Wu Y, Wei SH, Noufi R, Al-Jassim MM, Yan Y. Engineering grain boundaries in Cu2ZnSnSe4 for better cell performance: a first-principle study. Adv Energy Mater, 2014, 4: 1300712
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Zou, Y., Chen, T. et al. Optoeletronic investigation of Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 thin-films & Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4/CdS interface with scanning probe microscopy. Sci. China Chem. 59, 231–236 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5444-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5444-4