Abstract
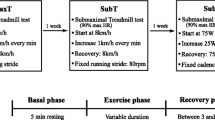
The aim of this paper is to describe and analyse the behaviour of heart rate variability (HRV) during constant-load, high-intensity exercise using a time frequency analysis (Wavelet Transform). Eleven elite cyclists took part in the study (age: 18.6±3.0 years; VO2max: 4.88±0.61 litres·min−1). Initially, all subjects performed an incremental cycloergometer test to determine load power in a constant load-test (379.55±36.02 W; 89.0%). HRV declined dramatically from the start of testing (p <0.05). The behaviour of power spectral density within the LF band mirrored that of total energy, recording a significant decrease from the outset LF peaks fell rapidly thereafter, remaining stable until the end of the test. HF-VHF fell sharply in the first 20 to 30 seconds. The relative weighting (%) of HF-VHF was inverted with the onset of fatigue, [1.6% at the start, 7.1 (p <0.05) at the end of the first phase, and 43.1% (p <0.05) at the end of the test]. HF-VHFpeak displayed three phases: a moderate initial increase, followed by a slight fall, thereafter increasing to the end of the test. The LF/HF-VHF ratio increased at the start, later falling progressively until the end of the first phase and remaining around minimal values until the end of the test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akselrod S D, Gordon D, Ubel F A, Shannon D C, Berger A C, and Cohen R J, Power spectrum analysis of heart rate fluctuations: A quantitative probe of beat-to-beat cardiovascular control, Science, 1981, 213(4504): 220–222.
Pomeranz B, Macauley R J, Caudil M A, et al., Assessment of autonomic function in humans by heart rate spectral analysis, Am. J. Phys. (Heart Circ Physiol), 1985, 248(1): H151–H153.
Perini R and Veicsteinas A, Heart rate variability and autonomic activity at rest and during exercise in various physiological conditions, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol, 2003, 90(3–4): 317–325.
Aubert A E, Spes B, and Beckers F, Heart rate variability in athletes, Sport Med., 2003, 33(12): 889–919.
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology, Heart rate variability, Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use, Eur. Heart J., 1976, 17: 354–381.
Tulppo M P, Makikallio T H, Takala T E, Seppanen T, and Huikuri H V, Quantitative beat-to-beat analysis of heart rate dynamics during exercise, Am J Phys. (Heart Circ Physiol), 1996, 271(1): H244–H252.
Cottin F, Médigue C, Leprêtre L M, Papelier Y, Koralsztein J P, and Billat V, Heart rate variability during exercise performed below and above ventilatory threshold, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc., 2004, 36(4): 594–600.
Pichon A P, De Bisschop C, Rouland M, Denejan A, and Papelier Y, Spectral analysis of heart rate variability during exercise in trained subjects, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc., 2004, 36(10): 1702–1708.
Sumi K, Suzuki S, Matsubara M, Ando Y, and Kobayashi F, Heart rate variability during high-intensity field exercise in female distance runners, Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports, 2006, 16(5): 314–320.
Anosov O, Patzak A, Kononovich Y, and Persson P B, High-frequency oscillations of the heart rate during ramp load reflect the human anaerobic threshold, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol, 2000, 83(4-5): 388–394.
Cottin F, Médigue C, Lopes P, Leprêtre P M, Heubert R, and Billat V, Ventilatory thresholds assessment from heart rate variability during an incremental exhaustive running test, Int. J. Sports Med., 2007, 28(4): 287–294.
Sarmiento S, Variabilidad de la frecuencia cardiaca (VFC), en deportistas, durante la aplicación de cargas incrementales y estables de diferentes intensidades: Un análisis tiempo-frecuencia (Wavelet), Ph. D. Thesis, Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, GC, Spain, 2008.
Bernardi L and Piepoli M F, Autonomic nervous system adaptation during exercise, Ital. Hearth J., 2001, 2(8): 831–839.
Carter J B, Banister E W, and Blaber A P, Effect of endurance exercise on autonomic control of heart rate, Sports Med., 2003, 33(1): 33–46.
Borresen J and Lambert M I, Autonomic control of heart rate during and after exercise: Measurements and implications for monitoring training status, Sport Med., 2008, 38(8): 633–646.
Pichot V, Busso T, Roche F, Garet M, Costes F, Duverney D, Lacour J R, and Barthélémy J C, Autonomic adaptations to intensive and overload training periods: A laboratory study, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc., 2002, 34(10): 1660–1666.
Malpas S C, Neural influences on cardiovascular variability: Possibilities and pitfalls, Am. J. Physiol (Heart Circ Physiol), 2002, 282(1): H6–H20.
Perini R, Milesi S, Fisher N M, Pendergast D R, and Veicsteinas A, Heart rate variability during dynamic exercise in elderly males and females, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol, 2000, 82(1–2): 8–15.
Hirsch J A and Bishop B, Respiratory sinus arrhythmia in humans: How breathing pattern modulates heart rate, Am. J. Physiol, 1981, 241(4): H620–H629.
Casadei B, Cochrane S, Johnston J, Conway J, and Sleight P, Pitfalls in the interpretation of spectral analysis of the heart rate variability during exercise in humans, Acta Physiol Scand, 1995, 153(2): 125–131.
Rowell L B and O’Leary D S, Reflex control of the circulation during exercise: Chemoreflexes and mechanoreflexes, J. Appl. Physiol, 1990, 69(2): 407–418.
Casadei B, Moon J, Johnston J, Caiazza A, and Sleight P, Is respiratory sinus arrhythmia a good index of cardiac vagal tone in exercise? J. Appl. Physiol, 1996, 81(2): 556–564.
Bechbache R R and Duffin J, The entrainment of breathing frequency by exercise rhythm, J. Physiol, 1977, 272(3): 553–561.
Bramble D M and Carrier D R, Running and breathing in mammals, Science, 1983, 219(4582): 251–256.
Kamath M V, Fallen E L, and McKelvie R, Effects of steady state exercise on the power spectrum of heart rate variability, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc., 1991, 23(4): 428–434.
Michelini L C and Stern J E, Exercise-induced neuronal plasticity in central autonomic networks: Role in cardiovascular control, Exp. Physiol, 2009, 94(9): 947–960.
Vanderlei L C, Silva R A, Pastre C M, Azevedo F M, and Godoy M F, Comparison of the Polar S810i monitor and the ECG for the analysis of heart rate variability in the time and frequency domains, Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res., 2008, 41(10): 854–859.
Nunan D, Jakovljevic G, Donovan G, Hodges L D, Sandercock G R, and Brodie D A, Levels of agreement for RR intervals and short-term heart rate variability obtained from the Polar S810 and an alternative system, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol, 2008, 103(5): 529–537.
Mainardi L T, Bianchi A M, and Cerutti S, Time-frequency and time-varying analysis for assessing the dynamic responses of cardiovascular control, Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng., 2002, 30(1–3): 175–217.
Lewis M J, Kingsley M, Short A L, and Simpson K, Influence of high-frequency bandwidth on heart rate variability analysis during physical exercise, Biomed Signal Process Control, 1991, 2(1): 34–39.
Torrence C and Compo G P, A practical guide to wavelet analysis, Bull Am. Met. Soc., 1998, 79: 61–78.
Percival D and Walden A, Wavelet Methods for Time Series Analysis, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2000.
Victor R G, Bertocci L A, Pryor S L, and Nunnally R L, Sympathetic nerve discharge is coupled to muscle cell pH during exercise in humans, J. Clin. Invest., 1988, 82(4): 1301–1305.
Rotto D M, Stebbins C L, and Kaufman M P, Reflex cardiovascular and ventilatory responses to increasing H+ activity in cat hindlimb muscle, J. Appl. Physiol, 1989, 67(1): 256–263.
Sinoway L, Phophet S, Gorman I, Mosher T, Shenberger J, Dolecki M, Briggs R, and Zelis R, Muscle acidosis during static exercise is associated with calf vasoconstriction, J. Appl. Physiol, 1989, 66(1): 429–436.
Vissing J, Vissing S F, MacLean D A, Saltin B, Quistorff B, and Haller R G, Sympathetic activation in exercise is not dependent on muscle acidosis: Direct evidence from studies in metabolic myopathies, J. Clin. Invest., 1998, 101(8): 1654–1660.
Hartley L H, Mason J W, Hogan R P, Jones L G, Kotchen T A, Mougey E H, Wherry F E, Pennington L L, and Ricketts P T, Multiple hormonal responses to graded exercise in relation to physical training, J. Appl. Physiol, 1972, 33: 602–606.
Galbo H, Holst J J, and Christensen N J, Glucagon and plasma catecholamine responses to graded and prolonged exercise in man, J. Appl. Physiol, 1975, 38(1): 70–76.
Mazzeo R S, Catecholamine response to acute and chronic exercise, Med. Sci. Sports Exerc., 1991, 23(7): 839–845.
Yamamoto Y, Hughson R L, and Peterson J C, Autonomic control of heart rate during exercise studied by heart rate variability spectral analysis, J. Appl. Physiol, 1991, 71(3): 1136–1142.
Kannankeril P J, Le F K, Kadish A H, and Goldberger J J, Parasympathetic effects on heart rate recovery after exercise, J. Investig. Med., 2004, 52(6): 394–401.
O’Leary D S, Rossi N F, and Churchill P C, Substantial cardiac parasympathetic activity exists during heavy dynamic exercise in dogs, Am. J. Physiol (Heart Circ Physiol), 1997, 273(5): H2135–H2140.
Potts J T, Shi X R, and Raven P B, Carotid baroreflex responsiveness during dynamic exercise in humans, Am. J. Physiol (Heart Circ Physiol), 1993, 265(6): H1928–H1938.
Papelier Y, Escourrou P, Gauthier J P, and Rowell L B, Carotid baroreflex control of blood pressure and heart rate in men during dynamic exercise, J. Appl. Physiol, 1994, 77(2): 502–506.
Robinson B F, Epstein S E, Beiser G D, and Braunwald E, Control of heart rate by the autonomic nervous system: Studies in man on the interrelations between baroreceptor mechanisms and exercise, Circ. Res., 1996, 19: 400–411.
Nakamura Y, Yamamoto Y, and Muraoka I, Autonomic control of heart rate during physical exercise and fractal dimension of heart rate variability, J. Appl. Physiol, 1993, 74(2): 875–881.
Cottin F, Papelier Y, and Escourrou P, Effects of exercise load and breathing frequency on heart rate and blood pressure variability during dynamic exercise, Int. J. Sports Med., 1999, 20(4): 232–238.
Yamamoto Y, Hughson R L, and Nakamura Y, Autonomic nervous system responses to exercise in relation to ventilatory threshold, Chest, 1992, 101(5): 206S–210S.
Cottin F, Leprêtre P M, Lopes P, Papelier Y, Médigue C, and Billat V, Assessment of ventilatory thresholds from heart rate variability in well-trained subjects during cycling, Int. J. Sports Med., 2006, 27(12): 959–967.
García-Manso J M, Sarmiento S, Martín-González J M, Calderón F J, and Da Silva-Grigoletto M E, Wavelet transform analysis of heart rate variability for determining ventilatory thresholds in cyclists, Rev. Andal. Med. Deporte, 2008, 1(3): 90–97.
Blain G, Meste O, Blain A, and Bermon S, Time-frequency analysis of heart rate variability reveals cardiolocomotor coupling during dynamic cycling exercise in humans, Am. J. Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2009, 296(5): H1651-1659.
Lunt H C, Corbett J, Barwood M J, and Tipton M J, Cycling cadence affects heart rate variability, Physiol Meas, 2011, 32(8): 1133–1145.
Macor F, Fagaard R, and Amery A, Power spectral analysis of RR interval and blood pressure shortterm variability at rest and during dynamic exercise: Comparison between cyclists and controls, Int. J. Sports Med., 1996, 17(3): 175–171.
Niizeki K, Intramuscular pressure-induced inhibition of cardiac contraction: Implications for cardiaclocomotor synchronization, Am. J. Physiol Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol, 2005, 288(3): R645–R650.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper was recommended for publication by Editors FENG Dexing and HAN Jing.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarmiento, S., García-Manso, J.M., Martín-González, J.M. et al. Heart rate variability during high-intensity exercise. J Syst Sci Complex 26, 104–116 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-013-2287-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-013-2287-y