Abstract
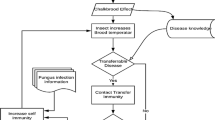
Since the spreading of harmful rumors can deeply endanger a society, it is valuable to investigate strategies that can efficiently prevent hazardous rumor propagation. To conduct this investigation, the authors modify the SIR model to describe rumor propagation on networks, and apply two major immunization strategies, namely, the random immunization and the targeted immunization to the rumor model on a small-world network. The authors find that when the average degree of the network is small, both two strategies are effective and when the average degree is large, neither strategy is efficient in preventing rumor propagation. In the latter case, the authors propose a new strategy by decreasing the credibility of the rumor and applying either the random or the targeted immunization at the same time. Numerical simulations indicate that this strategy is effective in preventing rumor spreading on the small-world network with large average degree.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Albert and A. L. Barabási, Statistical mechanics of complex networks, Rev. Mod. Phys., 2002, 74: 47–97.
M. E. J. Newman, The structure and function of complex networks, SIAM Rev., 2003, 45(2): 167–256.
S. Boccaletti, et al., Complex networks: Structure and dynamics, Physics Reports, 2006, 424: 175–308.
D. J. Watts and S. H. Strogatz, Collective dynamics of ’small-world’ networks, Nature, 1998, 393: 440–442.
M. E. J. Newman and D. J. Watts, Renormalization group analysis of the small-world network model, Physics Letters A, 1999, 263: 341–346.
M. E. J. Newman, Spread of epidemic disease on networks, Phys. Rev. E, 2002, 66: 016128.
Y. Moreno, R. Pastor-Satorras, and A. Vespignani, Epidemic outbreaks in complex heterogeneous networks, Euro. Phys. J. B, 2002, 26(4): 521–529.
M. Kuperman and G. Abramson, Small world effect in an epidemiological model, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2001, 86: 2909–2912.
C. Moore and M. E. J. Newman, Epidemics and percolation in small-world networks, Phys. Rev. E, 2000, 61: 5678–5682.
A. Vazquez, Spreading dynamics on small-world networks with connectivity fluctuations and correlations, Phys. Rev. E, 2006, 74: 056101.
F. Bagnoli, P. Liò, and L. Sguanci, Risk perception in epidemic modeling, Phys. Rev. E, 2007, 76: 061904.
R. Huerta and L. S. Tsimring, Contact tracing and epidemics control in social networks, Phys. Rev. E, 2002, 66: 056115.
R. Pastor-Satorras and A. Vespignani, Immunization of complex networks, Phys. Rev. E, 2002, 65: 036104.
R. Cohen, S. Havlin, and D. Ben-Avraham, Efficient immunization strategies for computer networks and populations, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2003, 91: 247901.
D. J. Daley and J. Gani, Epidemic Modelling, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2000.
D. H. Zanette, Critical behavior of propagation on small-world networks, Phys. Rev. E, 2001, 64: 050901.
D. H. Zanette, Dynamics of rumor propagation on small-world networks, Phys. Rev. E, 2002, 65: 041908.
Y. Moreno, M. Nekovee, and A. F. Pacheco, Dynamics of rumor spreading in complex networks, Phys. Rev. E, 2004, 69: 066130.
Z. H. Liu, Y. C. Lai, and N. Ye, Propagation and immunization of infection on general networks with both homogeneous and heterogeneous components, Phys. Rev. E, 2003, 67: 031911.
D. H. Zanette and M. Kuperman, Effects of immunization in small-world epidemics, Physica A, 2002, 309: 445–452.
N. Madar, et al., Immunization and epidemic dynamics in complex networks, Eur. Phys. J. B, 2004, 38: 269–276.
F. C. Santos, J. F. Rodrigues, and J. M. Pacheco, Epidemic spreading and cooperation dynamics on homogeneous small-world networks, Phys. Rev. E, 2005, 72: 056128.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61070069 and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. Y1100290.
This paper was recommended for publication by Editor Jinhu LÜ.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Jin, X. Preventing rumor spreading on small-world networks. J Syst Sci Complex 24, 449–456 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-011-8303-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-011-8303-1