Abstract
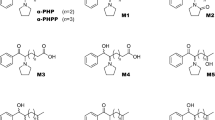
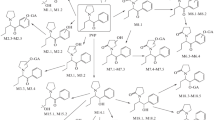
1-Phenyl-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)octan-1-one (PV9) and 16 metabolites, including diastereomers and conjugates, were identified or tentatively detected in human urine by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography–high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry. These urinary metabolites indicated that the metabolic pathways of PV9 include: (1) the reduction of ketone groups to their corresponding alcohols; (2) oxidation of the pyrrolidine ring to the corresponding pyrrolidone; (3) aliphatic oxidation of the terminal carbon atom to the corresponding carboxylate form, possibly through an alcohol intermediate (not detected); and (4) hydroxylation at the penultimate carbon atom to the corresponding alcohols followed by further oxidation to ketones, and combinations of these steps. In addition, results from the quantitative analyses of five phase-I metabolites using newly synthesized authentic standards suggested that the main metabolic pathway includes the aliphatic oxidation of terminal and/or penultimate carbons. Human metabolism of PV9 differed significantly from those of α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone and α-pyrrolidinobutiophenone, suggesting that the main metabolic pathways of α-pyrrolidinophenones significantly change depending on the alkyl chain length of the parent molecule.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Valente MJ, Guedes de Pinho P, de Lourdes Bastos M, Carvalho F, Carvalho M (2014) Khat and synthetic cathinones: a review. Arch Toxicol 88:15–45
Paillet-Loilier M, Cesbron A, Le Boisselier R, Bourgine J, Debruyne D (2014) Emerging drugs of abuse: current perspectives on substituted cathinones. Subst Abuse Rehabil 5:37–52
Cottencin O, Rolland B, Karila L (2014) New designer drugs (synthetic cannabinoids and synthetic cathinones): review of literature. Curr Pharm Des 20:4106–4111
Uchiyama N, Shimokawa Y, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Hakamatsuka T (2014) Chemical analysis of a benzofuran derivative, 2-(2-ethylaminopropyl)benzofuran (2-EAPB), eight synthetic cannabinoids, five cathinone derivatives, and five other designer drugs newly detected in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 32:266–281
Jane MP, Lewis SN (2012) The toxicology of bath salts: a review of synthetic cathinones. J Med Toxicol 8:33–42
Wyman JF, Lavins ES, Engelhart D, Armstrong EJ, Snell KD, Boggs PD, Taylor SM, Norris RN, Miller FP (2013) Postmortem tissue distribution of MDPV following lethal intoxication by “bath salts”. J Anal Toxicol 37:182–185
Meyer MR, Du P, Schuster F, Maurer HH (2010) Studies on the metabolism of the α-pyrrolidinophenone designer drug methylenedioxy-pyrovalerone (MDPV) in rat and human urine and human liver microsomes using GC–MS and LC–high resolution MS and its detectability in urine by GC–MS. J Mass Spectrom 45:1426–1442
Shima N, Katagi M, Kamata H, Matsuta S, Sasaki K, Kamata T, Nishioka H, Miki A, Tatsuno M, Zaitsu K, Ishii A, Sato T, Tsuchihashi H, Suzuki K (2014) Metabolism of the newly encountered designer drug α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone in humans: identification and quantitation of urinary metabolites. Forensic Toxicol 32:59–67
Tyrkkö E, Pelander A, Ketola R, Ojanperä I (2013) In silico and in vitro metabolism studies support identification of designer drugs in human urine by liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:6697–6709
Hasegawa K, Suzuki O, Wurita A, Minakata K, Yamagishi I, Nozawa H, Gonmori K, Watanabe K (2014) Postmortem distribution of α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone and its metabolite in body fluids and solid tissues in a fatal poisoning case measured by LC–MS-MS with the standard addition method. Forensic Toxicol 32:225–234
Sauer S, Peters FT, Haas C, Meyer MR, Fritschi G, Maurer HH (2009) New designer drug α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone (PVP): studies on its metabolism and toxicological detection in rat urine using gas chromatographic/mass spectrometric techniques. J Mass Spectrom 44:952–964
Saito T, Namera A, Osawa M, Aoki H, Inokuchi S (2013) SPME–GC–MS analysis of α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone in blood in a fatal poisoning case. Forensic Toxicol 31:328–332
Namera A, Konuma K, Kawamura M, Saito T, Nakamoto A, Yahata M, Ohta S, Miyazaki S, Shiraishi H, Nagao M (2014) Time-course profile of urinary excretion of intravenously administered α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone and α-pyrrolidinobutiophenone in a human. Forensic Toxicol 32:68–74
Matsuta S, Shima N, Kamata H, Kakehashi H, Nakano S, Sasaki K, Kamata T, Nishioka H, Miki A, Katagi M, Zaitsu K, Sato T, Tsuchihashi H, Suzuki K (2015) Metabolism of the designer drug α-pyrrolidinobutiophenone (α-PBP) in humans: identification and quantification of the phase I metabolites in urine. Forensic Sci Int 249:181–188
Namera A, Urabe S, Saito T, Torikoshi-Hatano A, Shiraishi H, Arima Y, Nagao M (2013) A fatal case of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone poisoning: coexistence of α-pyrrolidinobutiophenone and α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone in blood and/or hair. Forensic Toxicol 31:338–343
Sauer C, Hoffmann K, Schimmel U, Peters FT (2011) Acute poisoning involving the pyrrolidinophenone-type designer drug 4′-methyl-alpha-pyrrolidinohexanophenone (MPHP). Forensic Sci Int 208:20–25
Westphal F, Junge T, Rösner P, Fritschi G, Klein B, Girreser U (2007) Mass spectral and NMR spectral data of two new designer drugs with an alpha-aminophenone structure: 4′-methyl-alpha-pyrrolidinohexanophenone and 4′-methyl-alpha-pyrrolidinobutyrophenone. Forensic Sci Int 169:32–42
Meyer MR, Mauer S, Meyer GM, Dinger J, Klein B, Westphal F, Maurer HH (2014) The in vivo and in vitro metabolism and the detectability in urine of 3′,4′-methylenedioxy-alpha-pyrrolidinobutyrophenone (MDPBP), a new pyrrolidinophenone-type designer drug, studied by GC–MS and LC–MS(n.). Drug Test Anal 6:746–756
Hasegawa K, Wurita A, Minakata K, Gonmori K, Nozawa H, Yamagishi I, Suzuki O, Watanabe K (2014) Identification and quantitation of a new cathinone designer drug PV9 in an “aroma liquid” product, antemortem whole blood and urine specimens, and a postmortem whole blood specimen in a fatal poisoning case. Forensic Toxicol 32:243–250
Hasegawa K, Wurita A, Minakata K, Gonmori K, Nozawa H, Yamagishi I, Watanabe K, Suzuki O (2015) Postmortem distribution of PV9, a new cathinone derivative, in human solid tissues in a fatal poisoning case. Forensic Toxicol 33:141–147
Iversen L, White M, Treble R (2014) Designer psychostimulants: pharmacology and differences. Neuropharmacology 87:59–65
Zaitsu K, Katagi M, Tsuchihashi H, Ishii A (2014) Recently abused synthetic cathinones, α-pyrrolidinophenone derivatives: a review of their pharmacology, acute toxicity, and metabolism. Forensic Toxicol 32:1–8
Marusich JA, Antonazzo KR, Wiley JL, Blough BE, Partilla JS, Baumann MH (2014) Pharmacology of novel synthetic stimulants structurally related to the “bath salts” constituent 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV). Neuropharmacology 87:206–213
Kaizaki A, Tanaka S, Numazawa S (2014) New recreational drug 1-phenyl-2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-1-pentanone (alpha-PVP) activates central nervous system via dopaminergic neuron. J Toxicol Sci 39:1–6
Simmler LD, Buser TA, Donzelli M, Schramm Y, Dieu LH, Huwyler J, Chaboz S, Hoener MC, Liechti ME (2013) Pharmacological characterization of designer cathinones in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 168:458–470
Baumann MH, Partilla JS, Lehner KR, Thorndike EB, Hoffman AF, Holy M, Rothman RB, Goldberg SR, Lupica CR, Sitte HH, Brandt SD, Tella SR, Cozzi NV, Schindler CW (2013) Powerful cocaine-like actions of 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV), a principal constituent of psychoactive ‘bath salts’ products. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:552–562
Strano-Rossi S, Cadwallader AB, de la Torre X, Botrè F (2010) Toxicological determination and in vitro metabolism of the designer drug methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV) by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 24:2706–2714
Springer D, Fritschi G, Maurer HH (2003) Metabolism of the new designer drug α-pyrrolidinopropiophenone (PPP) and the toxicological detection of PPP and 4-methyl-α-pyrrolidinopropiophenone (MPPP) studied in rat urine using gas chromatography mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 796:253–266
Shin H-S, Shin Y-SO, Lee S, Park B-B (1996) Detection and identification of pyrovalerone and its hydroxylated metabolite in the rat. J Anal Toxicol 20:568–572
Minakata K, Yamagishi I, Nozawa H, Hasegawa K, Wurita A, Gonmori K, Suzuki M, Watanabe K, Suzuki O (2015) Determination of new pyrrolidino cathinone derivatives, PVT, F-PVP, MPHP, PV8, PV9 and F-PV9, in human blood by MALDI-Q-TOF mass spectrometry. Forensic Toxicol 33:148–154
Shima N, Katagi M, Kamata H, Matsuta S, Nakanishi K, Zaitsu K, Kamata T, Nishioka H, Miki A, Tatsuno M, Sato T, Tsuchihashi H, Suzuki K (2013) Urinary excretion and metabolism of the newly encountered designer drug 3,4-dimethylmethcathinone in humans. Forensic Toxicol 31:101–112
Zaitsu K, Katagi M, Kamata HT, Kamata T, Shima N, Miki A, Tsuchihashi H, Mori Y (2009) Determination of the metabolites of the new designer drugs bk-MBDB and bk-MDEA in human urine. Forensic Sci Int 188:131–139
Kamata HT, Shima N, Zaitsu K, Kamata T, Miki A, Nishikawa M, Katagi M, Tsuchihashi H (2006) Metabolism of the recently encountered designer drug, methylone, in humans and rats. Xenobiotica 36:709–723
Meyer MR, Wilhelm J, Peters FT, Maurer HH (2010) Beta-keto amphetamines: studies on the metabolism of the designer drug mephedrone and toxicological detection of mephedrone, butylone, and methylone in urine using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 397:1225–1233
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Informed consent was obtained from all healthy individuals included in the study, who supplied several 10 ml each of urine as blank matrix.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shima, N., Kakehashi, H., Matsuta, S. et al. Urinary excretion and metabolism of the α-pyrrolidinophenone designer drug 1-phenyl-2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)octan-1-one (PV9) in humans. Forensic Toxicol 33, 279–294 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-015-0274-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-015-0274-9