Abstract
Purpose
The earthworm species Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei are commonly used in ecotoxicological standard tests. In the present study, we compared the sensitivity of E. fetida with that of two soil-dwelling earthworm species (Aporrectodea caliginosa and Lumbricus terrestris) in order to evaluate the capacity of E. fetida to predict effects of the insecticide imidacloprid. Responses were compared using two endpoints, a biochemical (changes in heat shock protein level (hsp70)) and a behavioural (avoidance behaviour).
Materials and methods
For the hsp70 analysis, the earthworms were exposed for 1, 7 and 14 days and the avoidance tests were conducted using a 48-h incubation time. The tested imidacloprid concentrations ranged from 0.2 to 4 mg kg−1 soil dry weight (DW).
Results and discussion
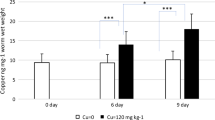
E. fetida showed significant avoidance behaviour towards all test concentrations (0.2, 0.66 and 2 mg kg−1 DW), while L. terrestris and A. caliginosa did not avoid imidacloprid-contaminated soil. Significant changes in hsp70 level in E. fetida occurred at the lowest concentration (0.2 mg kg−1 DW and 14 days), while no effects were observed until exposure to 2 (A. caliginosa; after 1, 7 and 14 days) and 4 mg kg−1 DW (L. terrestris; after 14 days). The present study revealed species-specific differences in sensitivity with E. fetida being the most sensitive species and L. terrestris the least sensitive. Moreover, some of the observed effects were detected at environmentally relevant concentrations.
Conclusions
Our study indicated different sensitivities between closely related species highlighting the importance of using a multiple selection of species in ecotoxicology to predict harmful environmental effects more accurately and minimise underestimations. In the case of testing only one species or one trophic level, a further increase of safety factors is advisable. Moreover, it can be concluded that hsp70 was not a good indicator of imidacloprid toxicity given the low induction for the selected test species. The results of the present study highlight the species dependency of the avoidance test in case of imidacloprid.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arts M-JSJ, Schill RO, Knigge T, Eckwert H, Kammenga JE, Köhler H-R (2004) Stress proteins (hsp70, hsp60) induced in isopods and nematodes by field exposure to metals in a gradient near Avonmouth, UK. Ecotoxicology 13:739–755
Bouché MB (1992) Earthworm species and ecotoxicological studies. In: Greig-Smith PW, Becker H, Edwards PJ, Heimbach F (eds) Ecotoxicology of earthworms. Intercept, Andover, pp 20–35
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein using the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cairns J (1986) The myth of the most sensitive species. Bioscience 36:670–672
Capowiez Y, Bérard A (2006) Assessment of the effects of imidacloprid on the behavior of two earthworm species (Aporrectodea nocturna and Allolobophora icterica) using 2D terrraria. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64:198–206
Capowiez Y, Rault M, Mazzia C, Belzunces L (2003) Earthworm behaviour as a biomarker—a case study using imidacloprid. Pedobiologia 47:542–547
Capowiez Y, Rault M, Costagliela G, Mazzia C (2005) Lethal and sublethal effects of imidacloprid on two earthworm species (Aporrectodea nocturna and Allobophora icterica). Biol Fertil Soils 41:135–143
Capowiez Y, Dittbrenner N, Rault M, Triebskorn R, Hedde M, Mazzia C (2010) Earthworm cast production as a new behavioural biomarker for toxicity testing. Environ Pollut 158:388–393
Christensen O, Mather J (1994) Earthworms as ecotoxicological test-organisms. Bekaempelsesmiddelforskning fra Miljostyrelsen. No. 5. Miljoministeriet Miljostyrelsen, Copenhagen, p 36
Curry JP, Baker GH (1998) Cast production and soil turnover by earthworms in soil cores from South Australian pastures. Pedobiologia 42:283–287
Dean-Ross D (1983) Methods for the assessment of the toxicity of environmental chemicals to earthworms. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 3:48–59
Dittbrenner N, Triebskorn R, Moser I, Capowiez Y (2010) Physiological and behavioural effects of imidacloprid on two ecologically relevant earthworm species (Lumbricus terrestris and Aporrectodea caliginosa). Ecotoxicology 19:1567–1573
Dittbrenner N, Moser I, Triebskorn R, Capowiez Y (2011a) Assessment of short- and long-term effects of imidacloprid on the burrowing behaviour of two earthworm species (Aporrectodea caliginosa and Lumbricus terrestris) by using 2D and 3D post-exposure techniques. Chemosphere 84:1349–1355
Dittbrenner N, Schmitt H, Capowiez Y, Triebskorn R (2011b) Sensitivity of Eisenia fetida in comparison to Aporrectodea caliginosa and Lumbricus terrestris after imidacloprid exposure. Body mass change and histopathology. J Soils Sediments 11:1000–1010
Doving KB (1991) Assessment of animal behaviour as a method to indicate environmental toxicity. Comp Biochem Physiol C 100:247–252
Duzguner V, Erdogan S (2010) Acute oxidant and inflammatory effects of imidacloprid on the mammalian central nervous system and liver in rats. Pestic Biochem Physiol 97:13–18
E.E.C. (2003) Guidance document on terrestrial ecotoxicology under council directive 91/414/EEC. SANCO/10329 Rev. 2
Eckwert H, Alberti G, Köhler H-R (1997) The induction of stress proteins (hsp) in Oniscus asellus (Isopoda) as a molecular marker of multiple heavy metal exposure. I. Principles and toxicological assessment. Ecotoxicology 6:249–262
Edwards CA, Bohlen PJ (1996) Biology and ecology of earthworms. Chapman and Hall, London, p 426
Fitzpatrick LC, Sassani R, Venables BJ, Goven AJ (1992) Comparative toxicity of polychlorinated biphenyls to earthworms Eisenia foetida and Lumbricus terrestris. Environ Pollut 77:65–69
Garcia M, Römbke J, Torres de Brito M, Scheffczyk A (2008) Effects of three pesticides on the avoidance behaviour of earthworms in laboratory tests performed under tropical conditions. Environ Pollut 153:450–456
Gilman AP, Vardanis A (1974) Carbofuran, comparative toxicity and metabolism in the worms Lumbricus terrestris and Eisenia fetida. J Agric Food Chem 22:625–628
Gunn A (1992) The use of mustard to estimate earthworm populations. Pedobiologia 36:65–67
Gupta SK, Sundararaman V (1991) Correlation between burrowing capability and AChE activity in the earthworm, Pheretima posthuma, on exposure to carbaryl. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 46:859–865
Haap T, Köhler H-R (2009) Cadmium tolerance in seven Daphnia magna clones is associated with reduced hsp70 baseline levels and induction. Aquat Toxicol 94:131–137
Hartl UF (1996) Molecular chaperons in cellular protein folding. Nature 381:571–580
Hodge S, Webster KM, Booth L, Hepplethwaite K, O’Halloran K (2000) Non-avoidance of organophosphate insecticides by the earthworm Aporrectodea caliginosa (Lumbricidae). Soil Biol Biochem 32:425–428
Homa J, Olchawa E, Stürzenbaum SR, Morgan AJ, Plytycz B (2005) Early-phase immunodetection of metallothionein and heat shock proteins in extruded earthworm coelomocytes after dermal exposure to metal ions. Environ Pollut 135:275–280
Hund-Rinke K, Lindemann M, Simon M (2005) Experiences with novel approaches in earthworm testing alternatives. J Soils Sediments 5:233–239
ISO (2008) Soil quality—avoidance test for determining the quality of soils and effects of chemicals on behaviour—Part 1: test with earthworms (Eisenia fetida and Eisenia andrei). ISO guideline 17512-1, Geneva
Iwasa T, Motoyama N, Ambrose JT, Roe RM (2004) Mechanism for the differential toxicity of neonicotinoid insecticides in the honey bee, Apis mellifera. Crop Prot 23:371–378
Köhler H-R, Triebskorn R (2004) Stress im Boden: Früherkennung ökotoxikologischer Effekte durch Biomarker. Biol Unserer Zeit 34:240–248
Köhler H-R, Triebskorn R, Stöcker W, Kloetzel P-M, Alberti G (1992) The 70 kD heat shock protein (hsp 70) in soil invertebrates: a possible tool for monitoring environmental toxicants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 22:334–338
Kula H, Kokta C (1992) Side effects of selected pesticides on earthworms under laboratory and field conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 24:1711–1714
Kula H, Larink O (1997) Development and standardization of test methods for the prediction of sublethal effects of chemicals on earthworms. Soil Biol Biochem 29:635–639
Lal OP, Palta RK, Srivastava YNS (2001) Impact of imidacloprid and carbofuran on earthworm castings in okra field. Ann Plant Prot Sci 9:137–138
Lavelle P, Barois I, Martin A, Zaidi Z, Schaefer R (1989) Management of earthworm populations in agro-ecosystems: a possible way to maintain soil quality? In: Clarholm M, Bergström L (eds) Ecology of arable land. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 109–122
Lindquist S, Craig EA (1988) The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet 22:631–677
Little EE (1990) Behavioral toxicology: stimulating challenges for a growing discipline. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:1–2
Luo Y, Zang Y, Zhong Y, Kong Z (1999) Toxicological study of two novel pesticides on earthworm Eisenia foetida. Chemosphere 39:2347–2356
Ma W, Bodt J (1993) Differences in toxicity of the insecticide chlorpyrifos to six species of earthworms (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae) in standardized soil tests. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 50:864–870
Matsuda K, Buckingham SD, Kleier D, Rauh JJ, Grauso M, Sattelle DB (2001) Neonicotinoids: insecticides acting on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:573–579
McCredie T, Parker L (1992) The role of earthworms in Western Australia agriculture. J Agric W Aust 33:160–165
Mostert MA, Schoeman AS, Van der Merwe M (2000) The toxicity of five insecticides to earthworms of the Pheretima group, using an artificial soil test. Pest Manag Sci 58:1093–1097
Mostert MA, Schoeman AS, Van der Merwe M (2002) The relative toxicity of insecticides to earthworms of the Pheretima group (Oligochaeta). Pest Manag Sci 58:446–450
Nadeau D, Corneu S, Plante I, Morrow G, Tanguay RM (2001) Evaluation of Hsp70 as a biomarker of effect of pollutants on the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris. Cell Stress Chaperones 6:153–163
Novais S, Soares AMVM, Amorim MJ (2010) Can avoidance in Enchytraeus albidus be used as a screening parameter for pesticides testing? Chemosphere 79:233–237
OECD (1984) Guidelines for testing of chemicals. 207: earthworm acute toxicity tests. Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
OECD (2004) Guidelines for testing of chemicals. 222: Earthworm reproduction test (Eisenia fetida/Eisenia andrei). Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris
Oi M (1999) Time-dependant sorption of imidacloprid in two different soils. J Agric Food Chem 47:327–332
Olvera-Velona A, Capowiez Y, Mascle O, Ortiz-Hernandez L, Benoit P (2008) Assessment of the toxicity of ethyl-parthion to earthworms (Aporrectodea caliginosa) using behavioural, physiological and biochemical markers. Appl Soil Ecol 40:476–483
Pereira JL, Cantunes SC, Ferreira AC, Goncalves F, Pereira R (2010) Avoidance behaviour of earthworms under exposure to pesticides: is it always chemosensorial? J Environ Sci Health B 45:229–232
Reinecke AJ, Maboeta MS, Vermeulen LA, Reinecke SA (2002) Assessment of lead nitrate and mancozeb toxicity in earthworms using the avoidance response. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 68:779–786
Ryan JA, Hightower LE (1996) Stress proteins as molecular biomarkers for environmental toxicology. In: Feige U, Morimoto RI, Yahara I, Polla B (eds) Stress-inducible cellular responses Birkhauser Verlag, Basel pp 411–424
Sawasdee B, Köhler H-R (2009) Embryo toxicity of pesticides and heavy metals to the ramshorn snail, Marisa cornuarietis (Prosobranchia). Chemosphere 75:1539–1547
Schäfer M (2003) Behavioural endpoints in earthworm ecotoxicology: evaluation of different test systems in soil toxicity assessment. J Soils Sediments 3:79–84
Scheil V, Zürn A, Triebskorn R, Köhler H-R (2010) Embryo development, stress protein (Hsp70) responses and histopathology in zebrafish (Danio rerio) following exposure to nickel chloride, chlorpyrifos and binary mixtures of them. Environ Toxicol 25:83–93
Scherrer E (1992) Behavioural responses as indicator of environmental alterations: approaches, results, developments. J Appl Ichtyol 8:122–131
Scheu S (1987) The role of substrate feeding earthworms (Lumbricidae) for bioturbation in a beechwood soil. Oecologia 72:192–196
Schlesinger MJ (1990) Heat shock proteins. J Biol Chem 265:12111–12114
Scott-Fordsmann JJ, Weeks JM (2000) Biomarkers in earthworms. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 165:117–159
Scullion J, Malik A (2000) Earthworm activity affecting organic matter, aggregation and microbial activity in soils restored after opencast mining for coal. Soil Biol Biochem 32:119–126
Slimak KM (1997) Avoidance response as a sublethal effect of pesticides on Lumbricus terrestris (Oligochaeta). Soil Biol Biochem 29:713–715
Yeardley RB, Lazorchak JM, Gast LC (1996) The potential of an earthworm avoidance test for evaluation of hazardous waste sites. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1532–1537
Zang Y, Zhong Y, Luo Y, Kong ZM (2000) Genotoxicity of two novel pesticides for the earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ Pollut 108:271–278
Zirbes L, Deneubourg JL, Brostaux Y, Haubruge E (2010) A new case of consensual decision: collective movement in earthworms. Ethology 116:546–553
Acknowledgements
The first author would like to thank the FAZIT-Stiftung and Teufel-Stiftung as well as the Evangelisches Studienwerk for financial support. All authors are grateful to Kathy Breitweg for proofreading and to the anonymous reviewers for their meaningful questions and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jörg Römbke
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dittbrenner, N., Capowiez, Y., Köhler, HR. et al. Stress protein response (Hsp70) and avoidance behaviour in Eisenia fetida, Aporrectodea caliginosa and Lumbricus terrestris when exposed to imidacloprid. J Soils Sediments 12, 198–206 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-011-0437-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-011-0437-1