Abstract
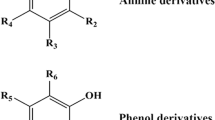
In this study, a chlorophenol (CP) 3D-QSAR model with a double activity (bioaccumulation and degradation) combination was established. 19 CPs were divided into a training set and test set according to the ratio of 4:1. The cross-validation coefficient (q2) and non-cross-validation coefficient (R2) of the model were 0.803 (> 0.5) and 0.925 (> 0.9), respectively, indicating a good stability and predictive ability of the 3D-QSAR. 2,4,6-trichlorophenol (2,4,6-TCP) was used as a target molecule, and 46 derivatives with low comprehensive effects were designed. Out of the 46 derivatives, 11 derivatives were screened to have the good insecticidal and preservative properties. From the perspective of the toxicity of zebrafish, 4 out of the 11 derivatives were found to have lower aquatic toxicity effects. Through the food chain simulation of cyanobacteria-daphnia-swamp-mandarin fish, it was found that the bioaccumulation effect of the four derivatives was lower than that of 2,4, 6-TCP. Finally, molecular dynamics simulation was conducted using 2-CH2NH2 substituted derivatives, and it was found that the degradation effect by laccase (white rot fungi) was significantly improved in the presence of violuric acid, hydroxybenzotriazole, and syringaldehyde. This study can provide theoretical support for the development of environment-friendly technology for emerging pollutants.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Ammeri RW, Simeone GDR, Hidri Y, Abassi MS, Mehri I, Costa S, Hassen A, Rao MA (2022) Combined bioaugmentation and bio-stimulation techniques in bioremediation of pentachlorophenol contaminated forest soil. Chemosphere 290:133359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.133359
Bearden AP, Sinks GD, Schultz TW (1999) Acclimation to sublethal exposures to a model nonpolar narcotic: population growth kinetics and membrane lipid alterations in tetrahymena pyriformis. Aquat Toxicol 46(1):11–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-445X(98)00110-6
Carr DL, Morse AN, Zak JC, Anderson TA (2011) Microbially mediated degradation of common pharmaceuticals and personal care products in soil under aerobic and reduced oxygen conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut 216:633–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0558-y
Chacón FJ, Cayuela ML, Cederlund H, Sánchez-Monedero MA (2022) Overcoming biochar limitations to remediate pentachlorophenol in soil by modifying its electrochemical properties. J Hazard Mater 426:127805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127805
Clarys T, Stuyver T, De Proft F, Geerlings P (2021) Extending conceptual DFT to include additional variables: oriented external electric field. Phys Chem Chem Phys 23(2):990–1005. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cp05277a
Deng W, Zhao W, Yang Y (2022) Degradation and detoxification of chlorophenols with different structure by LAC-4 laccase purified from white-rot fungus Ganoderma lucidum. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(13):8150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19138150
Do Nascimento NR, Nicola SMC, Rezende MOO, Oliveira TA, Öberg G (2004) Pollution by hexachlorobenzene and pentachlorophenol in the coastal plain of São Paulo state. Brazil Geoderma 121(3):221–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2003.11.008
Faber DS, Korn H (1991) Applicability of the coefficient of variation method for analyzing synaptic plasticity. Biophys J 60(5):1288–1294. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82162-2
Gu W, Zhao Y, Li Q, Li Y (2019) Environmentally friendly polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs) derivatives designed using 3D-QSAR and screened using molecular docking, density functional theory and health-based risk assessment. J Hazard Mater 363:316–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.060
Gu W, Zhao Y, Li Q, Li Y (2020) Plant-microorganism combined remediation of polychlorinated naphthalenes contaminated soils based on molecular directed transformation and Taguchi experimental design-assisted dynamics simulation. J Hazard Mater 396:122753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122753
Hendricks R, Pool EJ (2012) The effectiveness of sewage treatment processes to remove faecal pathogens and antibiotic residues. J Environ Sci Heal 47(2):289–297. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2012.637432
Hou Y, Zhao Y, Li Q, Li Y (2020) Highly biodegradable fluoroquinolone derivatives designed using the 3D-QSAR model and biodegradation pathways analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191:110186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110186
Huang Y (2019) Research and field application of molluscicides in China. Chin J Schistosomiasis Control 31(6):679–684. https://doi.org/10.16250/j.32.1374.2019080
Ishihara A, Sawatsubashi S, Yamauchi K (2003) Endocrine disrupting chemicals: interference of thyroid hormone binding to transthyretins and to thyroid hormone receptors. Mol Cell Endocrinol 199(1–2):105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0303-7207(02)00302-7
Karam J, Nicell JA (1997) Potential applications of enzymes in waste treatment. J Chem Technol Biot 69(2):141–153. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4660(199706)69:2%3c141::AID-JCTB694%3e3.0.CO;2-U
Karmen V, Bojana B, Margareta V, Franc P (2003) Effect of the antifungal activity of oxygenated aromatic essential oil compounds on the white-rot Trametes versicolor and the brown-rot Coniophora puteana. Int Biodeter Biodegr 51:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0964-8305(02)00075-6
Keith L, Telliard W (1979) ES&T special report: priority pollutants: I-a perspective view. Environ Sci Technol 13(4):416–423. https://doi.org/10.1021/es60152a601
Li Q, Gu W, Li Y (2019) 3D-QSAR/HQSAR-based analysis of bioconcentration and molecular modification of monophenyl aromatic compounds. Turk J Chem 43(1):286–306. https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-1807-47
Li Q, Qiu Y, Li Y (2020) Molecular design of environment-friendly PAE derivatives based on 3D-QSAR assisted with a comprehensive evaluation method combining toxicity and estrogen activities. Water Air Soil Poll 231(5):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04574-2
Li X, Gu W, Chen B, Zhu Z, Zhang B (2021) Functional modification of HHCB: strategy for obtaining environmentally friendly derivatives. J Hazard Mater 416:126116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126116
Li X, He W, Zhao Y, Chen B, Zhu Z, Kang Q, Zhang B (2022) Dermal exposure to synthetic musks: Human health risk assessment, mechanism, and control strategy. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 236:113463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113463
Likert R, Roslow S, Murphy G (1993) A simple and reliable method of scoring the Thurstone attitude scales. Pers Psychol 46(3):689–690. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6570.1993.tb00893.x
Liu J, Hu J, Wan Y, An W (2006a) Distribution of pentachorophenol in sediments and water from Haihe basin and Bohai bay. Environ Chem 25(5):539–542
Liu Y, Wen B, Shan XQ (2006b) Determination of pentachlorophenol in wastewater irrigated soils and incubated earthworms. Talanta 69(5):1254–1259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2005.12.051
Liu Q, Wang W, Zhang Y, Cui Y, Xu S, Li S (2020) Bisphenol A regulates cytochrome P450 1B1 through miR-27b-3p and induces carp lymphocyte oxidative stress leading to apoptosis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 102:489–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2020.05.009
Mandels M, Reese ET (1965) Inhibition of cellulases. Annu Rev Phytopathol 3(1):85–102. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.py.03.090165.000505
Manna S, Gopakumar DA, Roy D, Saha P, Thomas S (2018) 20-Nanobiomaterials for removal of fluoride and chlorophenols from water. New Polymer Nanocomposites for Environmental Remediation. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 487–498
Martinez M, Baeza J, Freer J, Rodríguez J (2000) Chlorophenol tolerant and degradative bacteria isolated from a river receiving pulp mill discharges. Toxicol Environ Chem 77(3–4):159–170. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772240009358947
Nordin K, Unell M, Jansson JK (2005) Novel 4-chlorophenol degradation gene cluster and degradation route via hydroxyquinol in Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus A6. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):6538–6544. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.11.6538-6544.2005
Persson Y, Lundstedt S, Öberg L, Tysklind M (2007) Levels of chlorinated compounds (CPs, PCPPs, PCDEs, PCDFs and PCDDs) in soils at contaminated sawmill sites in Sweden. Chemosphere 66(2):234–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.05.052
Pollack AZ, Mumford SL, Krall JR, Carmichael A, Andriessen VC, Kannan K, Schisterman EF (2020) Urinary levels of environmental phenols and parabens and antioxidant enzyme activity in the blood of women. Environ Res 186(109507). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109507
Rybnikova V, Singhal N, Hanna K (2017) Remediation of an aged PCP-contaminated soil by chemical oxidation under flow-through conditions. Chem Eng J 314:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.120
Salahinejad M, Ghasemi JB (2014) 3D-QSAR studies on the toxicity of substituted benzenes to tetrahymena pyriformis: CoMFA, CoMSIA and VolSurf approaches. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 105:128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.11.019
Saracci R, Kogevinas M, Winkelmann R, Bertazzi PA, de Mesquita BB, Coggon D, Green LM, Kauppinen T, Labbe KA, Littorin MD, Lynge E, Mathews MD, Neuberger MD, Osman J, Pearce N (1991) Cancer mortality in workers exposed to chlorophenoxy herbicides and chlorophenols. Lancet 338(8774):1027–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(91)91898-5
Singh AK, Chandra R (2019) Pollutants released from the pulp paper industry: aquatic toxicity and their health hazards. Aquat Toxicol 211:202–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.04.007
Tang B, Zou J, Wang X, Li B, Fu D, Thapa S, Sun X, Qi H (2022) Theoretical insights into the gas/heterogeneous phase reactions of hydroxyl radicals with chlorophenols: mechanism, kinetic and toxicity assessment. Sci Total Environ 807:150974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150974
Tong LD, Guo LX, Lv XJ, Li Y (2017) Modification of polychlorinated phenols and evaluation of their toxicity, biodegradation and bioconcentration using three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship models. J Mol Graph Model 71:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmgm.2016.10.012
Tropsha A (2010) Best practices for QSAR model development, validation, and exploitation. Mol Inform 29(6–7):476–488. https://doi.org/10.1002/minf.201000061
Van den Berg KJ (1990) Interaction of chlorinated phenols with thyroxine binding sites of human transthyretin, albumin and thyroid binding globulin. Chem Biol Interact 76(1):63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2797(90)90034-K
Widsten P, Kandelbauer A (2008) Laccase applications in the forest products industry: a review. Enzyme Microb Tech 42(4):293–307. https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.201600033
Yang LZ, Liu M (2020) A double-activity (green algae toxicity and bacterial genotoxicity) 3D-QSAR model based on the comprehensive index method and its application in fluoroquinolones’ modification. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(3):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030942
Yu L, Zhao G, Feng M, Li K, Wen W, Zhang P, Zou X, Zhou H (2013) Toxicological effects of typical chlorophenol chemicals on aquatic organisms. Asian J Ecotoxicology 8(5):658–670. https://doi.org/10.7524/AJE.1673-5897.20130105001
Zhang M, Yin D, Kong F (2008) The changes of serum testosterone level and hepatic microsome enzyme activity of crucian carp (Carassius carassius) exposed to a sublethal dosage of pentachlorophenol. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 71(2):384–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.10.014
Zhang W, Wei Z, Lin C, Wang Z, Zheng Z, Li S (2019) 3D-QSAR study of the phenyl-sulfamic acid derivatives as HPTPβ inhibitors. J Mol Struct 1186:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.02.107
Zhang L, Zhang L, Sun D (2023) Considering zooplankton as a black box in determining PAH concentrations could result in misjudging their bioaccumulation. Environ Pollut 316:120672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120672
Zhao Y, Li Y (2019) Design of environmentally friendly neonicotinoid insecticides with bioconcentration tuning and bi-directional selective toxic effects. J Clean Prod 221:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.156
Zhen YC, Zhang Q, Zhang XY, Zhang GT, Chen XX, Zhao CX (2020) A novel tubular up-flow magnetic film photocatalytic system optimized by main factors control for efficient removal of chlorophenols wastewater. J Hazard Mater 398:122963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122963
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. Zhao Wenjin from Jilin University for providing the Discovery Studio 2020 software to compute the molecular docking.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Shuhai Sun, Zeyang Liu, Qing Li, Yu Li; methodology: Shuhai Sun, Zeyang Liu, Qing Li; formal analysis and investigation: Shuhai Sun, Zeyang Liu, Qing Li; writing—original draft: Shuhai Sun, Zeyang Liu, Qing Li; supervision: Yu Li; resources: Shuhai Sun, Zeyang Liu; visualization: Qing Li; validation: Yu Li; writing—review & editing: Yu Li.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Marcus Schulz
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, S., Liu, Z., Li, Q. et al. Molecular design of environment-friendly chlorophenol (CP) derivatives based on 3D-QSAR assisted with a comprehensive evaluation method combining bioaccumulation and degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 83643–83656 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28322-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28322-1