Abstract
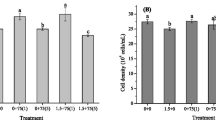
The extensive spread of microplastics (MPs) and nanoplastics (NPs) in the aquatic environment has attracted widespread attention. The toxicity of cadmium (Cd) combined with microplastics (MPs) and nanoplastics (NPs) toward freshwater algae Microcystis aeruginosa (M. aeruginosa) was investigated to evaluate the environmental behavior of the Cd complexation in fresh water. Cd alone has the highest toxicity to algae. Both MPs and NPs also have a negative effect on the growth of algae as individual components due to their adsorption of nutrients and disruption of the alga’s activity in a single MPs/NPs system. Compared with the single system, the toxicity of compound pollution including MPs + Cd and NPs + Cd becomes stronger, which presents a synergistic effect. In the presence of NPs, more extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) appeared, which helped to reduce the toxic effect on the algal cells. Moreover, MPs/NPs + Cd stimulate the production of microcystin-LR (MC-LR) under different treatments. Overall, the aquatic environmental assessment shows potentially elevated risks associated with combined MPs/NPs with Cd, which should be considered.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Anbumani S, Kakkar P (2018) Ecotoxicological effects of microplastics on biota: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:14373–14396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1999-x
Bellingeri A, Bergami E, Grassi G et al (2019) Combined effects of nanoplastics and copper on the freshwater alga Raphidocelis subcapitata. Aquat Toxicol 210:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.02.022
Bellingeri A, Casabianca S, Capellacci S et al (2020) Impact of polystyrene nanoparticles on marine diatom Skeletonema marinoi chain assemblages and consequences on their ecological role in marine ecosystems. Environ Pollut 262:114268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114268
Bhattacharya P, Lin S, Turner JP et al (2010) Physical adsorption of charged plastic nanoparticles affects algal photosynthesis. J Phys Chem C 114:16556–16561. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp1054759
Bhagat J, Nishimura N, Shimada Y (2021) Toxicological interactions of microplastics/nanoplastics and environmental contaminants: current knowledge and future perspectives. J Hazard Mater 405:123913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123913
Canniff PM, Hoang TC (2018) Microplastic ingestion by Daphnia magna and its enhancement on algal growth. Sci Total Environ 633:500–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.176
Cunha C, Faria M, Nogueira N et al (2019) Marine vs freshwater microalgae exopolymers as biosolutions to microplastics pollution. Environ Pollut 249:372–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.046
Chen B, Li F, Liu N et al (2015) Role of extracellular polymeric substances from Chlorella vulgaris in the removal of ammonium and orthophosphate under the stress of cadmium. Bioresource Technol 190:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.04.080
Deng J, Fu D, Hu W et al (2020) Physiological responses and accumulation ability of Microcystis aeruginosa to zinc and cadmium: Implications for bioremediation of heavy metal pollution. Bioresource Technol 303:122963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122963
Feng LJ, Sun XD, Zhu FP et al (2020) Nanoplastics promote microcystin synthesis and release from cyanobacterial Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Sci Technol 54:3386–3394. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b06085
Fu D, Zhang Q, Fan Z, Qi H, Wang Z, Peng L (2019) Aged microplastics polyvinyl chloride interact with copper and cause oxidative stress towards microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. Aquat Toxicol 216:105319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.105319
Hanachi P, Khoshnamvand M, Walker TR, Hamidian AH (2022) Nano-sized polystyrene plastics toxicity to microalgae Chlorella vulgaris: toxicity mitigation using humic acid. Aquat Toxicol 245:106123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2022.106123
Hartmann NB, Hüffer T, Thompson RC et al (2019) Are we speaking the same language? Recommendations for a definition and categorization framework for plastic debris. Environ Sci Technol 53:1039–1047. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b05297
Hernandez LM, Yousefi N, Tufenkji N (2017) Are there nanoplastics in your personal care products? Environ Sci Technol Lett 4:280–285. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.7b00187
He XX, Xie CJ, Ma YH et al (2019) Size-dependent toxicity of ThO2 nanoparticles to green algae Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Aquat Toxicol 209:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.02.003
Horcsik ZT, Kovács R, Láposi R et al (2007) Effect of chromium on photosystem 2 in the unicellular green alga, Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Photosynthetica 45:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-007-0010-8
Huang D, Tao JX, Cheng M et al (2021) Microplastics and nanoplastics in the environment: macroscopic transport and effects on creatures. J Hazard Mater 407:124399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124399
Jambeck JR, Geyer R, Wilcox C et al (2015) Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Sci 347:768–771. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260352
Jeong CB, Won EJ, Kang HM et al (2016) Microplastic size-dependent toxicity, oxidative stress induction, and p-JNK and p-p38 activation in the monogonont rotifer (Brachionus koreanus). Environ Sci Technol 50:8849. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b01441
Lee WS, Cho HJ, Kim E et al (2019) Bioaccumulation of polystyrene nanoplastics and their effect on the toxicity of Au ions in zebrafish embryos. Nanoscale 11:3173–3185. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr09321k
Liao Y, Jiang X, Xiao Y, Li M (2020) Exposure of microalgae Euglena gracilis to polystyrene microbeads and cadmium: perspective from the physiological and transcriptional responses. Aquat Toxicol 228:105650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2020.105650
Li F, Kuang Y, Liu N, Ge F (2019) Extracellular polymeric substrates of Chlorella vulgaris F1068 weaken stress of cetyltrimethyl ammonium chloride on ammonium uptake. Sci Total Environ 661:678–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.472
Lin L, Zuo LZ, Peng JP et al (2018) Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in an urban river: a case study in the Pearl River along Guangzhou City, China. Sci Total Environ 644:375–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.327
Liu G, Jiang R, You J, Muir DCG, Zeng EY (2020) Microplastic impacts on microalgae growth: effects of size and humic acid. Environ Sci Technol 54:1782–1789. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b06187
Lu K, Qiao R, An H, Zhang Y (2018a) Influence of microplastics on the accumulation and chronic toxic effects of cadmium in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 202:514–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.145
Lu T, Zhu Y, Xu J et al (2018b) Evaluation of the toxic response induced by azoxystrobin in the non-target green alga Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Environ Pollut 234:379–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.11.081
Ma Y, Huang A, Cao S et al (2016) Effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on toxicity, bioaccumulation, and environmental fate of phenanthrene in fresh water. Environ Pollut 219:166–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.10.061
Mao Y, Ai H, Chen Y et al (2018) Phytoplankton response to polystyrene microplastics: perspective from an entire growth period. Chemosphere 208:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.170
Miao L, Hou J, You G, Liu Z, Qu H (2019) Acute effects of nanoplastics and microplastics on periphytic biofilms depending on particle size, concentration and surface modification. Environ Pollut 255:113300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113300
Middepogu A, Hou J, Gao X, Lin DH (2018) Effect and mechanism of TiO2 nanoparticles on the photosynthesis of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 161:497–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.027
Morelli E, Gabellieri E, Bonomini A et al (2018) TiO2 nanoparticles in seawater: aggregation and interactions with the green alga Dunaliella tertiolecta. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:184–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.10.024
Moy NJ, Dodson J, Tassone SJ, Bukaveckas PA, Bulluck LP (2016) Biotransport of algal toxins to riparian food webs. Environ Sci Technol 50:10007–10014. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02760
Naveed S, Li C, Lu X et al (2019) Microalgal extracellular polymeric substances and their interactions with metal(loid)s: a review. Crit Revi Environ Sci Technol 34:1769–1802. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1583052
Nava V, Leoni B (2021) A critical review of interactions between microplastics, microalgae and aquatic ecosystem function. Water Res 188:116476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116476
Ni L, Rong S, Gu G et al (2018) Inhibitory effect and mechanism of linoleic acid sustained-release microspheres on Microcystis aeruginosa at different growth phases. Chemosphere 212:654–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.08.045
OECD 201 (2011) Test No. 201: Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 2. OECD Publishing Paris. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264069923-en
Peng L, Fu D, Qi H, Lan CQ, Yu H, Ge C (2020) Micro-and nano-plastics in marine environment: source, distribution and threats—a review. Sci Total Environ 698:134254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134254
Prata JC, da Costa JP, Lopes I, Duarte AC, Rocha-Santos T (2019) Effects of microplastics on microalgae populations: a critical review. Sci Total Environ 665:400–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.132
Rist S, Baun A, Hartmann NB (2017) Ingestion of micro- and nanoplastics in Daphnia magna – quantification of body burdens and assessment of feeding rates and reproduction. Environ Pollut 228:398–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.048
Sandra R, Nadia C, Bodil KL, Kit G, Alejandro B (2018) Combined effects of microplastics and chemical contaminants on the organ toxicity of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Res 162:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.12.019
Samadani M, Dewez D (2018) Cadmium accumulation and toxicity affect the extracytoplasmic polyphosphate level in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 166:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.09.094
Samadani M, Perreault F, Oukarroum A, David D (2018) Effect of cadmium accumulation on green algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and acid-tolerant Chlamydomonas CPCC 121. Chemosphere 191:174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.017
Sendra M, Yeste MP, Gatica JM, Garridoa M, Blasco J (2017) Homoagglomeration and heteroagglomeration of TiO2, in nanoparticle and bulk form, onto freshwater and marine microalgae. Sci Total Environ 592:403–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.127
Shen L, Li Z, Wang J et al (2018) Characterization of extracellular polysaccharide/protein contents during the adsorption of Cd (II) by Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:20713–20722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2163-3
Shiu RF, Vazquez CI, Chiang CY et al (2020) Nano- and microplastics trigger secretion of protein-rich extracellular polymeric substances from phytoplankton - ScienceDirect. Sci Total Environ 748:141469. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141469
Si M, Zhou K, Yang K, Lin D (2015) Heteroagglomeration of oxide nanoparticles with algal cells: effects of particle type, ionic strength and pH. Environ Sci Technol 49:932–939. https://doi.org/10.1021/es504730k
Sjollema SB, Redondo-Hasselerharm P, Leslie HA et al (2016) Do plastic particles affect microalgal photosynthesis and growth? Aquat Toxicol 170:259–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.12.002
Summers S, Henry T, Gutierrez T (2018) Agglomeration of nano- and microplastic particles in seawater by autochthonous and de novo-produced sources of exopolymeric substances. Mar Pollut Bull 130:258–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.03.039
Thiagarajan V, Iswarya V, Abraham JP et al (2019) Influence of differently functionalized polystyrene microplastics on the toxic effects of P25 TiO2 NPs towards marine algae Chlorella sp. Aquat Toxicol 207:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2018.12.014
Ting Z, Li JT, Wen QH, Jiang TW (2019) The interactions between micro polyvinyl chloride (mPVC) and marine dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi: The inhibition of growth, chlorophyll and photosynthetic efficiency. Environ Pollut 247:883–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.01.114
Wang Q, Wang JXX, Zhang Y, at el, (2020) The toxicity of virgin and UV-aged PVC microplastics on the growth of freshwater algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Sci Total Environ 749:141603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141603
Wang S, Li Q, Huang S, Zhao W, Zheng Z (2021) Single and combined effects of microplastics and lead on the freshwater algae Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 208:111664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111664
Wang B, Zhang L, Bae SC, Granick S (2008) Nanoparticleinduced surface reconstruction of phospholipid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:18171–18175. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0807296105
Wei H, Biao S, Jie L et al (2021) Microplastics and associated contaminants in the aquatic environment: a review on their ecotoxicological effects, trophic transfer, and potential impacts to human health. J Hazard Mater 405:124187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124187
Wu Y, Guo P, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Xie S, Deng J (2019) Effect of microplastics exposure on the photosynthesis system of freshwater algae. J Hazard Mater 374:219–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.04.039
Wu D, Wang T, Wang J, Jiang LJ, Yin Y (2020) Size-dependent toxic effects of polystyrene microplastic exposure on Microcystis aeruginosa growth and microcystin production. Sci Total Environ 761:143265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143265
Wu G, Cheng J, Wei J et al (2021) Growth and photosynthetic responses of Ochromonas gloeopara to cadmium stress and its capacity to remove cadmium. Environ Pollut 273:116496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116496
Xu D, Xiao Y, Pan H, Mei Y (2019) Toxic effects of tetracycline and its degradation products on freshwater green algae. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:43–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.063
Yan Z, Xu LM, Zhang WM et al (2021) Comparative toxic effects of microplastics and nanoplastics on Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: growth inhibition, oxidative stress, and cell morphology. J Water Process Eng 43:102291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102291
Yeung ACY, D’Agostino PM, Poljak A et al (2016) Physiological and proteomic responses of continuous cultures of Microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806 to changes in iron bioavailability and growth rate. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:5918–5929. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01207-16
Zhang C, Chen X, Wang J, Tan L (2017) Toxic effects of microplastic on marine microalgae Skeletonema costatum: interactions between microplastic and algae. Environ Pollut 220:1282–1288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.11.005
Zhang Q, Qu Q, Lu T et al (2018) The combined toxicity effect of nanoplastics and glyphosate on Microcystis aeruginosa growth. Environ Pollut 243:1106–1112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.073
Zhang J, Jiang L, Wu D, Yin Y, Guo H (2020) Effects of environmental factors on the growth and microcystin production of Microcystis aeruginosa under TiO2 nanoparticles stress. Sci Total Environ 734:139443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139443
Zhou K, Hu Y, Zhang L, Yang K, Lin D (2016) The role of exopolymeric substances in the bioaccumulation and toxicity of Ag nanoparticles to algae. Sci Rep 6:32998. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32998
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the participants.
Funding
The work was financially supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51808002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qiongjie Wang: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, data curation, writing—review and editing. Jinxiaoxue Wang: investigation, formal analysis, visualization, software. Huijuan Chen: formal analysis, software, investigation, data. Yangyang Zhang: investigation, formal analysis, visualization, software.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Vitor Vasconcelos
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• MPs/NPs combined with Cd showed a significant toxicity effect on M. aeruginosa.
• There was no significant difference in toxicity between MPs and NPs in the combined system.
• The content of protein in EPS had an impact on the toxicity of pollutants.
• MC-LR of alga was lower in the presence of MPs/NPs compared to Cd alone.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wang, J., Chen, H. et al. Toxicity effects of microplastics and nanoplastics with cadmium on the alga Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 17360–17373 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23278-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23278-0