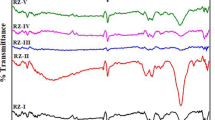
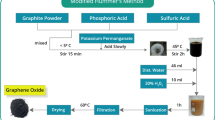
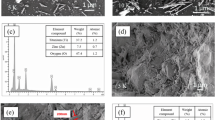
Abstract
Here, silica sand–supported heterojunction composite of nano zinc oxide (nZnO) and graphene oxide nanosheet (nZnO-GO@SS) was prepared, and its potential as an efficient photocatalyst for the degradation of methylene blue (MB) and Rhodamine-B (Rh-B) under sunlight was demonstrated. Transmission electron microscopy confirmed the uniform distribution of spherically shaped nZnO of average size of approximately 8 nm over graphene oxide nanosheet (GO) in the composites. Photodegradation yields of 95.3% and 97.5% for 100 ppm of MB and Rh-B dye within 150 and 220 min, respectively, were achieved under sunlight by the prepared nanocatalyst (nZnO-GO), while sand microparticle–supported nanocatalyst (nZnO-GO@SS) demonstrated faster degradation of MB and Rh-B, i.e., within 120 and 160 min, respectively. Furthermore, when the recyclability of the photocatalyst was studied, the nZnO-GO exhibited more than 80% degradation efficiency after five cycles for both the dyes and nZnO-GO@SS demonstrated 10% higher (~90%) removal capability after five cycles of reuse. Furthermore, the antibacterial assay showed complete inactivation of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus bacterial strain by nZnO-GO@SS. Hence, our proposed strategy for the removal of toxic dyes from the aquatic environment under sunlight proved that sand microparticle–supported nanocatalyst (nZnO-GO@SS) might be a superior, cost-effective, and suitable photocatalytic system for industrial applications toward toxic dye removal and decontamination from industrial wastewater.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Majority of the data were presented in this manuscript and its supplementary information file. Additional raw data may be made available upon request.
References
Abdolhosseinzadeh S, Asgharzadeh H, Sadighikia S, Khataee A (2016) UV-assisted synthesis of reduced graphene oxide–ZnO nanorod composites immobilized on Zn foil with enhanced photocatalytic performance. Res Chem Intermed 42(5):4479–4496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-015-2291-z
Afsharpour M, Amoee S (2022) Porous biomorphic silica@ZnO nanohybrids as the effective photocatalysts under visible light. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(33):49784–49795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19377-7
Ahmad M, Ahmed E, Hong ZL, Xu JF, Khalid NR, Elhissi A, Ahmed W (2013) A facile one-step approach to synthesizing ZnO/graphene composites for enhanced degradation of methylene blue under visible light. Appl Surf Sci 274:273–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.03.035
Ahmad M, Yousaf M, Wang S, Cai W, Sang L, Li Z, Zhao Z-P (2022) Development of rapid CO2 utilizing microbial ecosystem onto the novel & porous FPUF@nZVI@TAC@ASP hybrid for green coal desulphurization. Chem Eng J 433:134361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.134361
Akyıldırım O, Yüksek H, Saral H, Ermiş İ, Eren T, Yola ML (2016) Platinum nanoparticles supported on nitrogen and sulfur-doped reduced graphene oxide nanomaterial as highly active electrocatalysts for methanol oxidation. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 27(8):8559–8566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4873-y
Alamdari S, Ghamsari MS, Afarideh H, Mohammadi A, Geranmayeh S, Tafreshi MJ et al (2019) Preparation and characterization of GO-ZnO nanocomposite for UV detection application. Opt Mater 92:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2019.04.041
Ali MA, Idris MR, Quayum ME (2013) Fabrication of ZnO nanoparticles by solution-combustion method for the photocatalytic degradation of organic dye. J Nanostruct Chem 3(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-8865-3-36
Ani IJ, Akpan UG, Olutoye MA, Hameed BH (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of pollutants in petroleum refinery wastewater by TiO2- and ZnO-based photocatalysts: Recent development. J Clean Prod 205:930–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.189
Atar N, Eren T, Yola ML (2015) Ultrahigh capacity anode material for lithium ion battery based on rod gold nanoparticles decorated reduced graphene oxide. Thin Solid Films 590:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2015.07.075
Atchudan R, Edison TNJI, Perumal S, Karthikeyan D, Lee YR (2016) Facile synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles decorated graphene oxide composite via simple solvothermal route and their photocatalytic activity on methylene blue degradation. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 162:500–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.07.019
Atchudan R, Edison TNJI, Chakradhar D, Karthik N, Perumal S, Lee YR (2018) One-pot dual product synthesis of hierarchical Co3O4@N-rGO for supercapacitors, N-GDs for label-free detection of metal ion and bio-imaging applications. Ceram Int 44(3):2869–2883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.034
Azmina MS, Md Nor R, Rafaie HA, Razak NSA, Sani SFA, Osman Z (2017) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles grown on porous silica microparticles. Appl Nanosci 7(8):885–892. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-017-0626-3
Bai J, Zhong X, Jiang S, Huang Y, Duan X (2010) Graphene nanomesh. Nat Nanotechnol 5(3):190–194. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2010.8
Bai L, Liu L, Pang J, Chen ., Wei M, Wu Y, … Wang B (2022). N,P-codoped carbon quantum dots-decorated TiO2 nanowires as nanosized heterojunction photocatalyst with improved photocatalytic performance for methyl blue degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 29(7), 9932–9943. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16295-y
Balasubramani V, Sureshkumar S, Rao TS, Sridhar TM (2019) Impedance spectroscopy-based reduced graphene oxide-incorporated ZnO composite sensor for H2S investigations. ACS Omega 4(6):9976–9982. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b00754
Ban DK, Paul S (2016) Nano zinc oxide inhibits fibrillar growth and suppresses cellular toxicity of lysozyme amyloid. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(46):31587–31601. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b11549
Chakrabarti S, Dutta BK (2004) Photocatalytic degradation of model textile dyes in wastewater using ZnO as semiconductor catalyst. J Hazard Mater 112(3):269–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.05.013
Chauhan PS, Kant R, Rai A, Gupta A, Bhattacharya S (2019) Facile synthesis of ZnO/GO nanoflowers over Si substrate for improved photocatalytic decolorization of MB dye and industrial wastewater under solar irradiation. Mater Sci Semicond Process 89:6–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2018.08.022
Chen W, Zhang N, Zhang MY, Zhang XT, Gao H, Wen J (2014) Controllable growth of ZnO–ZnSe heterostructures for visible-light photocatalysis. CrystEngComm 16(6):1201–1206. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CE42068J
Chen G, Sun H, Hou S (2016) Electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of myoglobin immobilized in sulfonated graphene oxide and Nafion films. Anal Biochem 502:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.03.003
Chung C, Kim Y-K, Shin D, Ryoo S-R, Hong BH, Min D-H (2013) Biomedical applications of graphene and graphene oxide. Acc Chem Res 46(10):2211–2224. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar300159f
Darvishi-Farash S, Afsharpour M, Heidarian J (2021) Novel siligraphene/g-C3N4 composites with enhanced visible light photocatalytic degradations of dyes and drugs. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(5):5938–5952. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10969-9
Das S, Somu P, Paul S (2021) Visible light induced efficient photocatalytic degradation of azo dye into nontoxic byproducts by CdSe quantum dot conjugated nano graphene oxide. J Mol Liq 340:117055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117055
Das S, Mondal US, Paul S (2022a) Nanophytoremediation technology: A better approach for environmental remediation of toxic metals and dyes from water. In: Kumar V, Shah MP, Kumar Shahi S (eds) Phytoremediation technology for the removal of heavy metals and other contaminants from soil and water, vol 21 Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 459–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-85763-5.00002-7
Das S, Singh V, Paul S (2022b) Surface conjugation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on nano-graphene oxide enhances photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes under sunlight. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:40226–40240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-18796-w
Fan H, Zhao X, Yang J, Shan X, Yang L, Zhang Y, … Gao M (2012). ZnO–graphene composite for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. Catal Commun, 29, 29–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2012.09.013
Gao P, Ng K, Sun DD (2013) Sulfonated graphene oxide–ZnO–Ag photocatalyst for fast photodegradation and disinfection under visible light. J Hazard Mater 262:826–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.09.055
Ghaderi A, Abbasi S, Farahbod F (2018) Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic performance of modified ZnO nanoparticles with SnO2 nanoparticles. Mater Res Express 5(6):65908. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aacd40
Goktas S, Goktas A (2021) A comparative study on recent progress in efficient ZnO based nanocomposite and heterojunction photocatalysts: a review. J Alloys Compd 863:158734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158734
Hejazi I, Hajalizadeh B, Seyfi J, Sadeghi GMM, Jafari S-H, Khonakdar HA (2014) Role of nanoparticles in phase separation and final morphology of superhydrophobic polypropylene/zinc oxide nanocomposite surfaces. Appl Surf Sci 293:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.12.112
Hossain MM, Ku B-C, Hahn JR (2015) Synthesis of an efficient white-light photocatalyst composite of graphene and ZnO nanoparticles: application to methylene blue dye decomposition. Appl Surf Sci 354:55–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.01.191
Huang K, Li YH, Lin S, Liang C, Wang H, Ye CX, … Lei M (2014). A facile route to reduced graphene oxide–zinc oxide nanorod composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity. Powder Technolo 257, 113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2014.02.047
Idris NJ, Bakar SA, Mohamed A, Muqoyyanah M, Othman MHD, Mamat MH, … Soga T (2021). Photocatalytic performance improvement by utilizing GO_MWCNTs hybrid solution on sand/ZnO/TiO2-based photocatalysts to degrade methylene blue dye. Environ Sci Pollut Res, 28(6), 6966–6979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10904-y
Kavitha R, Kumar SG (2019) A review on plasmonic Au-ZnO heterojunction photocatalysts: preparation, modifications and related charge carrier dynamics. Mater Sci Semicond Process 93:59–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2018.12.026
Khan S, Sadiq M, Muhammad N (2022) Enhanced photocatalytic potential of TiO2 nanoparticles in coupled CdTiO2 and ZnCdTiO2 nanocomposites. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19807-6
Khataee AR, Kasiri MB (2010) Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes in the presence of nanostructured titanium dioxide: influence of the chemical structure of dyes. J Mol Catal A Chem 328(1):8–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2010.05.023
Kumar A, Khan M, He J, Lo IMC (2020) Visible–light–driven magnetically recyclable terephthalic acid functionalized g−C3N4/TiO2 heterojunction nanophotocatalyst for enhanced degradation of PPCPs. Appl Catal B Environ 270:118898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.118898
Lee J-E, Khoa NT, Kim SW, Kim EJ, Hahn SH (2015) Fabrication of Au/GO/ZnO composite nanostructures with excellent photocatalytic performance. Mater Chem Phys 164:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.08.017
Lei C, Pi M, Jiang C, Cheng B, Yu J (2017) Synthesis of hierarchical porous zinc oxide (ZnO) microspheres with highly efficient adsorption of Congo red. J Colloid Interface Sci 490:242–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.11.049
Li Y, Zhang H, Liu P, Wang D, Li Y, Zhao H (2013) Cross-linked g-C3N4/rGO nanocomposites with tunable band structure and enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Small 9(19):3336–3344. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201203135
Mao B, Sidhureddy B, Thiruppathi AR, Wood PC, Chen A (2020) Efficient dye removal and separation based on graphene oxide nanomaterials. New J Chem 44(11):4519–4528. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NJ05895H
Maruthupandy M, Qin P, Muneeswaran T, Rajivgandhi G, Quero F, Song J-M (2020) Graphene-zinc oxide nanocomposites (G-ZnO NCs): synthesis, characterization and their photocatalytic degradation of dye molecules. Mater Sci Eng B 254:114516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2020.114516
Mitch WA, Gerecke AC, Sedlak DL (2003) A N-Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) precursor analysis for chlorination of water and wastewater. Water Res 37(15):3733–3741. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00289-6
Mohamed Isa ED, Che Jusoh NW, Hazan R, Shameli K (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange using pullulan-mediated porous zinc oxide microflowers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(5):5774–5785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10939-1
Mohsin M, Bhatti IA, Ashar A, Khan MW, Farooq MU, Khan H, … Mahmood N (2021). Iron-doped zinc oxide for photocatalyzed degradation of humic acid from municipal wastewater. Appl Mater Today, 23, 101047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2021.101047
Murali A, Sarswat PK, Free ML (2020) Minimizing electron-hole pair recombination through band-gap engineering in novel ZnO-CeO2-rGO ternary nanocomposite for photoelectrochemical and photocatalytic applications. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(20):25042–25056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08990-z
Nemiwal M, Zhang TC, Kumar D (2021) Recent progress in g-C3N4, TiO2 and ZnO based photocatalysts for dye degradation: strategies to improve photocatalytic activity. Sci Total Environ 767:144896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144896
Nguyen CH, Tran ML, Van Tran TT, Juang R-S (2020) Enhanced removal of various dyes from aqueous solutions by UV and simulated solar photocatalysis over TiO2/ZnO/rGO composites. Sep Purif Technol 232:115962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115962
Owen G, Bandi M, Howell JA, Churchouse SJ (1995) Economic assessment of membrane processes for water and waste water treatment. J Membr Sci 102:77–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/0376-7388(94)00261-V
Panda D, Tseng T-Y (2013) One-dimensional ZnO nanostructures: fabrication, optoelectronic properties, and device applications. J Mater Sci 48(20):6849–6877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7541-0
Pare B, Jonnalagadda SB, Tomar H, Singh P, Bhagwat VW (2008) ZnO assisted photocatalytic degradation of acridine orange in aqueous solution using visible irradiation. Desalination 232(1):80–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.01.007
Pithan F, Staudt-Bickel C, Lichtenthaler RN (2002) Synthesis of highly fluorinated copolyimide membranes for the removal of high boiling organics from process water and wastewater by pervaporation. Desalination 148(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0011-9164(02)00643-4
Priyadarsini S, Mohanty S, Mukherjee S, Basu S, Mishra M (2018) Graphene and graphene oxide as nanomaterials for medicine and biology application. J Nanostruct Chem 8(2):123–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40097-018-0265-6
Rajakumaran R, Boddu V, Kumar M, Shalaby MS, Abdallah H, Chetty R (2019) Effect of ZnO morphology on GO-ZnO modified polyamide reverse osmosis membranes for desalination. Desalination 467:245–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2019.06.018
Saravanan R, Karthikeyan S, Gupta VK, Sekaran G, Narayanan V, Stephen A (2013) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of ZnO/CuO nanocomposite for the degradation of textile dye on visible light illumination. Mater Sci Eng C 33(1):91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2012.08.011
Sharma S, Bhattacharya A (2017) Drinking water contamination and treatment techniques. Appl Water Sci 7(3):1043–1067. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0455-7
Sharma M, Sondhi H, Krishna R, Srivastava SK, Rajput P, Nigam S, Joshi M (2020) Assessment of GO/ZnO nanocomposite for solar-assisted photocatalytic degradation of industrial dye and textile effluent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(25):32076–32087. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08849-3
Shaw R, Sharma R, Tiwari S, Tiwari SK (2016) Surface engineered zeolite: an active interface for rapid adsorption and degradation of toxic contaminants in water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(19):12520–12527. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b01754
Somu P, Kannan U, Paul S (2019) Biomolecule functionalized magnetite nanoparticles efficiently adsorb and remove heavy metals from contaminated water. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 94(6):2009–2022. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5984
Song Z, Williams CJ, Edyvean RGJ (2000) Sedimentation of tannery wastewater. Water Res 34(7):2171–2176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00358-9
Stoller MD, Park S, Zhu Y, An J, Ruoff RS (2008) Graphene-based ultracapacitors. Nano Lett 8(10):3498–3502. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl802558y
Sun J-H, Dong S-Y, Feng J-L, Yin X-J, Zhao X-C (2011) Enhanced sunlight photocatalytic performance of Sn-doped ZnO for Methylene Blue degradation. J Mol Catal A Chem 335(1):145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2010.11.026
Tichonovas M, Krugly E, Racys V, Hippler R, Kauneliene V, Stasiulaitiene I, Martuzevicius D (2013) Degradation of various textile dyes as wastewater pollutants under dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment. Chem Eng J 229:9–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.095
Uddin MT, Nicolas Y, Olivier C, Toupance T, Servant L, Müller MM, … Jaegermann W (2012). Nanostructured SnO2–ZnO heterojunction photocatalysts showing enhanced photocatalytic activity for the degradation of organic dyes. Inorg Chem, 51(14), 7764–7773. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic300794j
Uma R, Ravichandran K, Sriram S, Sakthivel B (2017) Cost-effective fabrication of ZnO/g-C3N4 composite thin films for enhanced photocatalytic activity against three different dyes (MB, MG and RhB). Mater Chem Phys 201:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.08.015
Varadavenkatesan T, Lyubchik E, Pai S, Pugazhendhi A, Vinayagam R, Selvaraj R (2019) Photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B by zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized using the leaf extract of Cyanometra ramiflora. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 199:111621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.111621
Varnagiris S, Urbonavicius M, Sakalauskaite S, Daugelavicius R, Pranevicius L, Lelis M, Milcius D (2020) Floating TiO2 photocatalyst for efficient inactivation of E. coli and decomposition of methylene blue solution, Science of The Total Environment. 720:137600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137600
Venkatesh N, Aravindan S, Ramki K, Murugadoss G, Thangamuthu R, Sakthivel P (2021) Sunlight-driven enhanced photocatalytic activity of bandgap narrowing Sn-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(13):16792–16803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11763-3
Xiao J, Lv W, Xie Z, Tan Y, Song Y, Zheng Q (2016) Environmentally friendly reduced graphene oxide as a broad-spectrum adsorbent for anionic and cationic dyes via π–π interactions. J Mater Chem A 4(31):12126–12135. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA04119A
Yin H, Yu K, Song C, Huang R, Zhu Z (2014) Synthesis of Au-decorated V2O5@ZnO heteronanostructures and enhanced plasmonic photocatalytic activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(17):14851–14860. https://doi.org/10.1021/am501549n
Zhang H, Fan X, Quan X, Chen S, Yu H (2011) Graphene sheets grafted Ag@AgCl hybrid with enhanced plasmonic photocatalytic activity under visible light. Environ Sci Technol 45(13):5731–5736. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2002919
Zhang G, Chen D, Li N, Xu Q, Li H, He J, Lu J (2019) Fabrication of Bi2MoO6/ZnO hierarchical heterostructures with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal B Environ 250:313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.03.055
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank the Science and Engineering Research Board, Government of India, for financial support (Grant No. SERB/F/4290/2016-17) and the National Institute of Technology, Rourkela. for providing the infrastructural facility for carrying out this work.
Funding
The National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, provided the infrastructural facility for carrying out this work. The financial support to the researchers was provided by MHRD. Other experiment oriented financial support was provided by SERB, India (Grant No. SERB/F/4290/2016-17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
U. Mondal: conducted investigation, analysis and writing the original draft. Sohel Das: conducted partial investigation and analysis. Prathap S: conducted partial investigation S. Paul (also corresponding author): conceptualization, supervising the work, analysis, checking the draft, finalizing and responsible for the submission of the work to the journal, responsible for the overall procedural activities.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sami Rtimi
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2356 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, U.S., Das, S., Somu, P. et al. Silica sand–supported nano zinc oxide–graphene oxide composite induced rapid photocatalytic decolorization of azo dyes under sunlight and improved antimicrobial activity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 17226–17244 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23248-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23248-6