Abstract
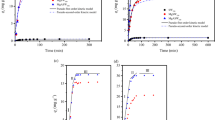
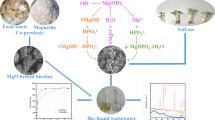
The performance, mechanisms, and effects of various coexisting ions on phosphorus (P) adsorptive capture in biogas slurry using MgO-doped biochar (MBC) were investigated. The results revealed that in comparison to the pristine biochar, the introduction of MgO significantly improved the P adsorptive capture feasibility of MBC. In addition, the process of P capture by MBC was not affected by the initial pH of the solution. The process of P capture could reach equilibrium within 120 min and be simulated using both the pseudo-first-order and the pseudo-second-order kinetic models. In addition, the highest P capture capacity calculated from the Langmuir isotherm model was approximately 129.35 mg/g. The coexisting of cations including NH4+, Ca2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, and Cr3+ in higher concentrations of promoted P adsorptive capture through precipitation and ionic atmosphere effects. The presence of coexisting ions including SO42−, HCO3−, and fulvic acid (FA) had a certain inhibitory effect on the P adsorptive capture through competitive adsorption with phosphate. The existence of monovalent ions such as K+, Na+, Cl−, and NO3− had no significant effect on P adsorptive capture. The adsorptive capture of P by MBC was affected by various processes including electrostatic attraction and surface complexation, and the presence of different coexisting substances had different impacts on the P adsorption. Adding to these, the P in the biogas slurry was completely adsorbed by the MBC during the experiment, indicating that MBC is a promising composite in the engineering application for the capture of P from wastewater.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Almanassra IW, McKay G, Kochkodan V, Ali Atieh M, Al-Ansari T (2021) A state of the art review on phosphate removal from water by biochars. Chem Eng J 409:128211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.128211
Conley DJ, Paerl HW, Howarth RW, Donald FB, PSeitzinger SP, Karl EH, Lancelot C, Likens GE (2009) Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 323: 1014-1015. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1167755
Cui H, Bao B, Cao Y, Zhang S, Shi J, Zhou J, Zhou J (2022) Combined application of ferrihydrite and hydroxyapatite to immobilize soil copper, cadmium, and phosphate under flooding-drainage alternations. Environ Pollut 292:118323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118323
Deng Y, Li M, Zhang Z, Liu Q, Jiang K, Tian J, Zhang Y, Ni F (2021) Comparative study on characteristics and mechanism of phosphate adsorption on Mg/Al modified biochar. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105079
Fang C, Zhang T, Li P, Jiang R, Wu S, Nie H, Wang Y (2015) Phosphorus recovery from biogas fermentation liquid by Ca–Mg loaded biochar. J Environ Sci (China) 29:106–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.08.019
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Ghodszad L, Reyhanitabar A, Maghsoodi MR, Asgari Lajayer B, Chang SX (2021) Biochar affects the fate of phosphorus in soil and water: a critical review. Chemosphere. 283:131176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131176
Hong SH, Lee CG, Jeong S, Park SJ (2020) Synthesis of polysulfone beads impregnated with Ca-sepiolite for phosphate removal, Membr Water Treat 11: 69-77. https://doi.org/10.12989/mwt.2020.11.1.069
Hu X, Ding Z, Zimmerman AR, Wang S, Gao B (2015) Batch and column sorption of arsenic onto iron-impregnated biochar synthesized through hydrolysis. Water Res 68:206–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.009
Jeong CY, Dodla SK, Wang JJ (2016) Fundamental and molecular composition characteristics of biochars produced from sugarcane and rice crop residues and by-products. Chemosphere 142:4–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.05.084
Jiang YH, Liu AY, Deng H, Ye CH, Li Y (2019) Phosphate adsorption from wastewater using ZnAl-LDO-loaded modified banana straw biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:18343–18353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05183-1
Jiang L, Liu X, Yin H, Liang Y, Liu H, Miao B, Peng Q, Meng D, Wang S, Yang J, Guo Z (2020) The utilization of biomineralization technique based on microbial induced phosphate precipitation in remediation of potentially toxic ions contaminated soil: a mini review. Ecotox Environ Safe 191:110009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110009
Jung KW, Ahn KH (2016) Fabrication of porosity-enhanced MgO/biochar for removal of phosphate from aqueous solution: application of a novel combined electrochemical modification method. Bioresour Technol 200:1029–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.10.008
Jung KW, Lee SY, Choi JW, Lee YJ (2019) A facile one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite/biochar nanocomposites: adsorption behavior and mechanisms for the removal of copper(II) from aqueous media. Chem Eng J 369:529–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.102
Kamali N, Rashidi Mehrabadi A, Mirabi M, Zahed MA (2021) Comparison of micro and nano MgO-functionalized vinasse biochar in phosphate removal: Micro-nano particle development, RSM optimization, and potential fertilizer. J Water Process 39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101741
Ke L, Liu X, Du B, Wang Y, Zheng Y, Li Q (2021) Component analysis and risk assessment of biogas slurry from biogas plants. Chin J Chem Eng 44:182–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2021.05.039
Lee JI, Kang JK, Oh JS, Yoo SC, Lee CG, Jho EH, Park SJ (2021) New insight to the use of oyster shell for removing phosphorus from aqueous solutions and fertilizing rice growth. J Clean Prod 328:129536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129536
Li L, Quinlivan Patricia A, Knappe DRU (2002) Effects of activated carbon surface chemistry and pore structure on the adsorption of organic contaminants from aqueous solution. Carbon 40:2085–2100. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(02)00069-6
Li RH, Wang JJ, Zhou BY, Awasthi MK, Ali A, Zhang ZQ, Gaston LA, Lahori AH, Mahar A (2016) Enhancing phosphate adsorption by Mg/Al layered double hydroxide functionalized biochar with different Mg/Al ratios. Sci Total Environ 559:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.151
Li RH, Wang JJ, Zhou BY, Zhang ZQ, Liu S, Lei S, Xiao R (2017) Simultaneous capture removal of phosphate, ammonium and organic substances by MgO impregnated biochar and its potential use in swine wastewater treatment. J Clean Prod 147:96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.01.069
Li RH, Wang JJ, Gaston LA, Zhou BY, Li ML, Xiao R, Wang Q, Zhang ZQ, Huang H, Liang W, Huang HT, Zhang XF (2018) An overview of carbothermal synthesis of metal–biochar composites for the removal of oxyanion contaminants from aqueous solution. Carbon 129:674–687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.12.070
Li T, Tong Z, Gao B, Li YC, Smyth A, Bayabil HK (2020) Polyethyleneimine-modified biochar for enhanced phosphate adsorption. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:7420–7429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07053-2
Liang F, Xu L, Ji L, He Q, Wu L, Yan S (2021)A new approach for biogas slurry disposal by adopting CO2-rich biogas slurry as the flower fertilizer of Spathiphyllum: Feasibility, cost and environmental pollution potential. Sci Total Environ 770: 145333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145333
Liu SB, Tan XF, Liu YG, Gu YL, Zeng GM, Hu XJ, Wang H, Zhou L, Jiang LH, Zhao BB (2016) Production of biochars from Ca impregnated ramie biomass (Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaud.) and their phosphate removal potential. RSC Adv 6:5871–5880. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra22142k
Liu X, Shen F, Smith RL Jr, Qi X (2019) Black liquor-derived calcium-activated biochar for recovery of phosphate from aqueous solutions. Bioresour Technol 294:122198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122198
Liu H, Shan J, Chen Z, Lichtfouse E (2021a) Efficient recovery of phosphate from simulated urine by Mg/Fe bimetallic oxide modified biochar as a potential resource. Sci Total Environ 784:147546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147546
Liu Q, Zhao Z, Xue Z, Li D, Wen Z, Ran Y, Mei Z, He L (2021b) Comprehensive risk assessment of applying biogas slurry in peanut cultivation. Front Nutr. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.702096. eCollection 2021
Ministry of Ecology and Environment, National Bureau of Statistics, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (2020) The second national census of pollution bulletin. Minist Ecol Environ. https://www.mee.gov.cn/. Accessed 8 June 2020
Mitrogiannis D, Psychoyou M, Koukouzas N, Tsoukalas N, Palles D, Kamitsos E, Pantazidis A, Oikonomou G, Baziotis I (2018) Phosphate recovery from real fresh urine by Ca(OH)2 treated natural zeolite. Chem Eng J 347:618–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.04.102
Nyenje PM, Foppen JW, Uhlenbrook S, Kulabako R, Muwanga A (2010) Eutrophication and nutrient release in urban areas of sub-Saharan Africa--A review. Sci Total Environ 408:447–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.10.020
Ok YS, Chang SX, Gao B, Chung HJ (2015) SMART biochar technology—a shifting paradigm towards advanced materials and healthcare research. Environ Technol Innov 4:206–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2015.08.003
Pathy A, Ray J, Paramasivan B (2021) Challenges and opportunities of nutrient recovery from human urine using biochar for fertilizer applications. J Clean Prod 304:127019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127019
Peng YT, Sun YQ, Fan BQ, Zhang S, Bolan NS, Chen Q, Tsang DCW (2021) Fe/Al (hydr)oxides engineered biochar for reducing phosphorus leaching from a fertile calcareous soil. J Clean Prod 279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123877
Song Z, Lian F, Yu Z, Zhu L, Xing B, Qiu W (2014) Synthesis and characterization of a novel MnOx-loaded biochar and its adsorption properties for Cu2+ in aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 242:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.12.061
Tawfik DS, Viola RE (2011) Arsenate replacing phosphate: alternative life chemistries and ion promiscuity. Biochemistry 50:1128–1134. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi200002a
Thant Zin MM, Kim DJ (2021) Simultaneous recovery of phosphorus and nitrogen from sewage sludge ash and food wastewater as struvite by Mg-biochar. J Hazard Mater 403:123704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123704
Wang D, Chen N, Yu Y, Hu W, Feng C (2016a) Investigation on the adsorption of phosphorus by Fe-loaded ceramic adsorbent. J Colloid Interface Sci 464:277–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.11.039
Wang YY, Lu HH, Liu YX, Yang SM (2016b) Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution by SiO2–biochar nanocomposites prepared by pyrolysis of vermiculite treated algal biomass. RSC Adv 6:83534–83546. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra15532d
Wang XB, Yan X, Li XY (2021) Environmental safety risk for application of anaerobic fermentation biogas slurry from livestock manure in agricultural land in China. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 54:110–139. https://doi.org/10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.01.009
Wei J, Meng X, Wen X, Song Y (2020) Adsorption and recovery of phosphate from water by amine fiber, effects of co-existing ions and column filtration. J Environ Sci (China) 87:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.05.009
Wu B, Wan J, Zhang Y, Pan B, Lo IMC (2020) Selective phosphate removal from water and wastewater using sorption: process fundamentals and removal mechanisms. Environ Sci Technol 54:50–66. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b05569
Yan LG, Xu YY, Yu HQ, Xin XD, Wei Q, Du B (2010) Adsorption of phosphate from aqueous solution by hydroxy-aluminum, hydroxy-iron and hydroxy-iron–aluminum pillared bentonites. J Hazard Mater 179:244–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.02.086
Yang Q, Wang X, Luo W, Sun J, Xu Q, Chen F, Zhao J, Wang S, Yao F, Wang D, Li X, Zeng G (2018) Effectiveness and mechanisms of phosphate adsorption on iron-modified biochars derived from waste activated sludge. Bioresour Technol 247:537–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.136
Yao Y, Gao B, Inyang M, Zimmerman AR, Cao X, Pullammanappallil P, Yang L (2011) Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution by biochar derived from anaerobically digested sugar beet tailings. J Hazard Mater 190:501–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.03.083
Zhang M, Gao B, Yao Y, Xue Y, Inyang M (2012) Synthesis of porous MgO-biochar nanocomposites for removal of phosphate and nitrate from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 210:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.08.052
Zhang ZR, Yu HQ, Zhu RX, Zhang X, Yan LG (2020) Phosphate adsorption performance and mechanisms by nanoporous biochar–iron oxides from aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:28132–28145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2014.09.005
Zhang YC, Shi GZ, Wu WL, Ali A, Wang HL, Wang Q, Xu ZY, Qi WD, Li R, Zhang ZQ (2022) Magnetic biochar composite decorated with amino-containing biopolymer for phosphorus recovery from swine wastewater. Colloids Surf 634:127980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127980
Zhu N, Yan T, Qiao J, Cao H (2016) Adsorption of arsenic, phosphorus and chromium by bismuth impregnated biochar: Adsorption mechanism and depleted adsorbent utilization. Chemosphere 164:32–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.036
Zhu D, Chen Y, Yang H, Wang S, Wang X, Zhang S, H. Chen (2020) Synthesis and characterization of magnesium oxide nanoparticle-containing biochar composites for efficient phosphorus removal from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 247: 125847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125847
Acknowledgement
We sincerely thank all individuals who volunteered to participate in this study.
Funding
The research work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32172679) and the National College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Programs, China (2021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yimeng Li: investigation, data curation, writing original draft. Muhammad Azeem: investigation, editing and writing original draft. Yuan Luo: investigation, writing original draft. Yaru Peng: investigation, writing original draft. Chuchu Feng: investigation and data curation. Ronghua Li: methodology, conceptualization, supervision, review and editing. Jin Peng: methodology and data curation. Lan Zhang: review and editing. Hailong Wang: review and editing. Zengqiang Zhang: review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The authors attest that this paper has not been published elsewhere, the work has not been submitted simultaneously for publication elsewhere, and the results presented in this work are true and not manipulated.
Consent to participate
All the individual participants involved in the study have received informed consent.
Consent for publication
The participants have consented to the submission of the study to the journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOC 167 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Azeem, M., Luo, Y. et al. Phosphate capture from biogas slurry with magnesium-doped biochar composite derived from Lycium chinensis branch filings: performance, mechanism, and effect of coexisting ions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 84873–84885 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21625-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21625-9